What Are Some Of The Surgical Options For Thyroid Eye Disease
In addition to various new and exciting medical treatments for thyroid eye disease, there are surgical treatments that can mitigate the symptoms of this appearance-altering disease. The surgeons at Eyesthetica correct the upper eyelid retraction with surgical approaches either through the inside of the eyelid or through the upper eyelid skin. Lower eyelid retraction can be repaired with lower eyelid surgery to reposition or strengthen the lid by borrowing tissue from the hard palate for other sites.
During The Surgical Operation
- This treatment is carried out in the operating theatre of the out-patients unit
- This surgical procedure can be carried out by means of various techniques, depending on each patients case, his/her type of eyelid malposition, its degree and location. The most common are the following:
- The canthoplasty
- El mid-facelift
Function And Structure Of Your Eyelids
The upper and lower eyelids are moveable structures made of tissue and muscle. The upper eyelid is larger and moves more freely. Inside the eyelids are meibomian glands that secrete the oily substance that makes up the tears.2
The eyelids serve various functions, including:2
- Distributing the tears over the surface of the eye to keep it moist and refreshed
- Protecting the eye from injury
- Limiting the amount of light entering the eye
Also Check: Why Does Armour Thyroid Cost So Much
The First Stage: Orbital Decompression
The principle of orbital decompression surgery is to expand the orbital space by widening the bony orbit and removal of excessive orbital fat. This decreases the venous congestion and mechanical pressure on the optic nerve, and also reduces proptosis. Theoretically, there are four bony orbital walls available for decompression: Medial, inferior, lateral, and superior wall. Historically, the inferior and medial walls were removed by the otorhinolaryngologists and the deep lateral wall by the neurosurgeons. The transantral approach created unbalanced inferomedial decompression with a high incidence of consecutive strabismus, infraorbital anesthesia, and sinusitis. The fourth wall, orbital roof decompression was initially advocated by Naffziger, but is fraught with potentially serious complications, and hence is best avoided except in extreme cases.
Mild right eye proptosis managed by trans-conjunctival fat decompression, also referred to as the first wall in orbital decompression
Lateral wall decompression
Medial wall decompression
Orbital floor decompression
Three wall decompression
A three-wall decompression is usually chosen for severe grades of proptosis , and all three walls: Lateral, medial, and floor are addressed along with intraconal fat removal .
