Get To Know Hashimotos Thyroiditis
Hashimotos thyroiditis is a condition in which immune system produces antibodies to attack the thyroid gland. It is an autoimmune disease that gradually leads to chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland. Hashimotos thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Inflammation caused by Hashimotos disease is often characterized by widespread chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis in the thyroid tissue.
Causes Of Hashimoto’s Disease And Risk Factors
The specific causes of Hashimoto’s disease are not entirely known. It is an autoimmune disease that happens when the immune system attacks healthy cells in the thyroid, which can prevent the body from being able to produce thyroid hormone. Hashimoto’s is believed to be caused by:
- Pregnancy and the postpartum phase
- Unhealthy lifestyle choices
What Is Hashimotos Thyroiditis
Hashimotos thyroiditis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune thyroid disease in which the immune system attacks and destroys the thyroid gland. The thyroid then produces too little hormone and metabolism is slowed. It is the most common of all the thyroid conditions in the US and women are affected 10 times more often than men. Most diagnoses occur between the ages of 30-50 and prevalence increases with age in both women and men. Symptoms, which often develop gradually, may include weight gain, cold sensitivity, tingling in the hands and feet, fatigue, hair loss, dry hair, fertility problems, and difficulty concentrating. Thyroid hormone should be monitored in women who plan pregnancy. Low thyroid function can affect the development of the baby. Post-partum thyroiditis can develop in the 12 months following childbirth. Women who are having trouble conceiving should also have their thyroid levels checked as thyroid hormone levels can affect ovulation.
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Papillary Thyroid Cancer
What Is Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is when your thyroid gland becomes irritated. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common type of this health problem. It is an autoimmune disease. It occurs when your body makes antibodies that attack the cells in your thyroid. The thyroid then can’t make enough of the thyroid hormone. Many people with this problem have an underactive thyroid gland. That’s also known as hypothyroidism. They have to take medicine to keep their thyroid hormone levels normal.
Complications Of Hashimotos Disease
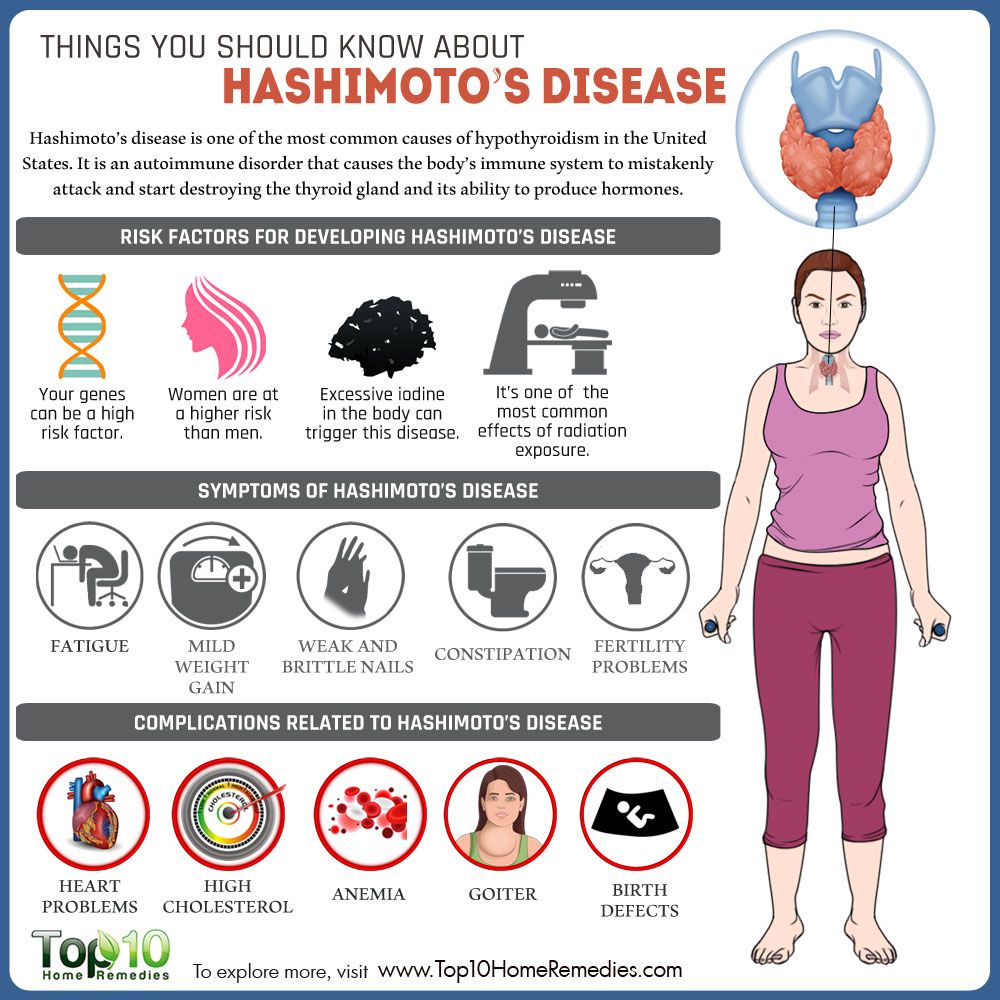
Complications of untreated Hashimotos disease may include:
- Goitre the thyroid gland enlarges. In severe cases, the throat looks as if a tennis ball is lodged under the skin. Occasionally, a large goitre can interfere with breathing or swallowing.
