Follicular Thyroid Cancer Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery for the thyroid was developed largely in South Korea and brought to the United States several years ago as a “tool” in thyroid surgery. Its proposed benefits were to be the following:
- Absent or less noticeable neck incisions
- Improved visualization
- Less Surgeon Fatigue
Although we have been trained and performed robotic thyroid surgery, the following is the reality of robotic thyroid surgery:
- Incisions are tremendously longer but just not located on the front of the neck
- In follicular thyroid cancer, it is a one sided surgery approach to a frequently required two-sided surgery!
- The instruments used to perform the surgery are not as refined or delicate as the instruments used to perform the minimally invasive neck surgeries.
- Multiple surgeons are required
- The surgeon has no ability to
- in the neck. The fingers are the surgeon’s third eye. Subtle changes in feel, hardness or extension of cancer can be totally unappreciated.
- t is not minimally invasive by any measure. It is maximally invasive but just at a distance from where the surgery is focusing.
- It is a much longer surgical procedure by any measure .
- It is an inferior surgical approach to manage follicular thyroid cancer
- Unanticipated findings during surgery may not be able to be adequately addressed robotically.
- It may be an acceptable surgical approach for clearly known benign thyroid surgery.
Extended Or Complicated Thyroidectomy
Follicular thyroid cancer may sometimes be more aggressive than ultrasound or CT imaging suggested prior to undergoing surgery. In these cases, an expert surgeon that recognizes those “more aggressive” intraoperative findings such as growth or extension of the cancer outside of the thyroid gland or invasion of the cancer into adjacent structures such as the nerve to the voice box , breathing tube , voice box, or esophagus-must adapt the surgery to adequately address the complete removal of the cancer. Unfortunately, occasional thyroid surgeons are commonly unprepared to perform the appropriate surgery and a subsequent surgery for persistent disease will be required.
Potential Reasons To Consider Removing The Entire Thyroid Gland :
- The follicular thyroid cancer is large (more than 4 centimeters or 1.75 inches
- The follicular thyroid cancer appears to have extended outside of the surface of the thyroid gland
- The follicular thyroid cancer has spread to the lymph nodes underneath the thyroid gland
- The follicular thyroid cancer has spread to lymph nodes along the side of the neck
- The follicular thyroid cancer has spread to distant sites outside of the neck
- The follicular thyroid cancer patient with a small thyroid cancer, does not accept the potential of another surgery to remove the remainder of the thyroid gland if a new thyroid cancer should develop within the remaining thyroid tissue.
Don’t Miss: What Percentage Of Calcified Thyroid Nodules Are Cancerous
What Is The Difference Between Follicular Thyroid Cancer And Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancers are neuroendocrine tumors. This cancer occurs in the C-cells of your thyroid and often runs in families. C-cells make calcitonin, which regulates calcium levels in your blood. Medullary thyroid cancers are more aggressive and less differentiated than follicular thyroid cancers. They are more likely to spread to lymph nodes and other areas of your body.
Fineneedle Aspiration Cytology And Histopathology
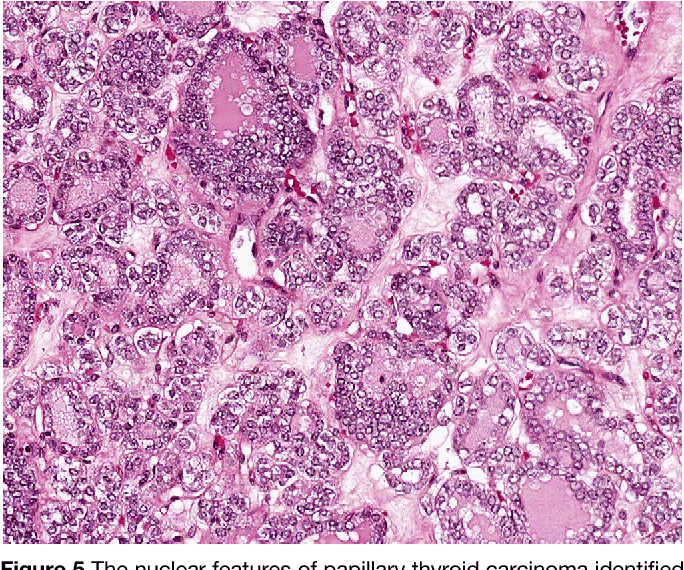
Histopathologic examination of tumor tissue from 23 of the 41 dogs with sublingual thyroid tumors revealed thyroid adenocarcinoma in all of these cases. The histologic type of thyroid carcinoma was follicular carcinoma in 13 dogs and mixed compactfollicular in 10 dogs. None of the dogs were considered to have compact thyroid adenocarcinoma or medullary carcinoma. In none of these cases was immunocytochemistry used, however, to differentiate a follicular cell origin of the tumor from Ccell origin .
