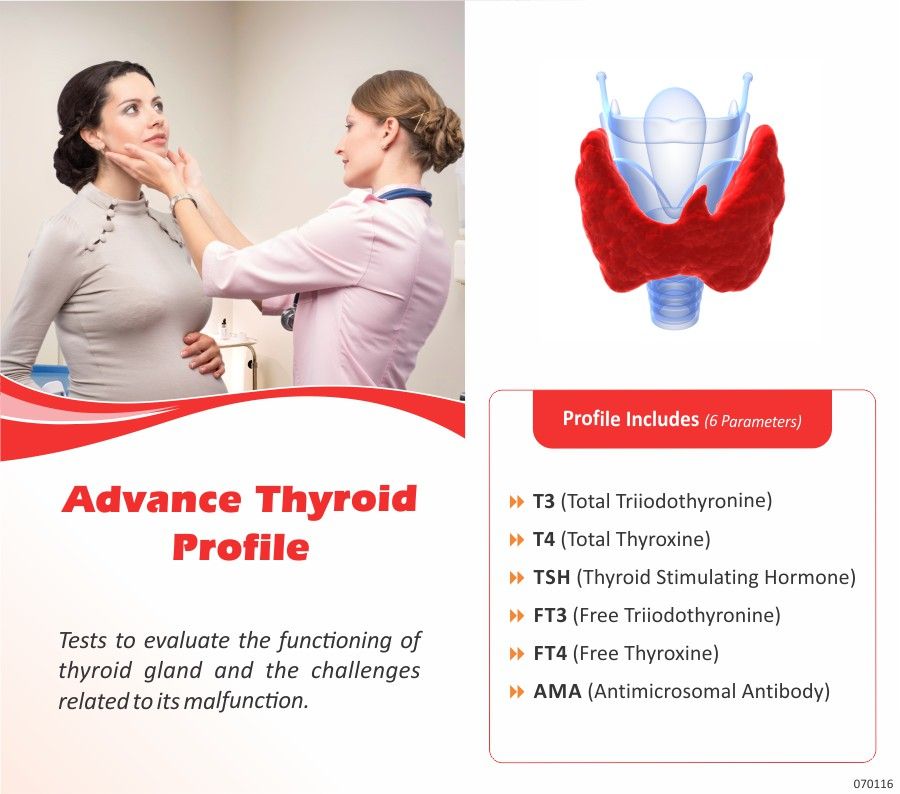
What Blood Tests Are Done To Test The Thyroid
Thyroid blood tests include:
These tests alone arent meant to diagnose any illness but may prompt your healthcare provider to do additional testing to evaluate for a possible thyroid disorder.
Additional blood tests might include:
- Thyroid antibodies: These tests help identify different types of autoimmune thyroid conditions. Common thyroid antibody tests include microsomal antibodies , thyroglobulin antibodies , and thyroid receptor antibodies .
- Calcitonin: This test is used to diagnose C-cell hyperplasia and medullary thyroid cancer, both of which are rare thyroid disorders.
- Thyroglobulin: This test is used to diagnose thyroiditis and to monitor treatment of thyroid cancer.
What Are The Symptoms Of Thyroid Cancer
- A lump or swelling on the side of the neck is the most common symptom.
- Having trouble breathing.
- Having trouble swallowing.
- Having a hoarse voice.
These symptoms can also come from other conditions. If you have any of these symptoms, talk to your doctor right away. Dont wait until the symptoms get worse.
How Is Thyroid Cancer Managed Or Treated
Treatments for thyroid cancer depend on the tumor size and whether the cancer has spread. Treatments include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer. Depending on the tumorâs size and location, a surgeon may remove part of your thyroid gland or all of the gland . The surgeon also removes any nearby lymph nodes where cancer cells have spread.
- Radioiodine therapy: With radioiodine therapy, you swallow a pill or liquid containing a higher dose of radioactive iodine than whatâs used in a diagnostic radioiodine scan. The radioiodine shrinks and destroys the diseased thyroid gland along with cancer cells. This treatment is very safe. Your thyroid gland absorbs almost all of the radioiodine and the rest of your body has minimal radiation exposure.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation kills cancer cells and stops them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver strong beams of energy directly to the tumor site. Internal radiation therapy involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Intravenous or oral chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stops cancer growth. Very few people diagnosed with thyroid cancer will ever need chemotherapy.
- Hormone therapy: This treatment blocks the release of hormones that can cause cancer to spread or come back.
What are the complications of thyroid cancer?
How does thyroid cancer affect pregnancy?