- Emotional problems low thyroid levels can increase the risk of depression and libido problems, such as reduced sex drive.
- Heart conditions low levels of thyroid hormones allow levels of the bad cholesterol to rise. This can increase the risk of heart disease, including heart attack. In some cases, Hashimotos disease causes other cardiac conditions such as heart enlargement or heart failure.
- Congenital defects the unborn baby of a woman who has untreated Hashimotos disease risks various birth defects including cleft palate, and heart, kidney or brain malformations.
- Myxoedema this severe form of hypothyroidism produces symptoms and signs which may include unnatural sleepiness, extreme sensitivity to cool temperatures and coma. This condition may be fatal in severe cases. However, myxoedema is a very rare complication of untreated Hashimotos disease.
Recommended Reading: When Should I Have My Thyroid Checked
How Is Hashimoto Thyroiditis Treated
Patients with elevated TPO antibodies but normal thyroid function tests do not require treatment. Patient with only a slightly elevated TSH may not require medication and should have repeat testing after 3-6 months if this has not already been done. For patients with overt hypothyroidism treatment consists of thyroid hormone replacement . Synthetic levothyroxine taken orally at an appropriate dose, is inexpensive, very effective in restoring normal thyroid hormone levels, and results in an improvement of symptoms of hypothyroidism. Most patients with Hashimotos thyroiditis will require lifelong treatment with levothyroxine. Finding the appropriate dose, particularly at the beginning, may require testing with TSH every 6-8 weeks after any dose adjustment, until the correct dose is determined. After that, monitoring of TSH once a year is generally sufficient.
When levothyroxine is taken in the appropriate dose, it has no side effects. However, when an insufficient dose is taken, serum TSH remains elevated and patients may have persistent symptoms of hypothyroidism . If the dose is excessive, serum TSH will become suppressed and patients may develop symptoms of hyperthyroidism or have other side effects .
What Happens In Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an ongoing condition in which the immune system attacks the thyroid. Some people continue to have normal thyroid function. But often, over time the thyroid isn’t making enough thyroid hormone, causing hypothyroidism. The body responds by sending a message to the thyroid to work harder to make enough hormone.
This, and the swelling the immune system causes as it attacks the gland, can make the thyroid get bigger, leading to a goiter. The thyroid can keep changing size over months or years.