Fineneedle aspiration cytology was performed in remaining 18 dogs. In most of these dogs, it was not possible to differentiate thyroid adenoma from adenocarcinoma, nor was it possible to exclude medullary carcinoma with cytology.
Don’t Miss: How To Regulate Your Thyroid
If I Am Diagnosed With Niftp How Should I Be Treated
Experts agree that following a diagnosis of NIFTP, additional surgery and radioactive iodine are not necessary and these treatments would only expose the person to greater side effects and risks without providing benefits. Patients diagnosed with NIFTP tumors should continue to have at least yearly follow up that includes a neck examination with their endocrinologist or surgeon. Alternative: Since NIFTP is still a relatively new diagnosis, many experts continue to suggest that patients with NIFTP have at least a yearly follow up with an endocrinologist or surgeon for a neck examination. Whether additional testing like routine neck ultrasonography, or blood tests for tumor markers like thyroglobulin should also be done yearly is unclear. Your follow up plan will require discussion with your treating provider, but will likely be far less intensive than follow up for thyroid cancer.
Follicular Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Follicular thyroid cancer treatment depends upon the stage of the cancer , the patient’s overall health, and the patients desires. This section discusses the typical treatment options for your follicular thyroid cancer. Treatment decision making is based upon three important factors:
- What is the optimal treatment for the follicular thyroid cancer
- What are the patient’s desires
- What are the capabilities and outcomes of the thyroid cancer team
You May Like: Different Types Of Thyroid Tests
Management Of Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Considerable controversy exits when discussing the management of well differentiated thyroid carcinomas . Some experts contend than if these tumors are small and not invading other tissues then simply removing the lobe of the thyroid which contains the tumor will provide as good a chance of cure as removing the entire thyroid. These proponents of conservative surgical therapy relate the low rate of clinical tumor recurrence despite the fact that small amounts of tumor cells can be found in up to 88% of the opposite lobe thyroid tissues. They also site some studies showing an increased risk of hypoparathyroidism and recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in patients undergoing total thyroidectomy . Proponents of total thyroidectomy site several large studies that show that in experienced hands the incidence of recurrent nerve injury and permanent hypoparathyroidism are quite low . More importantly, these studies show that patients with total thyroidectomy followed by radioiodine therapy and thyroid suppression, have a significantly lower recurrence rate and lower mortality when tumors are greater than 1.0 cm. One must remember that it is also desirable to reduce the amount of normal gland tissue that will take up radioiodine.
Editorial Note
Follicular Thyroid Cancer Surgery In Sites Other Than The Neck
Follicular thyroid cancer surgery is uncommonly proposed as a treatment approach when disease has spread to distant sites. Although surgery is not commonly proposed for distant spread of follicular thyroid cancer, consideration for surgery for distant disease is based upon the expert thyroid cancer team evaluation and considers the following issues:
- Where is the follicular thyroid cancer distant disease located?
- What are the risks and benefits of surgery?
- Are there other sites of distant spread?
- What follicular thyroid cancer treatments have already been used?
- What were the outcomes of other treatments for the follicular thyroid cancer?
- How fast is the follicular thyroid cancer growing?
- What are the patient’s treatment desires?
- What are the other treatment options?
- What is the follicular thyroid cancer pathologic type (what do the cells look like under the microscope?
- What are the follicular thyroid cancer genetic mutations found?
Also Check: Best Thyroid Diet To Lose Weight
What Kind Of Long
All follicular thyroid cancer patients are followed lifelong for their disease and hormone monitoring. Patients should receive an annual blood thyroglobulin level as well as high resolution ultrasound surveillance of the neck. Serum thyroglobulin are generally not useful as a screen for the initial diagnosis of thyroid cancer but is quite useful in follow up of well differentiated carcinoma . A high serum thyroglobulin level that had previously been low following total thyroidectomy especially if gradually increased with TSH stimulation is virtually indicative of recurrence. A value of greater than 10 ng/ml is often associated with structural recurrence even if an iodine scan is negative. Elevated thyroglobulin levels should be followed by diagnostic imaging efforts to define the potential local , regional or distant site analysis for structural abnormalities. Low unstimulated thyroglobulin levels in the 1-3 pg/ml may not be associated with identifiable structural disease.
