Models Of Metastatic Progression
A model of metastatic progression in cancer. Primary tumor growth and invasion occur through the gain of genetic or epigenetic changes in the primary tumor often in cells that have a change in character through the process of epithelial to mesenchymal transition . Individual cells, or groups of cells, that have gone through this transition, as well as those that have not , gain access to blood vessels through incompletely defined mechanisms. Some of the cells are targeted to specific organs and enter their new microenvironment. Cells that have dedifferentiated are likely able to modify the premetastatic niche to allow for proliferation and invasion with short latency in the metastatic site. Cells shed into the circulation that are more differentiated likely enter a period of prolonged dormancy controlled by a number of factors that may be released over time through changes in the tumor cells or the metastatic microenvironment. In both cases, metastatic progression at the metastatic site likely requires interactions with immune cells, endothelial cells, and the stroma.
Donât Miss: What Are Breast Cancer Markers
What Does The Research Say
Researchers looked at 37 peer-reviewed studies containing data on the relationship between breast and thyroid cancers.
They noted in a 2016 paper that a woman whos had breast cancer is 1.55 times more likely to develop a second cancer of the thyroid than a woman without a history of breast cancer.
A woman with thyroid cancer is 1.18 times more likely to develop breast cancer than a woman without a history of thyroid cancer.
Researchers are unsure about the connection between breast and thyroid cancers. Some research has indicated the risk of developing a second cancer increases after radioactive iodine is used to treat thyroid cancer.
Iodine is generally considered safe, but it could trigger a second cancer in a small number of people. Radiation used to treat certain forms of breast cancer may increase the risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Certain genetic mutations like a germline mutation could link the two forms of cancer. Lifestyle factors like exposure to radiation, poor diet, and lack of exercise, could also increase the risk of both cancers.
Some researchers also noted the possibility of a surveillance bias, which means a person with cancer is more likely to follow up with screening after treatment. This improves detection of a secondary cancer.
They also analyzed the results by dividing the data into groups based on the time between the diagnosis of the first and the second cancer.
Both breast and thyroid cancers have unique screening guidelines.
Can Thyroid Cancer Be The Same As Other Cancers
People who have had thyroid cancer can still get the same types of cancers that other people get . In fact, they might be as risk for certain types of cancer. People who have or had thyroid cancer can get any type of second cancer, but they have an increased risk of developing: Adrenal cancer risk is especially high in people who had
Read Also: Thyroid Cancer Treatment Side Effects
How Is Thyroid Cancer Diagnosed
Once a thyroid nodule is found, the next step is to determine if the nodule represents a benign growth or malignant tumor. A careful physical exam should be done by a healthcare provider, with attention to the examination of the neck to evaluate for the presence of enlarged lymph nodes. You will also have blood tests to check your thyroid function and hormone levels. If these tests show an over-functioning thyroid gland, then additional tests will be performed to determine if the nodule is composed of benign thyroid tissue that is overproducing thyroid hormone.
A biopsy is not usually required for benign, âfunctioningâ nodules. A thyroid scan will help distinguish this nodule. This scan is a nuclear medicine study using radioactive iodine. Functioning thyroid tissue takes up iodine to produce normal thyroid hormones. The small amount of radioactive iodine used to take pictures will be taken up by those areas of the thyroid that are producing thyroid hormone. Thus, a nodule composed of functioning thyroid tissue will appear âhotâ in these nuclear medicine scans . These âhot nodulesâ are almost always benign and often require no further workup for thyroid cancer. Nodules that are âcoldâ are also often benign but can be malignant in 15-20% of cases. Therefore, these deserve more attention and further workup.
Use Of Radioactive Iodine And Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cells are unique in that they have the cellular mechanism to absorb iodine. The iodine is used by thyroid cells to make thyroid hormone. No other cell in the body can absorb or concentrate iodine in a similar fashion than does the thyroid. Physicians can take advantage of this fact and give radioactive iodine to patients as a treatment option for papillary thyroid cancer. The use of iodine as a cancer therapy was the first targeted therapy ever developed for any type of human cancer.
