Follicular Thyroid Cancer Surgery In Sites Other Than The Neck
Follicular thyroid cancer surgery is uncommonly proposed as a treatment approach when disease has spread to distant sites. Although surgery is not commonly proposed for distant spread of follicular thyroid cancer, consideration for surgery for distant disease is based upon the expert thyroid cancer team evaluation and considers the following issues:
- Where is the follicular thyroid cancer distant disease located?
- What are the risks and benefits of surgery?
- Are there other sites of distant spread?
- What follicular thyroid cancer treatments have already been used?
- What were the outcomes of other treatments for the follicular thyroid cancer?
- How fast is the follicular thyroid cancer growing?
- What are the patient’s treatment desires?
- What are the other treatment options?
- What is the follicular thyroid cancer pathologic type (what do the cells look like under the microscope?
- What are the follicular thyroid cancer genetic mutations found?
Extended Or Complicated Thyroidectomy
Follicular thyroid cancer may sometimes be more aggressive than ultrasound or CT imaging suggested prior to undergoing surgery. In these cases, an expert surgeon that recognizes those “more aggressive” intraoperative findings such as growth or extension of the cancer outside of the thyroid gland or invasion of the cancer into adjacent structures such as the nerve to the voice box , breathing tube , voice box, or esophagus-must adapt the surgery to adequately address the complete removal of the cancer. Unfortunately, occasional thyroid surgeons are commonly unprepared to perform the appropriate surgery and a subsequent surgery for persistent disease will be required.
Ethics Approval And Informed Consent
This study was approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Chinese PLA General Hospital and the requirement for informed consent was waived because the patients data were evaluated retrospectively and anonymously. All members of our team are committed to confidentiality of patients data and compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
You May Like: Treating Thyroid Cancer Without Surgery
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if thyroid cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually thyroid cancer cells. The disease is metastatic thyroid cancer, not lung cancer.
There Are Different Types Of Thyroid Cancer
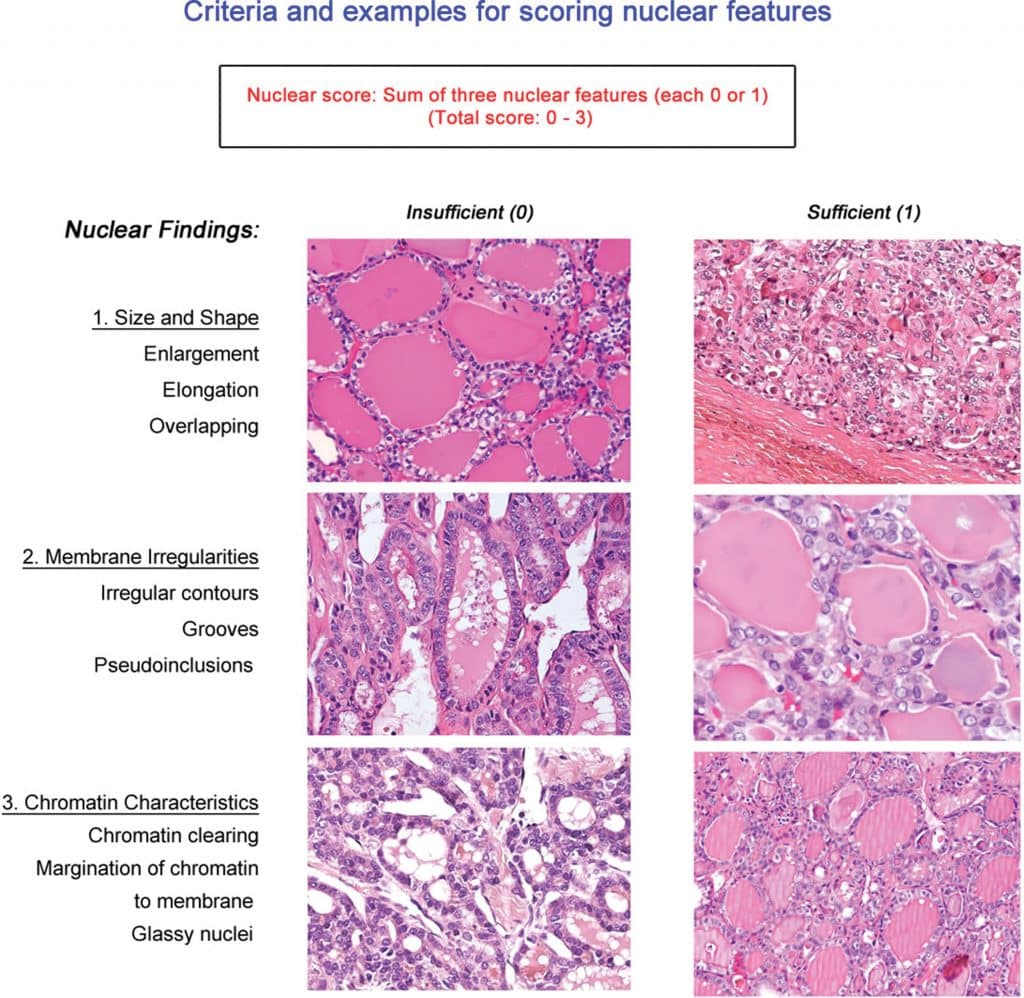
Thyroid cancer can be described as either:
- Differentiated thyroid cancer, which includes well-differentiatedtumors, poorly differentiated tumors, and undifferentiated tumors or
Well-differentiated tumors can be treated and can usually be cured.