Also Check: How To Reset Thyroid To Burn Fat
Tests Are Used To Screen For Different Types Of Cancer When A Person Does Not Have Symptoms
Scientists study screening tests to find those with the fewest harms and most benefits. Cancer screening trials also are meant to show whether early detection helps a person live longer or decreases a person’s chance of dying from the disease. For some types of cancer, the chance of recovery is better if the disease is found and treated at an early stage.
First Way To Check For Thyroid Cancer
Feeling your neck on a regular basis can be your best way to self-check for thyroid cancer. The thyroid is a butterfly shaped organ that lays in the middle of your neck right above your collar bone. It sits on top of your windpipe. Growths or nodules can form within the thyroid gland and can cause slight bulges within the thyroid gland. If you regularly perform a self-check for thyroid cancer, these growths can sometimes be felt with your own fingers. These nodules can harbor thyroid cancer and will clearly need an expert thyroid surgeon for removal. Thyroid cancers can also spread to lymph nodes in the sides of your neck. In the same fashion, performing a self-check for thyroid cancer can detect an enlarged lymph node.
The way to perform a self-check for thyroid cancer would involve moving your fingers around the middle of your neck where your thyroid is. It would also involve moving your fingers throughout both sides of your neck. Lymph nodes that can harbor thyroid cancer are located anywhere from below your ear to you collar bone on both sides of your neck. Therefore, you would want to make sure that you are feeling the whole front and sides of your neck during your self-check for thyroid cancer.
Recommended Reading: Poorly Differentiated Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Why Dont We Just Test Everyone For Thyroid Cancer
The problem with testing everyone for thyroid cancer is that doctors likely would over-diagnose the disease, which already may be a problem. The rate of people being diagnosed with thyroid cancer has gone up dramatically in the past few decades. In 1975, 4.85 out of every 100,000 people were diagnosed with thyroid cancer, as shown by data from the National Cancer Institutes Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. In 2013, that number had skyrocketed to 15.31 out of every 100,000 peoplean increase of more than 215 percent in less than 40 years.
The number of people diagnosed with #thyroidcancer has increased more than 215% in less than 40 years. via @MedStarWHC
Much of this increase in the number of diagnoses is thought to be due to better methods of detecting thyroid cancer growths, also known as nodules, with imaging technologies such as thyroid ultrasound. The idea is that were diagnosing more people because we can see more thyroid nodules than we could before, especially those that are smaller and earlier in the disease process.
But better testing may contribute to over-diagnosis of thyroid cancer. The USPSTF stated that there hasnt been an increase in the number of people dying from thyroid cancer despite the rise in the number of people who have been diagnosed with the disease. This could mean that doctors are diagnosing thyroid cancer in people who might not need treatment.
Estimate Of Magnitude Of Net Benefit
The USPSTF found inadequate direct evidence on the benefits of screening but determined that the magnitude of the overall benefits of screening and treatment can be bounded as no greater than small, given the relative rarity of thyroid cancer, the apparent lack of difference in outcomes between treatment and surveillance , and observational evidence showing no change in mortality over time after introduction of a mass screening program. Similarly, the USPSTF found inadequate direct evidence on the harms of screening but determined that the magnitude of the overall harms of screening and treatment can be bounded as at least moderate, given adequate evidence of harms of treatment and indirect evidence that overdiagnosis and overtreatment are likely to be substantial with population-based screening. Therefore, the USPSTF determined with moderate certainty that the net benefit of screening for thyroid cancer is negative.
You May Like: Low Thyroid Symptoms In Dogs
Tests For Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer may be diagnosed after a person goes to a doctor because of symptoms, or it might be found during a routine physical exam or other tests. If there is a reason to suspect you might have thyroid cancer, your doctor will use one or more tests to confirm the diagnosis. If cancer is found, other tests might be done to find out more about the cancer.
Medical History And Physical Exam
If you have any signs or symptoms that suggest you might have thyroid cancer, your health care professional will want to know your complete medical history. You will be asked questions about your possible risk factors, symptoms, and any other health problems or concerns. If someone in your family has had thyroid cancer or tumors called pheochromocytomas, it is important to tell your doctor, as you might be at high risk for this disease.
Your doctor will examine you to get more information about possible signs of thyroid cancer and other health problems. During the exam, the doctor will pay special attention to the size and firmness of your thyroid and any enlarged lymph nodes in your neck.
Recommended Reading: Thyroid And Adrenal Support Supplements
What Is The Significance Of The Uspstf Recommendation
The USPSTF gave thyroid cancer screening a grade of D, meaning that there is a good chance it provides no net benefit or that the harms outweigh the benefits. The goal is to advise doctors not to routinely look for thyroid cancer in people without any symptoms by feeling for lumps on the neck, doing ultrasound imaging, or using other techniques. This sends a clear signal about something that may seem counterintuitive to many doctors and patients, who may assume that more information is always better.
