What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Read Also: How Can I Get Armour Thyroid
Thyroid Cancer As A Population Problem
The increase in the prevalence of thyroid cancer, which is the most common endocrine carcinoma has been observed within the last three decades. It is estimated that by 2019 thyroid cancer will have been the third most prevalent malignant tumor in women in the USA . This phenomenon is observed worldwide. For instance, the standardized incidence rate in Poland was 4.9 per 100,000 inhabitants whereas in 1990 it was only 1.0 . The fact whether it is a real increase in incidence or the increase in the detection due to the development of more precise diagnostic approaches is of lesser significance. As a consequence, the population of newly detected low-advanced thyroid cancers is constantly growing . This has one more time resulted in the discussion on optimization of therapeutic strategy. The strategy is related to avoid overtreatment and undertreatment .
Effect Of Braf V600e Mutation On Ptmc Recurrence
During the median follow-up period of 75 months , tumor recurrence occurred in 2.6% patients. The recurrence rate was 2.9% and 2.1% for BRAF mutation-positive and -negative patients, respectively , with an unadjusted HR of 1.48 . After adjustments for age, sex, tumor size, LNM, ETE, multifocality, surgical type, and RAI treatments, the effect of the BRAF mutation on tumor recurrence remained insignificant, with an HR of 1.05 . The KaplanMeier survival curve also showed no significant difference between BRAF mutation-positive and -negative patients in regard to recurrence-free survival .
| 0.802 |
CI: confidence interval, HR: hazard ratio, PTMC: papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
*Adjusted for patient age at diagnosis , sex , tumor size , cervical lymph node metastasis , extrathyroidal extension , multifocality , surgery type , and radioactive iodine treatment .
Adjusted for patient age at diagnosis, sex, tumor size, multifocality, surgery type, and radioactive iodine treatment.
Don’t Miss: How Long For Thyroid Medicine To Work
Validation Of Dynamic Risk Stratification
The ability of each of the prognostic system to predict final clinical status is presented in Table 3. As expected, AJCC stage IV patients were more likely to die from thyroid cancer . Considering recurrence rate, in AJCC stages I and II, the proportion of patients that have recurrent/persistent disease is relatively high . When we classified patients according to the ATA recurrence risk classification, the proportion of patients that have recurrent/persistent disease in low, intermediate, and high-risk categories was 10.2%, 38% and 96.8% respectively. Regarding mortality, high-risk patients were more likely to die than patients in the intermediate and the low-risk category .
Table 3 Final outcomes based on stratification by AJCC, ATA risk of recurrence at diagnosis and DRS.
Table 4Outcomes concerning no evidence of disease in the different DRS categories.
Table 5 Impact of response to initial therapy assessment on initial estimates of risk.
Figure 1 Recurrence Free Survival and proportion of variance explained to assess the performance of seventh AJCC TNM stage, ATA risk system, 4-tiered dynamic risk stratification and 3-tiered DRS . Adjusted Hazard Ratios with 95% confidence intervals were calculated in logistic regression model. A two-tailed P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The Analysis Of The Relationship Of The Mutation With The Risk Of Recurrence
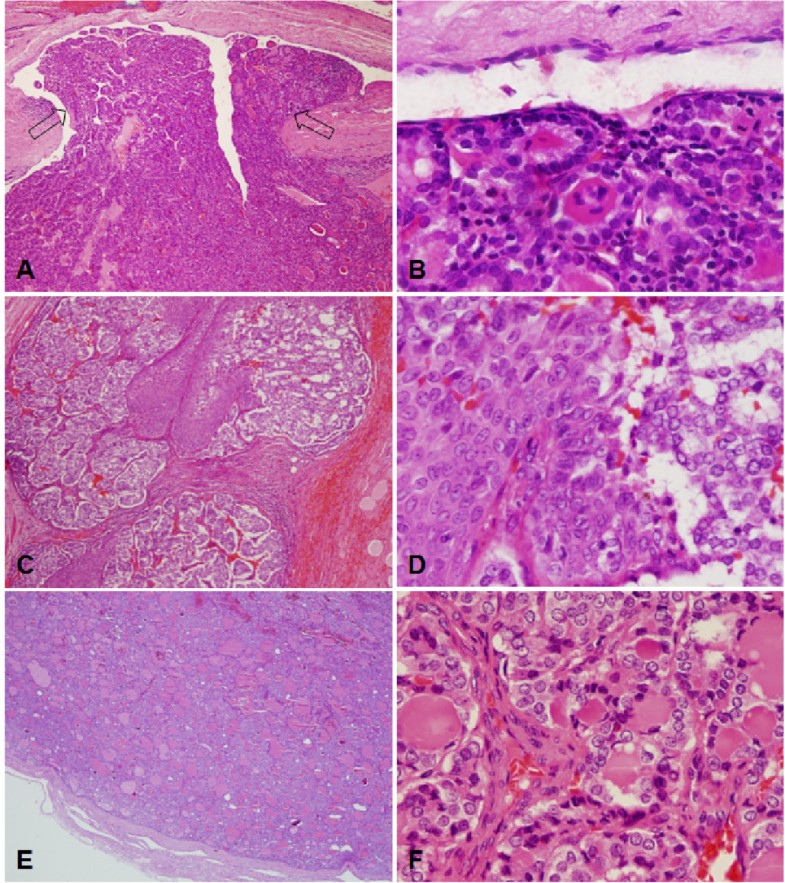
The next stage was based on the assessment of the relationship between BRAF mutation and the risk of recurrence. Two thousand ninety nine patients from 16 centers and eight countries with the mean follow-up of 36 months were enrolled in the analysis . Recurrence was defined altogether as local recurrence, distance recurrence and persistent disease. BRAF mutation was done on postoperative material therefore its status did not have an influence on the treatment applied. Disease recurrence was noted in 16.1% of patients. Recurrence was more frequent in patients with the mutation as compared to BRAF patients . A higher risk of relapse was typical of BRAF patients. The relationship