There are several types of radioactive iodine, with one type being highly toxic to cells. Papillary thyroid cancer cells absorb iodine therefore, they can be destroyed by giving the toxic isotope . Again, not everyone with papillary thyroid cancer needs this treatment, but those with larger tumors, tumors that have spread to lymph nodes or other areas including distant sites, tumors that are aggressive microscopically may benefit from this treatment.
Radioactive iodine therapy is particularly effective in children with thyroid cancer which has spread extensively to lymph nodes and even to distant sites in the body such as the lungs. Although in theory, radioactive iodine is a very attractive treatment approach for papillary thyroid cancer, its use has decreased over the years except for the specific indications as described above.
Recommended Reading: Can Underactive Thyroid Cause Hair Loss
Is There A Link Between Breast Cancer And Thyroid Cancer
Previous studies have suggested an association between breast cancer and thyroid cancer however, there has not been a formal meta-analysis which collates the existing evidence supporting the hypothesis that breast cancer or thyroid cancer predisposes an individual to developing the other. A systematic search was carried out using PubMed
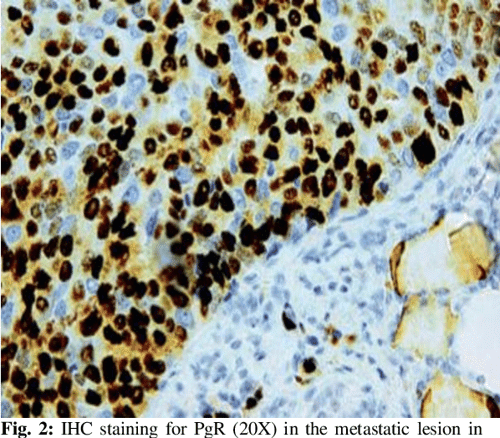
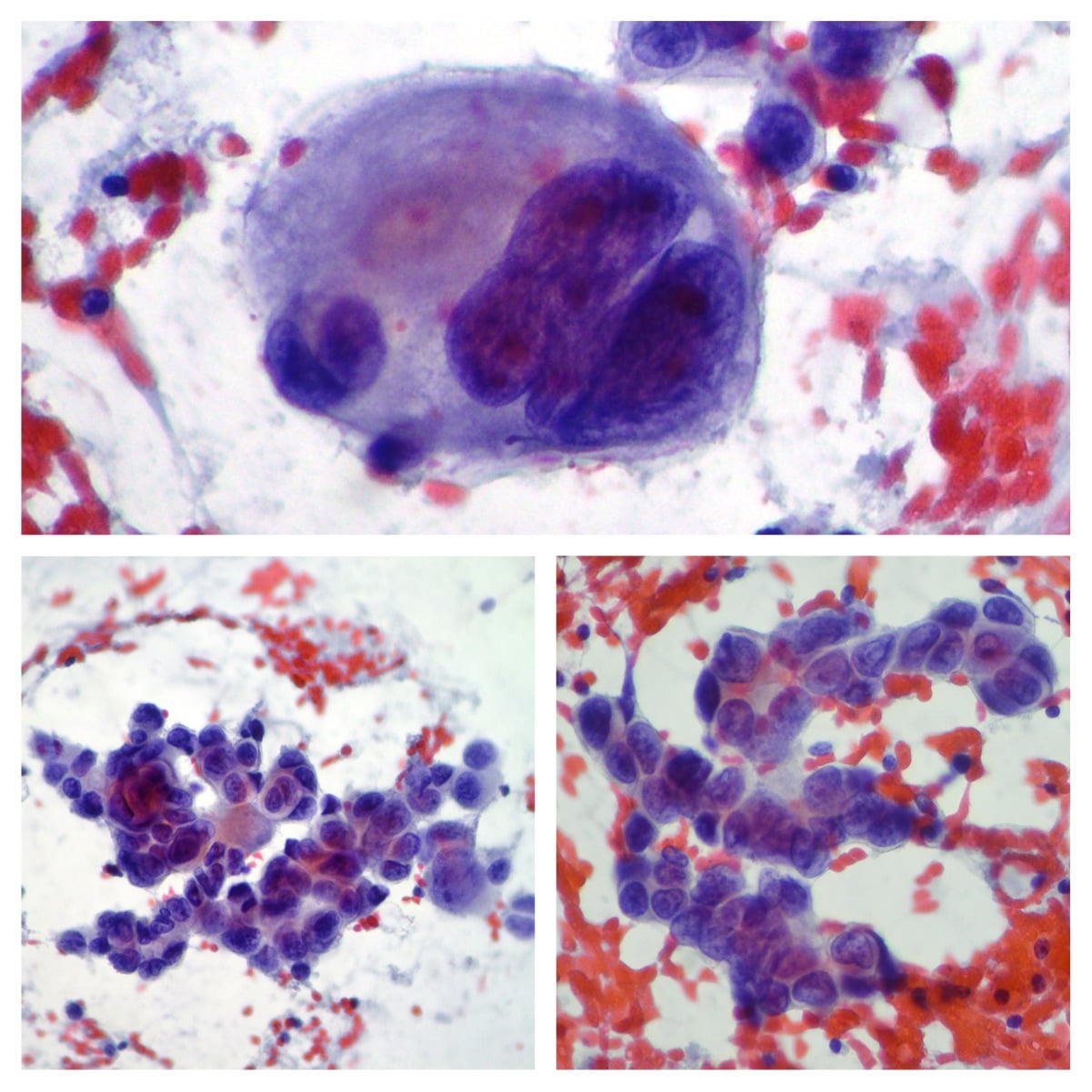
Tissue Processing And Analysis
Smear slides, prepared from the thyroid gland aspirate, were subject to histological and immunohistochemical analysis. FNAC was also performed for recurrent foci at chest wall which served as a reference standard for cellular morphological assessments. In addition to the above stains, the thyroid tissue samples obtained from thyroidectomy in 2 patients were subject to immunohistochemical analysis for estrogen receptor and Progesterone receptor . The slides were read by two qualified and experienced pathologists providing their diagnosis. For the study purpose, the H& E and immunohistochemistry images of all the cases were re-read