Thyroid Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea . It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin piece of tissue, connects the two lobes. A healthy thyroid is about the size of a walnut. It usually cannot be felt through the skin.
The thyroid uses iodine, a mineral found in some foods and in iodized salt, to help make several hormones. Thyroid hormones do the following:
- Control heart rate, body temperature, and how quickly food is changed into energy .
- Control the amount of calcium in the blood.
See the PDQ summary on Thyroid Cancer Treatment for more information about thyroid cancer.
Recommended Reading: Afirma Test For Thyroid Nodules
Whats The Thyroid Cancer Survival Rate
Eight out of 10 people who have thyroid cancer develop the papillary type. Papillary thyroid cancer has a five-year survival rate of almost 100% when the cancer is in their gland . Even when the cancer spreads , the survival rate is close to 80%. This rate means that, on average, youâre about 80% as likely to live for at least five years after diagnosis as someone who doesnât have metastatic papillary thyroid cancer.
Five-year survival rates for other thyroid cancer types include:
- Follicular: Close to 100% for localized around 63% for metastasized.
- Medullary: Close to 100% for localized around 40% for metastasized.
- Anaplastic: Close to 31% for localized 4% for metastasized.
Is thyroid cancer curable?
Yes, most thyroid cancers are curable with treatment, especially if the cancer cells havenât spread to distant parts of your body. If treatment doesnât fully cure thyroid cancer, your healthcare provider can design a treatment plan to destroy as much of the tumor as possible and prevent it from growing back or spreading.
And If A Thyroid Nodule Is Found To Be Cancerous What Then
There has been a growing acceptance in the medical community that low-risk thyroid cancers can be safely watched, and that less extensive treatment often produces the best outcomes. In 2015, the ATA issued treatment guidelines that stated, for the first time, that monitoring an early-stage papillary thyroid tumor instead of removing it is a reasonable option.
For several years at MSK, we have taken a tactic of active surveillance. This method was pioneered successfully here for men with low-risk prostate cancer, another slow-growing disease that historically has been overtreated. When someone comes in with a small papillary thyroid cancer that appears to be confined to the thyroid gland, our team of experts now tries to determine whether the patient is a good candidate for observation with ultrasounds at regular intervals.
For thyroid cancers that do require treatment, we have been at the forefront of selecting the more conservative surgery, lobectomy. The ATA guidelines are also supportive of this concept for some thyroid cancers.
Don’t Miss: How To Heal My Thyroid Naturally
How Common Is Thyroid Cancer
First, the good news. According to 2016 American Cancer Society statistics, Americans have a less than one percent chance of developing thyroid cancer in their lifetime. And survival rates are high: 98 percent of patients diagnosed with thyroid cancer are alive five years after diagnosis, according to the American Cancer Society.
However, according to research published earlier this year in the Journal of the American Medical Association by Sosa and others, the incidence of thyroid cancer in the U.S. has increased three percent each year between 1974 and 2013. Some doctors and scientists have argued the increase is largely due to doctors using more imaging, such as ultrasound, CT, and PET scans, which are bringing doctors attention to thyroid nodules, even when the nodules are too small to cause symptoms.
Sosa said the data show the U.S. has seen a rise in the incidence and death rates for advanced papillary thyroid cancer, the most common thyroid cancer, which suggests a true increase in the number of people getting thyroid cancer — not just a case of overdiagnosing small, clinically insignificant thyroid cancer.
Screening Tests Have Risks
Decisions aboutscreening tests can be difficult. Not all screening tests are helpful and most have risks. Before having any screening test, you may want to discuss the test with your doctor. It is important to know the risks of the test and whether it has been proven to reduce the risk of dying from cancer.
Read Also: How Do You Get Tested For Thyroid Issues
Papillary Cancer And Its Variants
Most cancers are treated with removal of the thyroid gland , although small tumors that have not spread outside the thyroid gland may be treated by just removing the side of the thyroid containing the tumor . If lymph nodes are enlarged or show signs of cancer spread, they will be removed as well.
In addition, recent studies have suggested that people with micro-papillary cancers may safely choose to be watched closely with routine ultrasounds rather than have immediate surgery.
Even if the lymph nodes arent enlarged, some doctors recommend central compartment neck dissection along with removal of the thyroid. Although this operation has not been shown to improve cancer survival, it might lower the risk of cancer coming back in the neck area. Because removing the lymph nodes allows them to be checked for cancer, this surgery also makes it easier to accurately stage the cancer. If cancer has spread to other neck lymph nodes, a modified radical neck dissection is often done.