was observed also in the multivariable analysis which considered age, sex, the center from which patients came from, tumor size, extrathyroid extension, LN metastases, multifocality and a histological subtype of the cancer. Disease-free survival was significantly lower in patients with PTC in whom the mutation was diagnosed . This relationship was also observed in the classic subtype and in follicular subtype of PTC. Additionally, the worst disease-free survival was noted in BRAF patients in whom LN metastases were diagnosed . A similar observation was related to the coexistence of the mutation with extracapsular infiltration and with the age of patients .
Read Also: Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Pathology Outlines
Tumor Testing Vs Liquid Biopsy
Historically, testing done on a sample of tissue obtained via a biopsy has been the gold standard. Unfortunately, tissue biopsies are invasive and may not always be possible.
In recent years, a simple blood test that looks for fragments of tumor DNA in the blood has offered an additional option for genomic testing. Liquid biopsies have been found to be comparable to tissue biopsies in some cases, though many oncologists believe that the ideal is to do genomic testing on both tissue and blood samples.
Quality Assessment And The Grading Of Recommendations Assessment Development And Evaluation Rating Scale
Two reviewers evaluated the risk of bias in our analyses, based on the original records and their supplementary materials, using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme scales , which were designed for the assessment of observational studies. Twelve aspects were assigned an assessment index associated with the risk of bias as yes,no, or cannot tell. Moreover, we used the GRADE framework to develop and present summaries of evidence .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Check Your Thyroid Function
Prevalence Of Tert Promoter And Braf V600e Mutations In Ptc
Among 7797 patients with PTC, TERT promoter mutations were found in 87 , of which the C228T mutation was observed in 76 and the C250T in 11 . Meanwhile, the BRAF V600E mutation was observed in 6546 patients . The coexistence of BRAF and TERT promoter mutations was identified in 70 patients , while 1234 had no mutations .
Thyroid Cancer Patients Demographics
AUBMC thyroid carcinoma database from 2001 to 2011 revealed 385 thyroid cancers with PTC as the predominant type constituting 91.7% of the cases. The overall female-to-male ratio of the PTC cases was 2.5:1. Approximately 26% of the patients were < 30 years old, 56% were between 3149 years old, and 18% were > 50 years old. The frequency of each PTC histopathologic subtype was as follows: 123 cases of cPTC , 76 cases of PTMC , 15 cases of PTMC-FV , and 39 cases of PTC-FV .
Read Also: Thyroid Cancer And Tailbone Pain
The Analysis Of The Relationship Of The Mutation And The Risk Of Death
The first stage included the assessment of the relationship of BRAF mutation with the risk of death in PTC patients. Xing et al. analyzed 1,849 patients treated in 13 centers in seven countries with the mean follow-up of 33 months .
The mortality in these patients was 3% . The mortality rate was significantly lower in patients with BRAF mutation , 45 deaths were reported in a group of BRAF patients and only 11 in a group of BRAF patients. The overall survival was lower in patients in whom the mutation was present. The additional analysis of the overall survival depending on the presence of the mutation and LN metastases demonstrated that BRAF patients with LN metastases constituted the group with the most unfavorable prognosis. The assessment of interactions between BRAF mutation and other risk factors such as LN metastases, distant metastases, age of patients, extrathyroid extension and IV stage of clinical involvement demonstrated a strong relationship between the mutation and each of the above factors except for extrathyroid extension. However, in the multivariate analysis after adding the features of unfavorable disease course such as age, sex, extrathyroid extension, LN metastases or distant metastases, the relationship between BRAF and mortality lost a statistical significance, probably due to a low incidence of deaths.