Poorly differentiated and undifferentiated tumors are less common. These tumors grow and spread quickly and have a poorer chance of recovery. Patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer should have molecular testing for a mutation in the BRAFgene.
Medullary thyroid cancer is a neuroendocrine tumor that develops in C cells of the thyroid. The C cells make a hormone that helps maintain a healthy level of calcium in the blood.
See the PDQ summary on Childhood Thyroid Cancer Treatment for information about childhood thyroid cancer.
Don’t Miss: Are Armour Thyroid And Np Thyroid Ab Rated
Signs Of Thyroid Cancer Include A Swelling Or Lump In The Neck
Thyroid cancer may not cause early signs or symptoms. It is sometimes found during a routine physical exam. Signs or symptoms may occur as the tumor gets bigger. Other conditions may cause the same signs or symptoms. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- A lump in the neck.
- Trouble breathing.
The Follicular Thyroid Cancer Tnm Staging System
A staging system is a standard way to sum up how large a cancer is and how far it has spread.
The most common system used to describe the stages of thyroid cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. The TNM system is based on 3 key pieces of information:
- T indicates the size of the main tumor and whether it has grown into nearby areas.
- N describes the extent of spread to nearby lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped collections of immune system cells to which cancers often spread first. Cells from thyroid cancers can travel to lymph nodes in the neck and chest areas.
- M indicates whether the cancer has spread to other organs of the body.
Numbers or letters appear after T, N, and M to provide more details about each of these factors. The numbers 0 through 4 indicate increasing severity. The letter X means a category can’t be assessed because the information is not available.
Read Also: How To Reset Thyroid To Burn Fat
Characteristics Of Follicular Thyroid Cancer
- Peak onset ages 40 through 60
- Females more common than males by 3 to 1 ratio
- Prognosis directly related to tumor size
- Rarely associated with radiation exposure
- Spread to lymph nodes is uncommon
- Invasion into vascular structures within the thyroid gland is common
- Distant spread is uncommon, but more common than with papillary cancer
- Overall cure rate high , decreases with advanced age
External Beam Radiation Therapy For Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Follicular thyroid cancer treatment with external beam radiation therapy is not commonly required or indicated. The planning and implementation of radiation therapy is beyond the goals for this website. However certain principles must be emphasized. Radiation therapy is not a substitute for incomplete surgery. What is meant by that is all the follicular thyroid cancer in the neck must be completely and effectively removed. Whenever feasible, follicular thyroid cancer patients should be reduced down to microscopic remaining neck disease, at most, also sparing voice box and swallowing tube function. Radiation therapy should not be given as a substitute for incomplete surgery. As a general rule, choosing to treat a follicular thyroid cancer with external beam radiation is a commitment that the surgeon believes that no meaningful re-operation will be feasible in the future and therefore radiation therapy is required to help control the follicular thyroid cancer remaining in the neck. In these circumstances, external beam radiation therapy is quite effective. Follicular thyroid cancer radiation therapy is also associated with significant short term and long term complications and effects that should not be taken lightly.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Thyroid Problems In Cats
What Is The Appropriate Extent Of Thyroidectomy For Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Most patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma should undergo a total or near-total thyroidectomy. Several studies have shown that for larger tumors, total or near-total thyroidectomy compared with lesser resections results in lower recurrence rates and improved survival. A recent study reviewed data from the National Cancer Data Base and found that there was no difference in outcome between patients who underwent lobectomy versus near-total or total thyroidectomy when the size of the tumor was less than 1 cm. However, near-total or total thyroidectomy for tumors larger than 1 cm resulted in lower recurrence and improved survival compared with patients who underwent lobectomy. This improved outcome was seen even in the subset of patients with tumors 1 to 2 cm in size. Therefore the majority of patients should undergo total or near-total thyroidectomy. In addition, near-total or total thyroidectomy facilitates postoperative treatment with radioiodine and permits accurate long-term surveillance for disease recurrence by thyroglobulin measurement.