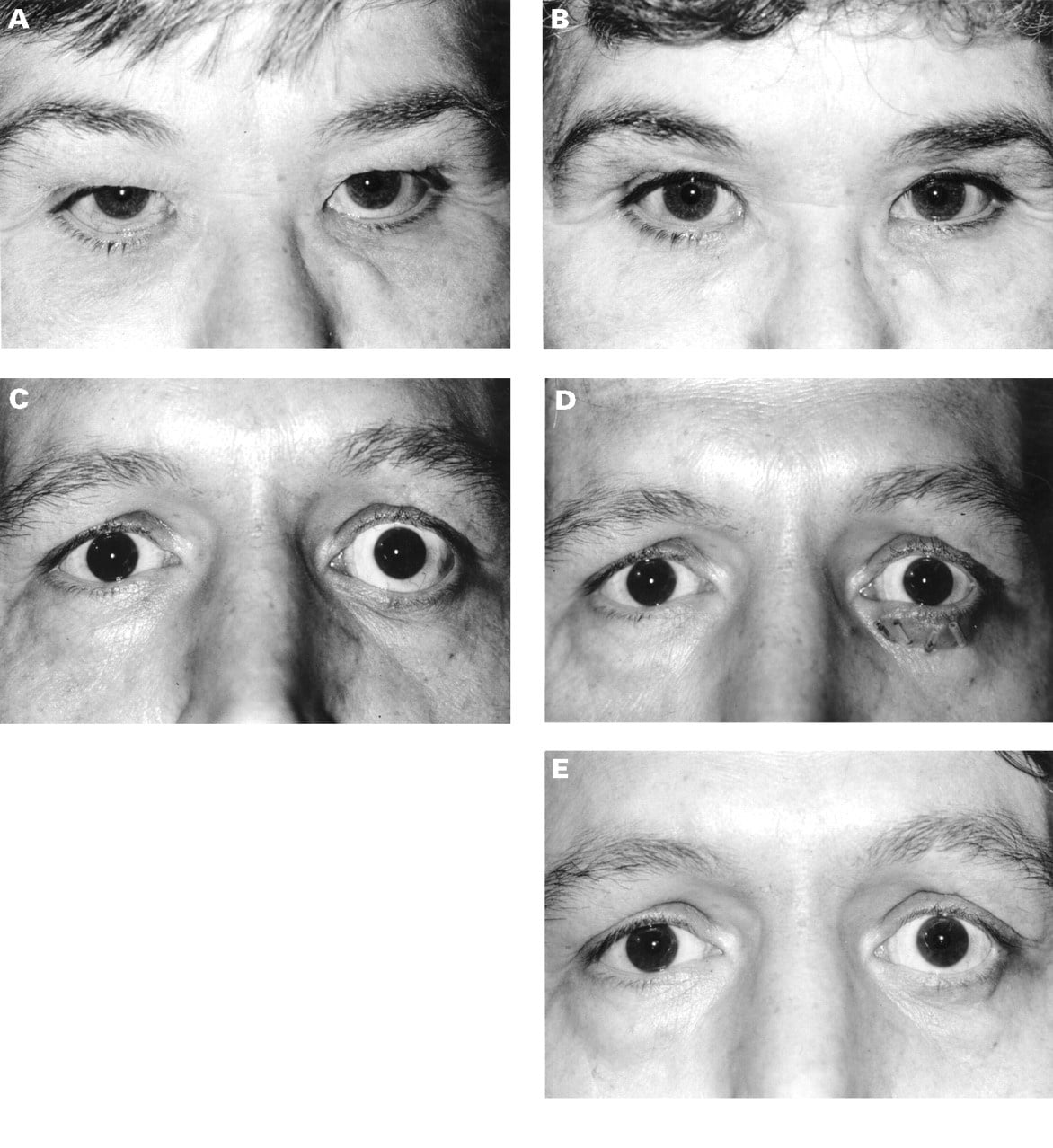
Group A Surgery: Donor Sclera
Donor sclera was obtained from donors without known neurological disease and tested negative for HIV and hepatitis B, prepared in alcohol and washed before use. Surgery was performed under either local anaesthetic infiltration or general anaesthesia, according to the patients preference. Two 4/0 nylon traction sutures were placed in the lower eyelid margin and the eyelid everted over a Desmarres retractor. The conjunctiva and the anterior part of the lower eyelid retractors were divided from the lower border of the tarsal plate, dissected off the orbital septum and orbicularis anteriorly, and the ALER separated from the conjunctiva. Alternatively, the conjunctiva was initially dissected free of the underlying ALER and then the lower eyelid retractors disinserted from the tarsal edge. The medial and lateral horns of the ALER were divided. The prepared scleral graft was interposed between the retractors and lower border of the tarsal plate, covered by the conjunctiva. The vertical height of the scleral graft size was selected as 6 mm greater than the lower scleral show this extra 6 mm allowing 34 mm loss of height due to suturing and 23 mm loss due to postoperative fibrosis.
Read Also: How Do You Develop Thyroid Cancer
Evaluation Of Lower Eyelid Retraction
Lower eyelid retraction occurs in some patients with thyroid ophthalmopathy. The amount of retraction is measured by the distance from the inferior limbus to the lower eyelid temporally, centrally, and nasally. Normally, the lower eyelid is at the level of the inferior limbus. This measurement is helpful in determining the size of the grafts used to treat lower eyelid retraction .
Another measurement is the margin reflex distance-2 .5 The MRD2 is the distance from a corneal light reflex to the lower eyelid as the examiner and patient’s eyes line up at the same level and the examiner shines a muscle light at the patient’s eyes. This distance normally is about 5.5 mm but increases with lower eyelid retraction. The MRD2 also is helpful in determining the size of the grafts used to treat lower eyelid retraction .
Henry B. Burch, Rebecca S. Bahn, in, 2016
What Causes Thyroid Eye Disease
TED is usually associated with systemic hyperthyroidism or Graves’ disease. This disease is caused by what is described as an autoimmune process. Autoimmune disease may be understood as a process by which the body sees some part of itself as being foreign and reacts to it much the same way that it would to any bacteria or virus.
In the case of Graves’ disease, the body sees the thyroid gland as the foreign object and produces antibodies that attack the thyroid gland. This often causes the thyroid gland to become over active.