Read Also: What Happens If Your Thyroid Is High
Future Directions Of Research
To date, much progress has been made in knowledge and understanding of AIT. Nevertheless the mechanisms that induce the breaking of the tolerance of the immune system, with consequent autoimmune response towards the thyroid gland and the beginning of the disease, are still unclear. In subjects with a genetic predisposition, also environmental factors can contribute to the beginning of the immune system’s anomaly, but the molecular mechanisms that regulate this interaction are not yet clear. It
Is Hashimotos Disease Dangerous Or Fatal
If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to some serious complications and, in rare cases, death. These include:
- Heart problems, such as enlarged heart or heart failure.
- Mental health issues, including depression.
- Myxedema coma, which needs immediate emergency care. Myxedema is a rare, life-threatening condition that can lead to heart failure, seizures, coma and death.
Recommended Reading: Can Armour Thyroid Cause High Blood Pressure
How Are Hypothyroidism And Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Diagnosed
To diagnose hypothyroidism and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, doctors ask about a person’s symptoms, do an exam, and order blood tests. The tests measure:
- Thyroid hormone levels, particularly thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone . T4 is the thyroid hormone made in the thyroid that works throughout the body. TSH is a hormone made in the pituitary gland . More TSH is released into the blood when the brain and pituitary sense that the levels of thyroid hormone in the blood are too low. TSH stimulates the thyroid to work harder to make more thyroid hormone.
- Some antibodies . High levels of these antibodies in the blood are a sign that the gland is being attack by the immune system in Hashimoto’s. The two antibodies commonly measured are thyroglobulin antibodies and thyroid peroxidase antibodies .
What Are The Symptoms Of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
There are no signs or symptoms that are unique to Hashimotos thyroiditis.
Because the condition usually progresses very slowly over many years, people with Hashimotos thyroiditis may not have any symptoms early on, even when the characteristic thyroid peroxidase antibodies are detected in blood tests. TPO is an enzyme that plays a role in the production of thyroid hormones. If Hashimotos thyroiditis causes cell damage leading to low thyroid hormone levels, patients will eventually develop symptoms of hypothyroidism . Hypothyroid symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, increased sensitivity to cold, dry skin, depression, muscle aches and reduced exercise tolerance, and irregular or heavy menses. In some cases, the inflammation causes the thyroid to become enlarged , which rarely may cause neck discomfort or difficulty swallowing.
Also Check: How Long Does Thyroid Cancer Take To Spread
What Are The Symptoms Of Hashimotos Disease
Many people with Hashimotos disease have no symptoms at first. As the disease progresses, you may have one or more of the symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Some common symptoms of hypothyroidism include
- dry skin or dry, thinning hair
- heavy or irregular menstrual periods or fertility problems
- slowed heart rate
Hashimotos disease causes your thyroid to become damaged. Most people with Hashimotos disease develop hypothyroidism. Rarely, early in the course of the disease, thyroid damage may lead to the release of too much thyroid hormone into your blood, causing symptoms of hyperthyroidism.3
Your thyroid may get larger and cause the front of the neck to look swollen. The enlarged thyroid, called a goiter, may create a feeling of fullness in your throat, though it is usually not painful. After many years, or even decades, damage to the thyroid may cause the gland to shrink and the goiter to disappear.
What Causes Hashimoto’s Disease

Researchers aren’t sure exactly what causes Hashimoto’s disease. Studies show that it is more common in women than men.
Your risk is higher if you:2
- Have a family history. Hashimoto’s disease may run in families. Researchers are working to find the gene or genes involved.