Rebecca Chernock, Michelle D. Williams, in, 2021
Outlook For Thyroid Cancer
Around 9 in every 10 people are alive 5 years after a diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Many of these are cured and will have a normal lifespan.
But the outlook varies depending on the type of thyroid cancer and how early it was diagnosed. At present the outlook is:
- more than 9 in 10 people with papillary carcinoma live at least 5 years after diagnosis
- more than 9 in 10 people with follicular carcinoma live at least 5 years after diagnosis
- more than 7 in 10 men, and around 9 in 10 women with medullary thyroid carcinoma live at least 5 years after diagnosis
- around 1 in 10 people with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma live at least 5 years after diagnosis
Up to 1 in 4 people treated for thyroid cancer are later diagnosed with cancer in another part of the body, such as the lungs or bones, but cancer can often be treated again if this happens.
Page last reviewed: 28 August 2019 Next review due: 28 August 2022
Read Also: How To Help Someone With Thyroid Problems
Potential Reasons To Consider Removing The Entire Thyroid Gland :
- The follicular thyroid cancer is large (more than 4 centimeters or 1.75 inches
- The follicular thyroid cancer appears to have extended outside of the surface of the thyroid gland
- The follicular thyroid cancer has spread to the lymph nodes underneath the thyroid gland
- The follicular thyroid cancer has spread to lymph nodes along the side of the neck
- The follicular thyroid cancer has spread to distant sites outside of the neck
- The follicular thyroid cancer patient with a small thyroid cancer, does not accept the potential of another surgery to remove the remainder of the thyroid gland if a new thyroid cancer should develop within the remaining thyroid tissue.
A Model Of The Cost Of Delaying Treatment Of Hashimotos Thyroiditis: Thyroid Cancer Initiation And Growth
- Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, 800 W. Main Street, Whitewater, WI 53190-1790, USA
- 2. Department of MSCS, Marquette University, WI 53201-1881, USA
- Received: 31 May 2019Accepted: 22 August 2019 05 September 2019
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder that drives the function of thyroid gland to the sequential clinical states:euthyroidism , subclinical hypothyroidism and overt hypothyroidism . In this disease, serum thyroidstimulating hormone levels increase monotonically, stimulating the thyroid follicular cells chronically and initiating benign thyroid nodules at various sites of the thyroid gland. This process can also encourage growth of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Due to prolonged TSH stimulation, thyroid nodules may grow and become clinically relevant without the administration of treatment by thyroid hormone replacement. Papillary thyroid cancer whose incidence is increasing worldwide, is associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. A stochastic model is developed here to produce the statistical distribution of thyroid nodule sizes and growth by taking serum TSH value as the continuous input to the model using TSH values from the output of the patientspecific deterministic model developed for the clinical progression of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- Keywords:
Read Also: Afirma Test For Thyroid Nodules
What Are The Symptoms Of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer often presents as a lump or nodule in the thyroid and usually does not cause any other symptoms . Blood tests generally do not help to find thyroid cancer and thyroid blood tests such as TSH are usually normal, even when a cancer is present. Neck examination by your doctor is a common way in which thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer are found. Often, thyroid nodules are discovered incidentally on imaging tests like CT scans and neck ultrasounds done for completely unrelated reasons. You may have found a thyroid nodule by noticing a lump in your neck while looking in a mirror, buttoning your collar, or fastening a necklace. Rarely, thyroid cancers and nodules may cause symptoms. You may complain of pain in the neck, jaw, or ear. If a nodule is large enough to compress your windpipe or esophagus, it may cause difficulty with breathing, swallowing, or cause a tickle in the throat sensation. Even less commonly, you may develop hoarseness if a thyroid cancer invades the nerve that controls your vocal cords.
Cancers arising in thyroid nodules generally do not cause symptoms, and thyroid function tests are typically normal even when you have cancer. The best way to find a thyroid nodule is to make sure that your doctor examines your neck as part of your periodic check-up.