Hopkins Researcher Links Gene Mutation With Poor Outcomes In People With Most Common Thyroid Cancer
Johns Hopkins Medicine
HOPKINS RESEARCHER LINKS GENE MUTATION WITH POOR OUTCOMES IN PEOPLE WITH MOST COMMON THYROID CANCER– Discovery provides molecular marker to assess risk for patients with papillary thyroid cancer
Scientists at Johns Hopkins have found that a mutation in the gene that triggers production of a tumor growth protein is linked to poorer outcomes for patients with papillary thyroid cancer . A report on the study is published in the December issue of The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Mingzhao Xing, M.D., Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, led the multi-center study. This discovery should help physicians rate risk levels for patients with PTC, he says.
The gene, called BRAF, is part of a signaling pathway that, when activated, is known to cause tumor growth, and mutations in BRAF have been linked to a variety of human cancers, the researchers say.
For the study, Xing and colleagues looked at information from 219 PTC patients from 1990 to 2004. The relationship among BRAF mutations, initial tumor characteristics, cancer recurrence and clinical outcomes was analyzed.
BRAF mutation was also an independent predictor of recurrence in patients with early disease, with 22 percent recurrence in those who had BRAF mutations versus only 5 percent in patients without the mutation.
Also Check: How To Regulate Your Thyroid
C Mapk Pathway And Its Activating Genetic Alterations
As illustrated in , the RET/PTC Ras Raf mitogen extracellular kinase MAPK/ERK pathway is a classical conserved intracellular signaling pathway that plays a fundamental role in cell functions such as proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and survival , and, when aberrantly activated, tumorigenesis . Physiological activation of this pathway is triggered by a large array of growth factors, hormones, and cytokines through their receptors on the cell membrane. In normal cells, the activation of the Raf kinase occurs through direct interaction with GTP-bound Ras, a membrane-bound small G protein. Activated Raf, a serine/threonine protein kinase, phosphorylates and activates the immediate down-stream MEK, which, also a serine/threonine protein kinase, in turn phosphorylates and activates ERK. The activated ERK phosphorylates regulatory protein molecules in the nucleus and ultimately alters gene expression with consequent changes in the biological activities of the cell.
Fig. 1.
Recommended Reading: Best Thyroid Cancer Hospital In Us
Future Perspectives And Research Directions

Currently, researchers are working on determining the role of BRAF mutation in the relapse risk assessment in patients from a low-risk group as indicated by the ATA scale.
Elisei et al. initiated such studies and observed only 3% of structural relapse in patients with thyroid limited carcinoma . However, in the case of BRAF carcinoma, the recurrence rate was 8% as compared to the population of BRAF 1% . In the multivariable analysis only BRAF mutation was a predictive factor of persistent disease in a 5-year follow-up. If these observations were confirmed by other studies, the analysis of BRAF mutation for patients with carcinoma limited to the thyroid could result in better selection of low and intermediate risk groups, as suggested by Yarchoan et al. .
Recent reports suggest that tumors in which BRAF mutation coexists with other mutations such as TERT, PIK3CA and/or TP53 may be characterized by more aggressive clinical course. It is believed that more accurate tumor prognostication is possible due to a genetic analysis .
Studies on the formation of sensitive and specific molecular classifiers are being conducted. Such classifiers might help in better assessment of the risk of relapse. Additionally, they might be valuable in the assessment of an unfavorable course of the disease and might be useful in personalized therapeutic strategy. Currently, it seems that the analysis of molecular factors will be one of the major research trends in the following years .
You May Like: Thyroid Gland Function In Endocrine System
The Risk Of Recurrence In Papillary Thyroid Cancer
PTC represents the majority of thyroid carcinomas . It is characterized by excellent prognosis, almost 100% probability of 5-year overall survival . Therefore, in PTC the risk of disease recurrence is most frequently analyzed in relation to the prognosis, i.e., the disease-free survival but not the overall survival unlike in other types of cancers with higher mortality rates .
The risk of relapse or persistent disease is related to about 30% of PTC patients and depends, among other things, on the adopted definition of recurrence .
The incidence of recurrence depends on whether clinical detection is considered alone or whether it is analyzed together with biochemical recurrence.
From the perspective of a surgeon, structural recurrence seems to be the most significant due to the fact that these patients are most frequently scheduled for surgery. In the context of the therapeutic strategy, the significance of biochemical recurrence cannot be omitted since such patients require a change in routine diagnostic and therapeutic management, e.g., additional treatment with radioactive iodine or increased follow-ups.