by a pathologist who was blinded to the prior diagnosis and other patient data. Any discrepancy was resolved through discussion with the respective pathologist who provided the prior diagnosis. Clinical records of all the patients were further analyzed for details of the primary condition, interval between primary condition diagnosis and TM, serum thyroid hormone level, primary pathology, other associated metastasis, therapeutic strategy undertaken, and survival time after diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Is There A Relationship Between Thyroid Cancer
the thyroidcancer. There has been a long standing debate regarding the relationshipbetweenthyroidcancer and Hashimotos thyroiditis. Specifically, it is unclear if the thyroid inflammation seen in Hashimotos thyroiditis causes the cancer or if the inflammation is the result of the cancer. Also, it is uncertain if thyroid cancers surrounded
Is Radioactive Iodine Safe
Radioactive iodine is a common treatment for both an overactive thyroid gland and thyroid cancer. This treatment is considered safe and effective, but its possible that radioactive iodine could trigger cancer in a very small number of people. Other research has shown that cancer risk, including breast cancer risk,
You May Like: How To Regulate Your Thyroid
What Should I Do If I Have Symptoms Of Metastatic Thyroid Cancer
As with other types of cancer, thyroid cancer that is detected in its early stages is more easily treatable and more likely to lead to a positive outcome and quality of life. If you are experiencing any symptoms associated with thyroid cancer, it is important to consult a physician as soon as possible to receive an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Moffitt Cancer Center offers comprehensive diagnostic, treatment and supportive care services for individuals with thyroid cancer. Whether you have been diagnosed with thyroid cancer or are experiencing metastatic thyroid cancer symptoms, you can find all of the services you need under a single roof at Moffitt.