Types Of Thyroid Cancer
There are 4 main types of thyroid cancer:
- papillary carcinoma the most common type, accounting for about 8 in 10 cases it usually affects people under 40, particularly women
- follicular carcinoma accounts for up to 1 in 10 cases and tends to affect middle-aged adults, particularly women
- medullary thyroid carcinoma accounts for less than 1 in 10 cases unlike the other types, it can run in families
- anaplastic thyroid carcinoma the rarest and most serious type, accounting for around 1 in 50 cases it usually affects people over the age of 60
Papillary and follicular carcinomas are sometimes known as differentiated thyroid cancers. They tend to be easier to treat than the other types.
Recommended Reading: Armor Thyroid And Weight Loss
Diagnosis Of Follicular Thyroid Cancer
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer cannot be made by fine needle aspiration of a thyroid nodule!
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer in a thyroid nodule can only be obtained by complete removal of the thyroid mass
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer accounts for less than 10% of all thyroid cancers
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is three times more common in women than in men
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer occurs most commonly above 40 years of age and rarely occurs in children
- Follicular thyroid cancer rarely spreads to lymph nodes
- The diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer is rarely associated with a history of radiation exposure
What Is The Difference Between Follicular Thyroid Cancer And Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancers are neuroendocrine tumors. This cancer occurs in the C-cells of your thyroid and often runs in families. C-cells make calcitonin, which regulates calcium levels in your blood. Medullary thyroid cancers are more aggressive and less differentiated than follicular thyroid cancers. They are more likely to spread to lymph nodes and other areas of your body.
Read Also: What Are The Symtoms Of Thyroid Cancer
Total Or Partial Thyroidectomy
Surgical removal of the tumor and any affected areas is the first-line treatment for follicular thyroid cancer. There is disagreement among medical professionals on whether the entire thyroid or only the affected lobe of the thyroid should be removed in cases where tumors are only found on one side. Whether you have a full or partial removal of the thyroid gland will depend on your specific circumstances and be between you and your healthcare provider.
If the tumor is small and has not spread surgery may be the only treatment you need. If the cancer has spread to any of the lymph nodes in the neck these will also need to be surgically removed and you may need follow up treatments .
If your thyroid is completely removed you will need to take oral medication for the remainder of your life to replace the thyroid hormones your body is no longer able to make.
Following a thyroidectomy most people spend the night in the hospital. You can expect to have some pain, a sore throat and hoarseness following surgery.
The parathyroid glands, glands which play an important part in regulating calcium, are in close proximity or sometimes actually located within the thyroid and can go into shock following surgery. If this happens calcium levels can drop. For this reason your calcium levels are closely monitored and you may be given oral or intravenous calcium following a thyroidectomy.
Treatment Of A Patient With A Follicular Neoplasm
A patient with a fine needle aspiration biopsy consistent with a follicular neoplasm should, at minimum, undergo a diagnostic thyroid lobectomy and isthmusectomy. Patients with a follicular neoplasm and a prior history of head or neck radiation or nodular disease involving the contralateral lobe of the thyroid gland should be treated with a definitive total thyroidectomy. Frozen section examination has not been helpful for intraoperative decision-making because it rarely distinguishes a follicular adenoma from a follicular carcinoma. This has been confirmed by a randomized clinical trial .
The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of frozen-section examination are similar to fine needle aspiration biopsy, and frozen-section examination rarely provides any additional information in patients with a fine needle aspiration biopsy consistent with a follicular neoplasm . In 95% of patients with a follicular neoplasm, the frozen-section exam diagnosis that is rendered at operation is consistent with a follicular neoplasm and a definitive diagnosis is deferred until all of the permanent sections have been reviewed . Chen and colleagues reported that, in patients with a follicular neoplasm, frozen-section exam rendered no useful information in 87% and was inaccurate in 5% .
Read Also: Diabetes And Thyroid Center Of Ft Worth
Causes Of Papillary And Follicular Thyroid Cancer
We do not know what causes thyroid cancer in most people. But there are some things that may increase your risk of developing it. These are called risk factors. Having one or more risk factors does not mean you will get thyroid cancer. And if you do not have any risk factors, it does not mean you will not get cancer.
Treatments For Thyroid Cancer

Treatment for thyroid cancer depends on the type of thyroid cancer you have and how far it has spread.
The main treatments are:
- surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid
- radioactive iodine treatment you swallow a radioactive substance that travels through your blood and kills the cancer cells
- external radiotherapy a machine is used to direct beams of radiation at the cancer cells to kill them
- chemotherapy and targeted therapies medicines used to kill cancer cells
After treatment, you’ll have follow-up appointments to check whether the cancer has come back.
Read more about how thyroid cancer is treated.
Don’t Miss: Armour Thyroid Manufacturer Coupon 2022