ThyroidCancer.com is an educational service of the Clayman Thyroid Center, the world’s leading thyroid surgery center operating exclusively at the new Hospital for Endocrine Surgery.
Phone: 940-3130| © Copyright 2015-2022 | All rights reserved. | Disclaimer | Become Our Patient
Now Operating Exclusively at the Hospital for Endocrine Surgery
Clayman Thyroid Center News
Papillary Cancer And Its Variants
Most cancers are treated with removal of the thyroid gland , although small tumors that have not spread outside the thyroid gland may be treated by just removing the side of the thyroid containing the tumor . If lymph nodes are enlarged or show signs of cancer spread, they will be removed as well.
In addition, recent studies have suggested that people with micro-papillary cancers may safely choose to be watched closely with routine ultrasounds rather than have immediate surgery.
Even if the lymph nodes arent enlarged, some doctors recommend central compartment neck dissection along with removal of the thyroid. Although this operation has not been shown to improve cancer survival, it might lower the risk of cancer coming back in the neck area. Because removing the lymph nodes allows them to be checked for cancer, this surgery also makes it easier to accurately stage the cancer. If cancer has spread to other neck lymph nodes, a modified radical neck dissection is often done.
Treatment after surgery depends on the stage of the cancer:
People who have had a thyroidectomy will need to take daily thyroid hormone pills. If RAI treatment is planned, the start of thyroid hormone therapy may be delayed until the treatment is finished .
Also Check: Armour Thyroid Manufacturer Coupon 2022
Follicular Thyroid Cancer Treatment For Persistent Or Recurrent Disease:
Follicular thyroid cancer treatment for recurrences or persistence depends mainly on where the cancer is, although other factors may be important as well. The recurrence may be found by either thyroglobulin blood tests or imaging studies such as ultrasounds, radioiodine scans, CAT scan or PET imaging.
If there is concern that the follicular thyroid cancer has come back in the neck, an ultrasound-guided biopsy is first done to confirm that it is really cancer. Then, if the follicular thyroid cancer appears to be resectable , surgery is often used. The extent of surgery would depend upon the location or locations of the persistent or recurrent follicular thyroid cancer and the prior surgeries and quality of surgeries that the patient has undergone. The sections of central compartment surgery and lateral neck dissection have been written for you and are appropriate for persistence or recurrent follicular thyroid cancer in either of those locations. We have examples of surgeries for just these types of circumstances for you to watch. Follicular thyroid cancer surgery very effectively manages neck disease, sparing function and cosmetic appearance but should only be performed by very high volume and experienced follicular thyroid cancer surgeons. We have publications establishing our ability to control follicular thyroid cancer recurrences or persistence in the neck approaching 98% in both of these areas of the neck lymph nodes.
External Beam Radiation Therapy For Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Follicular thyroid cancer treatment with external beam radiation therapy is not commonly required or indicated. The planning and implementation of radiation therapy is beyond the goals for this website. However certain principles must be emphasized. Radiation therapy is not a substitute for incomplete surgery. What is meant by that is all the follicular thyroid cancer in the neck must be completely and effectively removed. Whenever feasible, follicular thyroid cancer patients should be reduced down to microscopic remaining neck disease, at most, also sparing voice box and swallowing tube function. Radiation therapy should not be given as a substitute for incomplete surgery. As a general rule, choosing to treat a follicular thyroid cancer with external beam radiation is a commitment that the surgeon believes that no meaningful re-operation will be feasible in the future and therefore radiation therapy is required to help control the follicular thyroid cancer remaining in the neck. In these circumstances, external beam radiation therapy is quite effective. Follicular thyroid cancer radiation therapy is also associated with significant short term and long term complications and effects that should not be taken lightly.
Also Check: If Thyroid Levels Are High
The Types Of Thyroid Cancer
Different cancers can develop from different cells in the body. According to the National Health Service in the United Kingdom, there are four main types of thyroid cancer, falling under three umbrella categories that are known as differentiated, anaplastic, and medullary:
Papillary and follicular thyroid cancers are known as differentiated thyroid cancers. Differentiated thyroid cancers usually grow slowly over time.