Call or fill out a new patient registration form online to learn more about thyroid cancer treatment services at Moffitt. We welcome patients with or without a referral.
What Is The Impact Of Cancer Treatment On Future Risk
Radiation, despite being a treatment option for breast cancer, is a well-documented risk factor in the development of cancer and is a major risk factor for thyroid cancer . Multiple recent clinical studies demonstrate alteration of the ability of the thyroid to produce hormones following radiotherapy . Despite this evidence that radiotherapy harms the thyroid, a very large study from Taiwan of over 55,000 patients did not report any association between treating breast cancer with radiation and subsequent thyroid cancer, nonetheless the results did corroborate the previously discussed relationship between thyroid and breast cancers . Another study revealed that although the use of radiotherapy to treat breast cancer was associated with an increased risk of certain tumors, including leukemia and lung cancer, there was not an observed increase in the risk of thyroid cancer .
Although the impact of radiotherapy on thyroid function has been extensively studied, data on chemotherapy is sparse. Studies on patients with breast cancer receiving different chemotherapeutic treatments reveal a reduction in serum T4 levels, but subsequent recovery of thyroid function and thyroid cancer risk was not assessed . Critically, the impact of chemotherapeutic agents on thyroid function and cancer risk needs further study.
You May Like: Treating Thyroid Cancer Without Surgery
What Is The Epidemiologic Evidence Of The Relationship Between Breast And Thyroid Cancer
In the past few years alone, population studies in Asia, Europe, and the United States reveal increased incidence of breast cancer among women previously diagnosed with thyroid cancer . Of note, aggressive follicular thyroid cancer is detected in patients with a history of breast cancer more often than the more common papillary thyroid cancer . Furthermore, and importantly for determining etiology, nonmalignant thyroid nodules are more common in women with breast cancer than those without breast tumors . There is an increased risk of developing thyroid cancer following breast cancer . Women with prior benign breast disease also are reported to be at a greater risk of thyroid cancer . The increased risk of thyroid cancer following breast cancer and breast cancer following thyroid cancer is reported in both women and men . Women with breast cancer are 2-fold more likely to develop future thyroid cancer and women with thyroid cancer have a 67% greater chance of developing breast cancer than the general population. These recent studies are summarized in . Importantly, the metachronous relationship was evaluated in nations with widespread cancer screening and nations where screening is becoming more common. In particular, Zhang and colleagues evaluated patients with cancer between 2001 and 2010 in China, which corresponded with investments into cancer registries .
What Screening Tests Are Used For Thyroid Cancer
The early detection of thyroid cancers is generally through careful visual and physical examination of the neck. Palpation of the neck will detect many clinically significant thyroid nodules which may be cancer. This is part of a routine physical exam. In addition, the thyroid gland is included in many radiology studies performed to evaluate other organs, such as CT scans of the lungs and cervical spine.
All individuals suspected to have thyroid nodules, either from physical examination or from another radiology study, should have a thyroid ultrasound performed to take a picture of the thyroid. Thyroid ultrasound uses sound waves to produce an image of the thyroid gland and surrounding structures. The ultrasound appearance of the nodule can help healthcare providers determine if a fine-needle aspiration biopsy is required to further evaluate the nodule. There is no evidence that it is cost-effective to perform ultrasounds to screen for thyroid nodules in the general population. Notably, ultrasound detects the majority of small incidental thyroid cancers, which are unlikely to affect the survival of most patients.
Recommended Reading: Most Common Form Of Thyroid Cancer
Symptoms Of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer does not always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, what they are like and how often you have them will depend on the size and location of the metastatic tumors. Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:
- pain and fractures, when cancer has spread to the bone
- headache, seizures, or dizziness, when cancer has spread to the brain
- shortness of breath, when cancer has spread to the lung
- jaundice or swelling in the belly, when cancer has spread to the liver
You May Like: How Many Radiation Treatments For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Why Is It Important To Get A Recommended Biopsy
A biopsy is often the best way to definitively say whether or not you have cancer. Other tools, such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging , can tell the doctor if an area looks suspicious. But in most cases, the only way to make a definitive cancer diagnosis is to perform a biopsy and look at those suspicious cells under a microscope. Many biopsies are performed with imaging guidance, called image-guided biopsies, where tools like ultrasound or computed tomography scans are used to help locate areas of concern and obtain biopsy material.