Treatment after surgery depends on the stage of the cancer:
People who have had a thyroidectomy will need to take daily thyroid hormone pills. If RAI treatment is planned, the start of thyroid hormone therapy may be delayed until the treatment is finished .
Research Needs And Gaps
The USPSTF found no direct studies that compared screened vs unscreened populations or immediate surgery vs surveillance or observation and reported health outcomes . Trials or well-designed observational studies that address the benefit of screening in high-risk persons are important for understanding how to best advise these patients. Trials or well-designed observational studies of early treatment vs surveillance or observation of patients with small, well-differentiated thyroid cancer are also needed to identify patients at greatest risk for clinical deterioration. Finally, risk prediction tools and molecular markers are needed to help understand the prognosis of differentiated thyroid cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Are The 4 Main Types Of Thyroid Cancer
Can I Prevent Thyroid Cancer
Many people develop thyroid cancer for no known reason, so prevention isnât really possible. But if you know youâre at risk for thyroid cancer, you may be able to take these steps:
- Preventive surgery: Genetic tests can determine if you carry an altered gene that increases your risk for medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia. If you have the faulty gene, you may opt to have preventive surgery to remove your thyroid gland before cancer develops.
- Potassium iodide: If youâve had radiation exposure during a nuclear disaster, such as the 2011 incident at Fukushima, Japan, taking potassium iodide within 24 hours of exposure can lower your risk of eventually getting thyroid cancer. Potassium iodide blocks your thyroid gland from absorbing too much radioiodine. As a result, your gland stays healthy.
Benefits Of Early Detection And Treatment
The USPSTF found inadequate direct evidence to determine whether screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic persons using neck palpation or ultrasound improves health outcomes. However, the USPSTF determined that the magnitude of benefit can be bounded as no greater than small, based on the relative rarity of thyroid cancer, the apparent lack of difference in outcomes between patients who are treated vs. only monitored , and the observational evidence demonstrating no change in mortality over time after introduction of a population-based screening program.
Recommended Reading: Thyroid Cancer And Tailbone Pain
What Is The Thyroid
The thyroid gland is located in front of the neck. It looks sort of like a butterfly with one wing on each side of the neck. The thyroid is important in many ways for keeping your body healthy. It sends out certain chemicals that help control many activities in the body, such as breathing and pumping blood. The thyroid helps childrens bodies develop as they grow up, including getting taller and putting on muscle. It helps control weight and is also involved in other functions.
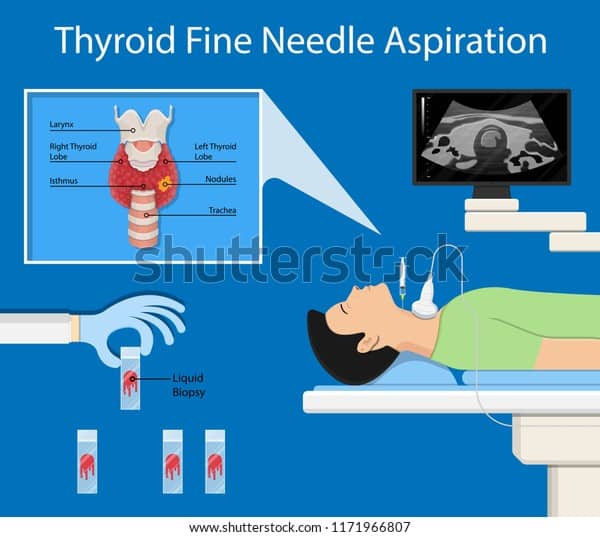
Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
If your healthcare provider thinks you may have thyroid cancer, you will need to have a biopsy to tell for sure. Thyroid nodules are typically biopsied using a needle in a procedure known as fine needle aspiration biopsy. In some cases, your healthcare provider will begin with this test, but some healthcare providers may do blood and imaging tests first.
An FNA is simple, safe, and performed in your healthcare provider’s office. During an FNA, your healthcare provider will use a needle to remove, or aspirate, cells from the nodule. To ensure the needle goes into the nodule, your healthcare provider may use ultrasound to guide the process and will likely take a number of samples from different places in the nodule.
Once the cells are aspirated, they are examined under a microscope by another healthcare provider called a pathologist to determine whether the nodule is malignant or benign. Sometimes, however, the results of an FNA are “indeterminate,” meaning that it’s unclear whether the nodule is cancerous or not.
You May Like: How Can Thyroid Problems Affect You