Braf V600e Mutation Related Molecular Events In Ptc
The most common genetic alterations in PTCs include BRAF mutation, RAS mutation, and RET/PTC rearrangement which mainly involve in the RAS/BRAF/MAPK signal pathway. Interesting, these molecular alterations are exclusive in PTC patients, suggesting that each of them alone is sufficient for malignant transformation of thyroid cells. BRAF V600E mutation strongly increases BRAF kinase activity by eliciting ERK1/2 phosphorylation which is 480-fold higher than wild type BRAF . The markedly increased ERK1/2 phosphorylation in BRAF V600E mutation mainly attributed to a negatively charged residue adjacent to the phosphorylation site at T598 and mimicking phosphorylation at Thr598 and Ser601 residues .
The activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in thyroid cancer by mutant BRAF. The most common genetic alternation in papillary thyroid cancer, BRAF mutation, stimulates constitutive signaling which bypasses the need for extracellular mitogenic signals. Subsequently phosphorylation of downstream MER1/2 and ERK1/2 results in transcriptional regulation of various genes which are involved in cell proliferation, differential, survival, tumorigenesis, and the process of EMT.
Read Also: Can Thyroid Disease Cause Hot Flashes
Braf And Nras Mutational Frequency
The frequency of BRAF and NRAS mutations varied among the different histopathologic subtypes of PTC. In cPTC and PTMC subtypes, BRAF mutations were predominant, while NRAS were less common. Conversely, in PTMC-FV and PTC-FV, NRAS mutations were more common than BRAF mutations with statistical significance of p< 0.0001. The BRAFV600E mutation subtype comprised 98.0% of the total BRAF mutated PTC cases followed by BRAFV600M identified in two cases: one cPTC case and a second cPTC case with a concomitant BRAFV600E and V600M. The NRAS mutational subtypes included c.182A> G c.181C> A , c.34G> A and c.38G> A . Concomitant BRAF and NRAS mutations were detected in five PTC cases inclusive of one cPTC, two PTMC and two PTMC-FV cases. KRAS mutations were detected in only 4 out of 246 cases tested therefore, no further statistical analysis was performed. No mutations were detected in all adenomatous goiter cases .
Study Design Specimen And Information Collection
As a total, 393 archival specimens were collected: 323 were PTCs and are the object of the present study. Additional 70 specimens that included normal thyroid tissue and colloid goiters, follicular adenomas and carcinomas, and anaplastic carcinomas were also examined at the same time.
Surgery medical records provided the information regarding patients and tumors . Clinical staging of thyroid cancer was classified according to the Tumor-node-metastasis classification . Persistent disease was evaluated in 118 patients, with a 2- to 4-year follow-up.
Information regarding environmental goitrogens were obtained by previous scientific publications regarding the presence of these goitrogens in different areas of Sicily .
Don’t Miss: Can Armour Thyroid Cause High Blood Pressure
Braf Kras And Nras Analysis Using Reverse Hybridization
The BRAF, KRAS, and NRAS StripAssays were utilized to detect different point mutations and deletions in the genes coding for BRAF and NRAS. The detection sensitivity for mutant alleles is 1%, performed according to the manufacturers instructions. Mutational analysis was performed by polymerase chain reaction and reverse hybridization as follows: first, a multiplex PCR amplification using biotinylated oligonucleotide primers was performed for BRAF, KRAS, and NRAS gene sequence amplification second, reverse hybridization of the amplification products was ensued via a test strip, which contains allele-specific oligonucleotide probes for mutations and controls immobilized on a parallel array and finally, bound biotinylated sequences were visualized using streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase conjugate and enzymatic color development. Positive control samples included defined mutated cell line DNA or clones.
Eligibility And Exclusion Criteria
Studies had to include at least two of the following genetic mutations molecular marker types: the BRAFV600E gene mutation, TERT promoter mutations, RAS gene mutations, CHEK2 mutations and RET/PTC gene rearrangements. Participants had to be adults with a primary diagnosis of TC, with no specific TC type restrictions. We excluded conference abstracts, reviews, meta-analyses, letters, and records, which did not meet our criteria, such as not reporting coexisting genetic mutations etc. After removing duplicate records and performing a preliminary screening of titles and abstracts, two researchers independently assessed full-text and supplementary materials of the selected records for final inclusion. Potentially relevant full-text published articles were also retrieved and assessed. Disagreements were resolved by consensus or by requesting an additional round of reviewing by ZYS or LZH.
You May Like: Braf Mutation Papillary Thyroid Cancer