Sometimes, a biopsy reveals that the suspicious area contains only benign, or non-cancerous, cells. This might mean you do not need treatment, such as surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. Other times, a biopsy can tell the doctor how aggressive a cancer appears to be and what the extent of the disease may be. This refers to a cancers stage and grade. A biopsy can also explain what type of cancer cells are inside the tumor. All of this information helps determine the best course of action for treating the cancer.
Also Check: How To Feel Your Thyroid
How Fast Breast Cancer Grows
People may wonder about growth or doubling time when considering how long to wait to begin treatment. This growth is also very important to understand if you have a lump and have been advised to simply observe it over time.
Unless your healthcare provider is extremely confident that a lump is benign, it should be evaluated right away rather than waiting.
In general, the growth of breast cancer can be quite variable, but several studies provide at least an estimate of what may be happening.
Read Also: When Was Breast Cancer Discovered
What Causes Thyroid Cancer And Am I At Risk
Most cases of thyroid cancer have no risk factors. Thyroid cancer is more common in women. Studies have shown an increased risk of certain types of thyroid cancer in geographic areas where there is a high incidence of goiters due to a lack of dietary iodine. This is further supported by the decrease of thyroid cancers in these areas when individuals are given supplemental iodine.
The most established risk factor for the development of thyroid cancer is exposure to ionizing radiation to the neck area at a young age . This is supported by the high incidence of thyroid cancer seen in many populations exposed to radiation. This includes children 18 years or younger who were treated with radiation therapy for cancers such as Hodgkinâs disease or nasopharyngeal cancer, or as part of their therapy to prevent leukemia from spreading to the brain. In addition, children who received total body irradiation in preparation for bone marrow transplantation are also at higher risk. Radiation therapy was also used in the 1940-1960s for benign conditions like acne, and this population has an increased risk for thyroid cancer.
Recommended Reading: Do You Get Breast Pain With Cancer
Don’t Miss: Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies 900 H
Value Of Diagnostics In Breast Metastasis
This study demonstrates the value of serum calcitonin in monitoring MTC progression and possible metastasis. In this case study, it was the increasing serum calcitonin levels that prompted further investigation and the subsequent discovery of metastatic breast cancer. Serum calcitonin is an important prognostic biomarker for MTC, according to Meng et al, and monitoring the serum calcitonin level, particularly for those patients with an increased preoperative calcitonin level is helpful in the diagnosis of MTC recurrence and metastasis. In addition, calcitonin levels of the washout fluid from FNA have a 97.9% sensitivity for MTC, regardless of cytologic findings.
In this case study, the histological finding of solid growth without tubular formation prompted physicians to suspect MTC metastasis. In fact, diagnosing metastatic breast tumors is challenging from a histological perspective. The presence of elastosis, carcinoma in situ, and calcification are common features of primary mammary carcinomas but rare in extramammary tumors, the authors of the case study explained. To arrive at a correct diagnosis, it is thus important to narrow down the diagnosis morphologically, in which case hematoxylin-eosin staining is incredibly useful.
Does Radioactive Iodine Cause Cancer
Other research has shown that cancer risk, including breast cancer risk, is higher after radioactive iodine is used to treat an overactive thyroid gland. Its also possible that the genetic or other factors that contributed to a person developing thyroid cancer might increase risk for other types of cancer. If youve been treated
Recommended Reading: Thyroid Cancer Follow Up Guidelines
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have thyroid cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. You may have heard other people say that their cancer was stage 1 or stage 2. Your doctor will want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the spread of the cancer through the thyroid gland. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other organs of your body that are close by or far away.
Your cancer can be stage 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread outside of the thyroid gland. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.