- Recently had a baby. Some women have thyroid problems after having a baby, called postpartum thyroiditis. The thyroid often returns to normal within 12 to 18 months after symptoms start. But if you have a history of postpartum thyroiditis, your risk is higher for developing permanent hypothyroidism.3
Read Also: What Are Some Thyroid Medications
Testing Your Thyroid Levels
Conventional medicine will only check your TSH levels., To get a clear picture of your thyroid health, ask your doctor to test FT4, FT3, RT3, and antibodies for optimal levels. Ive outlined the optimal levels of each hormone:
- TSH Levels: A high TSH level indicates hypothyroidism whereas a low TSH level indicates hyperthyroidism. The optimal levels of TSH should be 1-2 UIU/ML or lower.
- Free T4 : FT4 refers to the unbound T4 i.e. the one found in the bloodstream. High FT4 levels indicate hyperthyroidism whereas low FT4 levels indicate hypothyroidism. Optimal FT4 levels should be values greater than 1.1 NG/DL.
- Free T3 : High FT3 indicates hyperthyroidism whereas low FT3 indicates hypothyroidism. Optimal levels are values greater than 3.2 PG/ML.
- Reverse T3 : High RT3 levels indicate that theres a high conversion of T4 to RT3 instead of FT3. This is an indicator of hypothyroidism. The optimal level compares the ratio of RT3 to FT3 and that value should be less than 10:1.
- Antibodies test : Since the most common forms of thyroid disease are autoimmune diseases, detection of thyroid antibodies is essential to get an accurate result. There are two antibodies of concern: TPOAb and TgAb. TPOAb refers to the thyroid peroxidase antibodies that target the enzyme that mediates the iodination of thyroglobulin. TgAb relates to the antibodies that attack thyroglobulin. Optimal levels for both antibodies should either be negative or values lower than 4 IU/ML.
How Are Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders Treated
- Thyroid medicines replace, increase, or decrease your thyroid hormone levels. They may also help control your signs and symptoms. You may need other medicines to treat fast heartbeats, nervousness, or trembling.
- A radioactive form of iodine is given to treat hyperthyroidism. It damages or kills some of the thyroid gland cells.
- Surgery to remove your thyroid may be needed if other treatments do not work.
Don’t Miss: Over The Counter Thyroid Pills
Screening And Early Detection
It is important to seek the support of a medical professional if Hashimoto’s disease is suspected. This is especially true in pregnancy, when it can lead to negative health effects for both the mother and baby, including:
Hashimoto’s disease is diagnosed with a medical history to determine genetic risk, a physical exam, and blood tests to monitor hormone levels. Early screening, detection, and treatment can help to prevent possible complications such as heart disease and failure and the slowing of bodily functions.
Symptoms Of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s symptoms may be mild at first or take years to develop. The first sign of the disease is often an enlarged thyroid, called a goiter. The goiter may cause the front of your neck to look swollen. A large goiter may make swallowing difficult. Other symptoms of an underactive thyroid due to Hashimoto’s may include:
You May Like: What Happens If You Take To Much Thyroid Medication
Thyroid Autoimmunity & Other Autoimmune Diseases
There is an association between AITD and other organ specific/systemic autoimmune disorders in fact it’s not unusual to find patients with more than one immune-mediated endocrinopathy. As a result, polyglandular autoimmune syndromes , characterized by the failure of different endocrine glands, occur.
A recent study analyzed 15,000 adults with endocrine disorders and, among these, 360 patients were suffering from PAS. The high percentage of these patients showed Addison’s disease,
How Is Hashimoto’s Disease Treated
Hashimotos disease is treated with a daily dose of levothyroxine. This is the same hormone that your thyroid gland makes. You will probably need to take thyroid hormone pills for the rest of your life. Talk to your doctor or nurse about any questions or concerns.
You may have to see your doctor or nurse a few times to test the level of thyroid stimulating hormone in your body. Thyroid hormone acts very slowly in the body, so it can take several months after the start of treatment for symptoms to go away. Once your TSH level is normal, your doctor or nurse will need to see you less often.
The same treatment dose usually works for many years. But your TSH levels may change sometimes, especially during pregnancy, if you have heart disease, or if you take menopausal hormone therapy. Your doctor or nurse may need to adjust your dose.