The eye version of this disease is called Thyroid Eye Disease. However, in the case of TED, different antibodies attack the muscles associated with eye and eyelid movement. Although the thyroid gland and the eye may be under attack by the same immune system, it is felt that both conditions remain mostly independent of one another. The antibodies that attack the eye can cause inflammation and swelling of the fat and muscles around the eye, which is what can eventually cause bulging of the eyes, double vision and retraction of the eyelids.
Will my eyes go back to normal after treatment?
Read Also: Best Supplements For Underactive Thyroid
Thyroid Eye Disease Center
Quick link – Oculofacial Plastics and Reconstructive Surgery
The eye changes associated with thyroid disease are referred to as Thyroid Eye Disease . Your doctor may also use the term Thyroid Associated Orbitopathy . Although TED is seen in all types of thyroid disorders, it is most common in patients that are or were hyperthyroid. It also rarely occurs in those who are hypothyroid and even when there is an absence of thyroid abnormalities in the body.
Thyroid disease can cause multiple eye problems. These include redness and swelling, double vision, decreased vision, eyelid retraction , and a bulging of the eye itself. It is important to realize that if one of these occurs, it does not mean you will necessarily get all the other symptoms too.
Eye problems will usually occur and frequently change in type or severity for between six months and two years. Once stabilized, it is unusual for the eyes to start changing again. Some patients are left with permanent changes, and in others the eyes return to normal. A great deal can be done to improve these conditions with medical treatment, although some patients will need surgery to help ease their issues.
What Is Eyelid Repair
If your eyelids are pulled back, it is hard or impossible to blink or close your eyes. Also, your eyelids might open too wide and make it look like you are always staring.
Eyelid repair surgery may be needed to release the tight tissues and muscles around the eyelid. Surgical repair allows your eyelids to return to their natural shape and position. This not only helps with the cosmetic appearance of your face but also the function of your eyelids.1,3
Eyelid repair is performed after the inflammatory active phase of TED, when swelling and damage is reduced.3
Recommended Reading: Thyroid Eye Disease Vs Graves
Thyroid Eye Disease & Eyelid Retraction
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which there is overproduction of thyroid hormone. Abnormal antibodies that attack the thyroid gland cause it to become overactive. Abnormal antibodies may also cause swelling and inflammation of the soft tissues around the eyes and the muscles that move the eyes and eyelids. As a result the eyes may protrude, the lids may open too widely, or the eyes may not move together well causing double vision. Therefore, the eyes appear excessively prominent with a staring expression and infrequent blinking.
Many patients start experiencing eye problems as soon as their thyroid gland becomes overactive. For some, the eye changes may develop before hyperthyroidism is clinically detected, while others may not develop symptoms until months or years later. Both eyes are usually affected, however they may not be affected to the same degree or at the same time.
Some patients may also experience pressure around the eyes, ocular irritation and tearing from excessive exposure of the eyes. Overexposure during the day and difficulty closing the eyes at night can lead to dryness with injury and potential scarring of the cornea . Inflammation of the eye muscles may result in restricted eye movement causing persistent double vision. In some cases these muscles become so swollen that the enlarged muscles can compress the optic nerve resulting in progressive loss of vision.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
AFTER SURGERY
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
Clinical Significance And Management
Eyelid retraction can cause lagophthalmos and subsequent corneal and ocular surface disease, from dry eye symptoms to exposure keratopathy. Exposure keratopathy may progress to corneal ulceration and perforation. Thus, management of eyelid disease is vital to preserve vision. Treatment of upper eyelid retraction is aimed at correcting the underlying cause. If thyroid disease is suspected, serological tests should be ordered for thyroid hormone levels, thyrotropin receptor antibodies, and orbital imaging studies. Ocular lubrication using artificial tears, ointments or punctal plugs to relieve irritation from corneal exposure can be used in mild cases of upper eyelid retraction. Mild eyelid retraction in thyroid eye disease can resolve spontaneously with time.