- T describes the size of the tumor
- N signifies the involvement of lymph nodes
- M signifies metastasis, which means the spreading of the cancer cells to other parts of the body
For people under the age of 55, the staging is:
Staging for people over the age of 55 is as follows:
Diagnosing follicular thyroid cancer may include a doctor carrying out the following:
Thyroid Hormone Suppressive Therapy For Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid hormone is a necessary hormone for life. The thyroid gland normally produces thyroid hormone to adequate levels. The amount of thyroid hormone produced by the body is strictly controlled by a portion of the brain called the pituitary gland. When the body has too little thyroid hormone, the pituitary gland senses the low levels and produces TSH . When thyroid hormone levels are elevated , the pituitary does the opposite and lowers its production of TSH. This is called an endocrine feedback loop.
Most follicular thyroid cancer cells and all normal thyroid cells have a site on the surface of the cell that can stimulate their growth. This site is called a “receptor” and when stimulated by TSH in normal thyroid cells it causes increased production of thyroid hormone. In follicular thyroid cancer cells, this same TSH receptor can stimulate the growth of these cancer cells. Obviously, it is undesirable concept to have TSH stimulate follicular thyroid cancer cells to grow. Therefore the goal in the follicular thyroid cancer patient is to keep TSH levels low. So how is this done?
You May Like: Do I Have Thyroid Cancer
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The incidence of thyroid cancer has increased over the past few decades which is attributed to its over-diagnosis. As a result in 2017, USPTF recommended against the screening of thyroid cancer with either neck palpation or ultrasound in asymptomatic patients. In 2015, American thyroid association recommended active surveillance of low-risk thyroid carcinomas with serial ultrasound and that not all patients require surgery. Also, the organization released guidelines in 2015, not to biopsy thyroid nodules that are less than 1cm. Health providers including physicians, nurse practitioners and other healthcare professionals should be aware of these guidelines this will prevent potential harm to patient from overtreatment of low-risk thyroid cancers and help with appropriate treatment of those patients who have high-risk disease. Reportedly, the overall cost of thyroid cancer in 2019 was close to 21 billion dollars due to surgery cost. Not all thyroid neoplasms require surgery and physicians should keep this in mind when managing patients who develop thyroid cancer.
Targeted Therapy And/or Chemotherapy
For follicular thyroid cancer patients who have spread of their cancer to several places outside of the neck area and RAI and other treatments are not helpful or the cancer sites are getting bigger, new therapies have been developed and approved by the FDA . Although these FDA approved follicular thyroid cancer targeted medications have been shown to be effective, none of these treatments are curative. Skilled physicians in prescribing these medications are required because of the necessity for close monitoring of symptoms, toxicities, and monitoring of the patient’s follicular thyroid cancer.
The two approved targeted therapies in the management of follicular thyroid cancer are Lenvima and Sorafenib. These medications are taken by mouth and frequently cause weight loss, fatigue, muscle wasting, hand and foot pain, changes in blood pressure and skin symptoms. The toxicities are directly related to the dose and frequency the medication is taken. Again, these medications cannot be taken indefinitely and do not cure the follicular thyroid cancer.
ThyroidCancer.com is an educational service of the Clayman Thyroid Center, the world’s leading thyroid surgery center operating exclusively at the new Hospital for Endocrine Surgery.
Now Operating Exclusively at the Hospital for Endocrine Surgery
We were not affected by the Florida hurricane and are operating every day as usual.
Clayman Thyroid Center News
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Thyroid Cancer Returning
Follicular Thyroid Cancer Surgery For Central Compartment Lymph Nodes And Swallowing Tube
The removal of the lymph nodes of the central neck can be performed initially when the thyroid gland is removed in the treatment of follicular thyroid cancer or following the initial surgery in the less common circumstances when follicular thyroid cancer recurs or persists. The central compartment lymph node surgery spares all critical structures including the nerves to the voice box and all parathyroid glands not directly involved by cancer. Central compartment dissection extends from the carotid arteries on both sides of the neck, below to the blood vessels of the upper chest, and above to where the blood vessel of the upper portion of the thyroid gland begins off of the carotid artery .