Recommended Reading: What Vitamins Are Good For Your Thyroid
Do You Need Hypothyroid Medication
Lastly, I should say a word about thyroid medication.
Thyroid medication is the treatment for hypothyroidism and it may also be required if you have Hashimotos thyroiditis.
Thyroid medication is taken by mouth each and every day and its supposed to help normalize thyroid function in your body.
Because your own thyroid gland cant produce enough thyroid hormone on its own, you can take thyroid medication to help supplement the difference.
But its important that you dont confuse thyroid medication with other prescription medications.
While thyroid medication does require a prescription to get, its unlike other prescription medications because it is an exact replica of the same thyroid hormone that your body produces naturally.
Other medications, such as blood pressure medication and cholesterol-lowering medication, are artificially and synthetically created and are not normally found in your body.
These medications alter your physiology to create some desired outcome. As this occurs, its not unusual for people to experience negative and unwanted side effects.
Some people taking thyroid medication do experience side effects, but the vast majority should actually feel BETTER when taking thyroid medication.
If you are taking thyroid medication and not feeling better then that may be an indication that your dose of thyroid medication is off.
But, even having said all of this, it may not be required for all people with Hashimotos to take thyroid medication.
The Functional Medicine Approach To Hypothyroidism

Managing your thyroid levels through thyroid medication is only part of the process. The real work comes in identifying the underlying factors that caused your thyroid disease and making healthy lifestyle changes to remove them. I call this The Myers Way®.
In my New York Times bestseller, The Thyroid Connection I talk about this proven method that Ive used with thousands of patients and seen amazing results in my decades of experience as a physician.
To support optimal thyroid function while following The Myers Way®, I recommend adding The Myers Way® Multivitamin. I formulated this multivitamin with thyroid health in mind. It is packed with optimal levels of micronutrients in bioavailable forms your body wants and the amounts your thyroid needs. With optimal levels of thyroid-supporting minerals such as zinc, selenium, and iodine, alongside antioxidants including vitamins C and E and other free radical scavengers, no other multivitamin on the market does more to support your thyroid!
To get the additional benefit of supporting your thyroid health and immune system function, I designed my Hashimotos Support Plus Kit that includes The Myers Way® Multivitamin, along with Adrenal Support and ZenAdapt to facilitate optimal cortisol levels and balanced stress response.
Recommended Reading: Do I Need To Get My Thyroid Checked
What Is The Cause Of Hashimotos Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder. Normally, your autoimmune system protects your body by attacking bacteria and viruses. But with this disease, your immune system attacks your thyroid gland by mistake. Your thyroid then can’t make enough thyroid hormone, so your body can’t work as well.
How Are Hypothyroidism And Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Treated
Doctors treat an underactive thyroid with daily thyroid hormone replacement pills. The medicine is the same T4 that the body is no longer making. These will bring the body’s levels of thyroid hormone back to normal.
This treatment is fairly simple, but a person will have doctor visits several times a year for an exam, blood tests, and medicine changes as needed.
You May Like: Thyroid Cancer Signs To Never Ignore
Hashimotos Thyroiditis: Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinic And Therapy
, the most frequent , is the leading cause of hypothyroidism in the iodine-sufficient areas of the world. About 2030% of patients suffers from HT, whose cause is thought to be a combination of and environmental factors that causes the loss of , with a consequent autoimmune attack to the thyroid tissue and appearance of the disease.
The pathologic features of , especially of , and follicular destruction are the histological hallmark of autoimmune thyroiditis , that lead to gradual atrophy and fibrosis. An important role in the immune-pathogenesis of AITDs is due to and cytokines.
In about 20% of patients, AITDs are associated with other organ specific/systemic autoimmune disorders.
Many studies have demonstrated the relationship between and AITD.
The treatment of hypothyroidism, as result of AIT, consists in daily assumption of synthetic .