There are a variety of surgical techniques to correct eyelid retraction if the condition persists or the eyelid retraction causes an immediate threat to the cornea or vision. These techniques include release or recession of eyelid retractors, with or without use of spacers or grafts. Surgical intervention ranges from temporary suture tarsorrhaphy for ocular surface protection to eyelid-lengthening procedures to correct retraction and decrease scleral show.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Thyroid Booster
Eyelid Ptosis Or Retraction
A patient’s response to phenylephrine testing can also guide therapy. Müller’s muscle receives its innervation from sympathetic fibers within the oculomotor nerve and can be directly activated with -adrenergic eye drops. In general, the patient receives three drops of 2.5% phenylephrine over the course of 1min and a final drop applied 1min later. After several minutes, the patient’s eyelid position is re-measured. Posterior approaches to ptosis correction are typically reserved for patients with mild ptosis and a positive response.
In patients with unilateral eyelid ptosis, one may be tempted to operate on the normal eye, which may appear to be retracted, instead of the disguised ptotic eye. As a consequence of Hering’s Law, both levators are energized equally in an attempt to clear the visual axis of the ptotic lid, thereby making the normal lid appear retracted. Covering each eye separately and observing the lid position often leads to the discovery of the ptotic eye as the pathologic source. The retracted eye will drop to its normal position once the ptotic eye is covered, only to have the ptotic eye rise when it is uncovered. Symmetric elevation of the brow is similarly helpful in patients in whom asymmetric brow pseudoptosis obstructs peripheral vision.
Allen M. Putterman, in, 2008
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Options
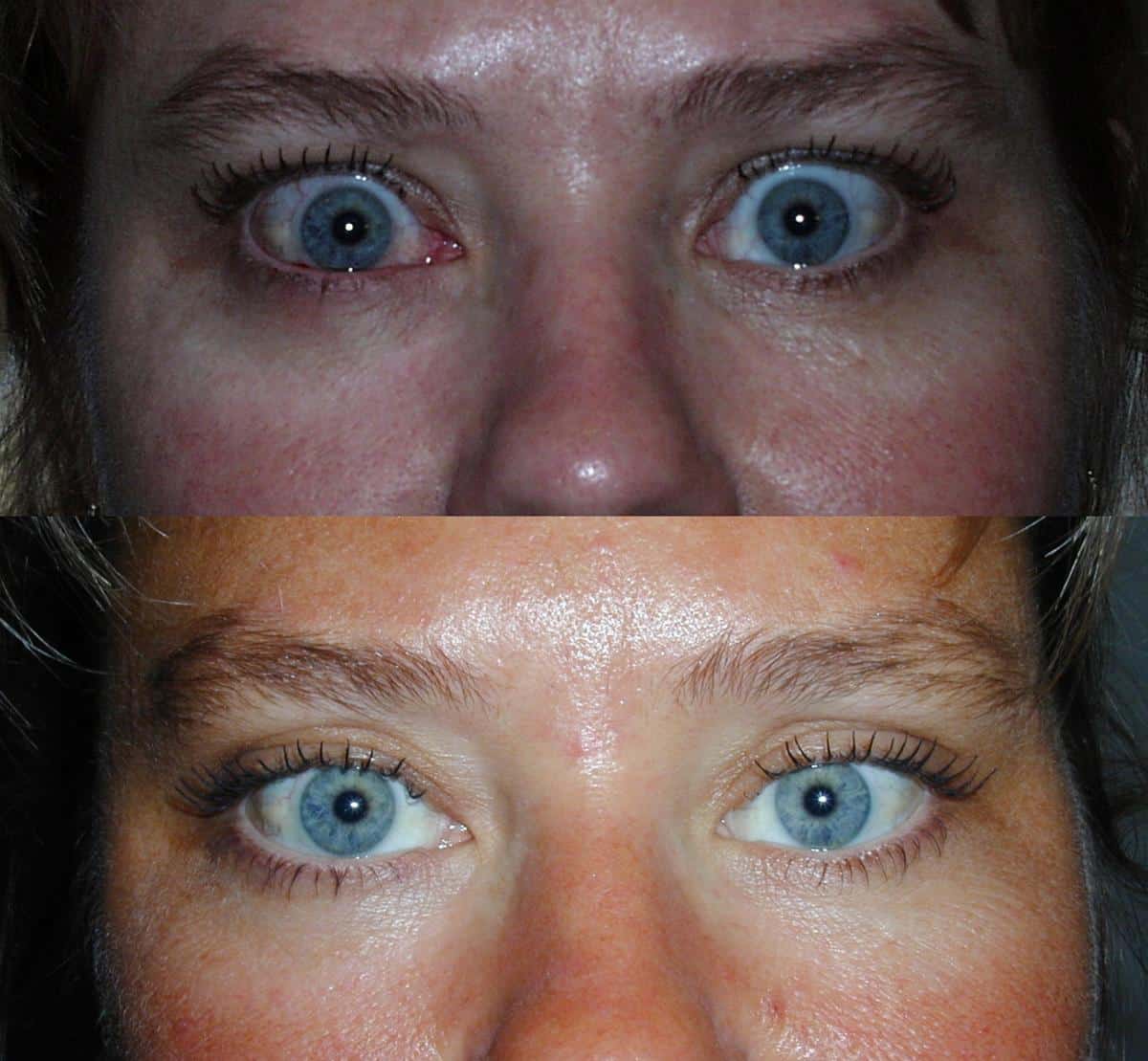
The two techniques that Oculoplastic surgeon Dr. Amiya Prasad often uses in thyroid eye treatment are as follows:
Eyelid Retraction Repair Surgery
Eyelid retraction repair surgery can be performed to improve the appearance of the eyes, as well as improve the function of the eyelids. The more retracted the eyelid is, the more complex the procedure typically is. Eyelid surgery is usually done after the inflammatory stage of thyroid eye disease has resolved, which allows Dr. Prasad to perform the surgery in a more predictable manner.
Orbital Decompression Surgery
Orbital decompression surgery reduces fat behind the eye and opens the bony structure around the eye to allow the swollen tissue to move into a space. This allows the eyes to move back to a more normal position and reduce pressure on the optic nerve. Orbital decompression is typically performed in our operating facilities under general anesthesia.
Read Also: Hair Loss From Thyroid Disease
Surgery For Eyelid Retraction
TED can cause muscles and fatty tissue behind your eye to swell. This can push your eye out of position.
In some cases, your eyelid is no longer able to cover the whole eye. When your eyelid cant close all the way, the exposed part of your eye becomes very irritated.
This surgery adjusts the position of your eyelid.
Why Aren’t There Any Ratings
There is no publicly available rating for this care provider for one of three reasons:
- Ophthalmology, Oculofacial Plastic Surgery and Ophthalmology Portland
Recommended Reading: Thyroid And Menopause Weight Gain
The Four Stages Of Surgical Rehabilitation
There are four components of TED that require attention from the surgical point of view: proptosis, restrictive strabismus, eyelid abnormality , and cosmetic concerns . Based on these four components, the surgical management of TED involves four major stages of rehabilitation: orbital decompression, extraocular muscle surgery, eyelid repositioning, and cosmetic soft tissue redraping. Not all patients require all four stages, but one may require more than one stage of surgery.
The second stage constitutes the correction of diplopia, which is the most disabling side-effect of TED, and the most challenging to treat. The current day decompression surgeries focus on decreasing the rate of new-onset strabismus.
Correction of eyelid abnormality constitutes the third stage, and most commonly includes correction of upper and lower eyelid retraction. There are several surgical options described for the correction of eyelid retraction. The fourth stage of cosmetic concerns includes eyelid fat bags, periorbital hollows, and rhytids such as glabellar folds. These are best treated toward the end of the surgical rehabilitation, addressing the esthetic concerns and restoring the normal appearance.
Effect Of Surgery On The Lower Eyelid Height And Contour
Group A
All 13 patients had a significant reduction in lower MRD and a good eyelid contour 1 month after surgery. The reduction in lower MRD and good contour was maintained at 3 and 6 months after surgery , and none required further surgery .
Scleral grafts. Case 1. Bilateral lower eyelid retraction in a patient who has had previous bilateral orbital decompression with later right medial and inferior rectus recession. She also has upper eyelid dermatochalasis which, combined with the lower eyelid retraction, has given her an apparent head tilt with chin down. Case 1. One year after bilateral lower eyelid scleral grafts and upper eyelid blepharoplasty. The upper eyelid blepharoplasty has greatly improved her overall appearance. Case 2. Left unilateral proptosis and marked lower eyelid retraction in a patient who has had previous inferior rectus recession. He had a variable mild left upper eyelid retraction and opted for lower eyelid surgery only. Case 2. After a large sized scleral graft with vertical bolsters. Case 2. Six months after left lower eyelid scleral graft. Note slightly bulky lower eyelid and skin crease lower than the unoperated right side.
Scleral show was significantly reduced at 1 month , 3 months , and 6 months after surgery .
Group B
There was no significant difference in the change of lower MRD and SS between patients treated with adjuvant 5-fluorouracil or mitomycin C.
Postoperative complications
You May Like: Thyroid Cancer And Colon Cancer Link
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Eyelid Repair Surgery
Along with minor pain, bruising, and discomfort after the repair, some side effects are possible. These include:5,6
- Vision problems Blurred or double vision are usually mild and last only a few days after surgery.
- Problems closing your eyes Some people have problems with closing their eyes after surgery. This is usually temporary but sometimes requires more treatment or another surgery.
- Swelling and misalignment of the eyelid Swelling and slight misalignment of the eyelid is not uncommon. This usually goes away with the healing process.
- Sagging of the lower eyelid Known as ectropion , rolling or sagging of the lower eyelid might occur after eyelid repair.
These are not all the possible side effects of eyelid repair. Talk to your doctor about what to expect with eyelid repair. You also should call your doctor if you have any changes that concern you after the procedure.
The Eye Specialist Role
Your specialist can provide simple solutions to the irritation, tearing and swelling often associated with TED. Often, this involves something as simple as using artificial tears during the day and lubrication ointment at night. Your specialist can determine when your eyes have stopped changing and whether corrective surgery is needed. Your specialist may also watch for the rare serious problems associated with TED that need prompt treatment.
Also Check: 3 Types Of Thyroid Cancer
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Thyroid Eye Disease
The visible changes associated with thyroid eye disease include bulging or protrusion of one or both eyes, and this is why an oculofacial specialist can be of particular help. Commonly, there is a change in the height of the upper eyelid and it may appear raised or retracted. The fat that surrounds the eye can become more prominent and create more swelling or bags around the upper and lower eyelids. Eyes can become red, irritated, dry, and painful.
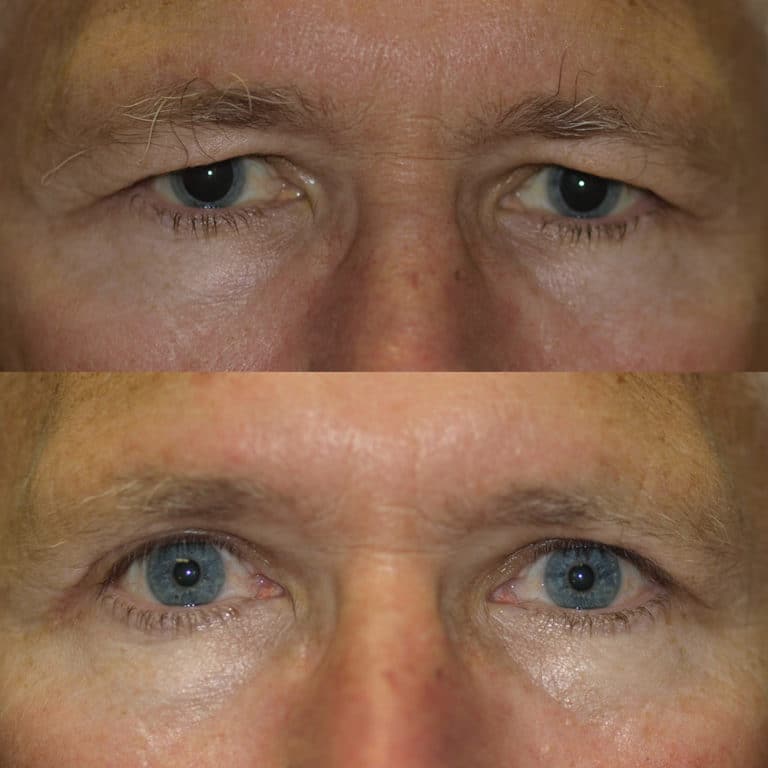
How Graves Disease / Orbital Decompression Affects The Eyes
Thyroid eye disease, also called Graves disease, afflicts patients, usually women, and can result in blindness, blurry vision, double vision, or uncomfortable eyes.
From a cosmetic standpoint, bulging of the eyes and eyelid retraction give Graves disease eyes a bug-eye appearance. They may look angry, worried or afraid. In our Philadelphia practice, we are accustomed to correcting complications from thyroid eye disease. Our techniques in patients with thyroid eye disease have been presented nationally and published in scientific journals and textbooks.
Read Also: Thyro-tabs For Dogs Side Effects