Gene And Protein Expression
About 20,000 protein coding genes are expressed in human cells: 70% of these genes are expressed in thyroid cells. Two-hundred fifty of these genes are more specifically expressed in the thyroid, and about 20 genes are highly thyroid specific. In the follicular cells, the proteins synthesized by these genes direct thyroid hormone synthesisthyroglobulin, TPO, and IYD while in the parafollicular c-cells, they direct calcitonin synthesisCALCA, and CALCB.
Are There Different Types Of Thyroid Removal Surgery
If your healthcare provider determines that your thyroid needs to be removed, there are a couple of ways that can be done. Your thyroid may need to be completely removed or just partially. This will depend on the severity of your condition. Also, if your thyroid is very big or has a lot of growths on it, that could prevent you from being eligible for some types of surgery.
The surgery to remove your thyroid is called a thyroidectomy. There are two main ways this surgery can be done:
- With an incision on the front of your neck.
- With an incision in your armpit.
The incision on the front of your neck is more of the traditional version of a thyroidectomy. It allows your surgeon to go straight in and remove the thyroid. In many cases, this might be your best option. You may need this approach if your thyroid is particularly big or has a lot of larger nodules.
Alternatively, there is a version of the thyroid removal surgery where your surgeon makes an incision in your armpit and then creates a tunnel to your thyroid. This tunnel is made with a special tool called an elevated retractor. It creates an opening that connects the incision in your armpit with your neck. The surgeon will use a robotic arm that will move through the tunnel to get to the thyroid. Once there, it can remove the thyroid back through the tunnel and out of the incision in your armpit.
- Are not at a healthy body weight.
- Have large thyroid nodules.
- Have a condition like thyroiditis or Gravess disease.
Overview Of The Thyroid Gland
, MD, MS, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The thyroid is a small gland, measuring about 2 inches across, that lies just under the skin below the Adams apple in the neck. The two halves of the gland are connected in the middle , giving the thyroid gland the shape of a bow tie. Normally, the thyroid gland cannot be seen and can barely be felt. If it becomes enlarged, doctors can feel it easily, and a prominent bulge may appear below or to the sides of the Adams apple.
The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormones, which control the speed at which the bodys chemical functions proceed . Thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate in two ways:
Thyroid hormones affect many vital body functions, such as the heart rate, the rate at which calories are burned, skin maintenance, growth, heat production, fertility, and digestion.
Read Also: Thyroid Cancer In The Neck
What Does The Thyroid Do
Your thyroid has an important job to do within your body releasing and controlling thyroid hormones that control metabolism. Metabolism is a process where the food you take into your body is transformed into energy. This energy is used throughout your entire body to keep many of your bodys systems working correctly. Think of your metabolism as a generator. It takes in raw energy and uses it to power something bigger.
The thyroid controls your metabolism with a few specific hormones T4 and T3 . These two hormones are created by the thyroid and they tell the bodys cells how much energy to use. When your thyroid works properly, it will maintain the right amount of hormones to keep your metabolism working at the right rate. As the hormones are used, the thyroid creates replacements.
This is all supervised by something called the pituitary gland. Located in the center of the skull, below your brain, the pituitary gland monitors and controls the amount of thyroid hormones in your bloodstream. When the pituitary gland senses a lack of thyroid hormones or a high level of hormones in your body, it will adjust the amounts with its own hormone. This hormone is called thyroid stimulating hormone . The TSH will be sent to the thyroid and it will tell the thyroid what needs to be done to get the body back to normal.
What Other Organs And Glands Interact With The Thyroid

Your endocrine system is an elaborate network of glands and hormones. Many glands and hormones rely on other glands and hormones to send them signals to start working. In addition, certain hormones can suppress other hormones.
Your body has a complex system for controlling the level of thyroid hormones in your body. First, your hypothalamus secretes thyroid-releasing hormone , which stimulates a part of your pituitary gland to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone . TSH then stimulates your thyroid follicular cells to release thyroxine and triiodothyronine if there are adequate levels of iodine in your body.
Your thyroid gland and its hormones affect almost every organ system of your body, including:
- Your cardiovascular system: Your thyroid helps regulate the amount of blood your heart pumps through your circulatory system , heart rate and strength and vigor of your heart’s contraction .
- Your nervous system: When your thyroid isnt working properly, it can cause symptoms that affect your nervous system, including numbness, tingling, pain or a sense of burning in the affected parts of your body. In addition, hypothyroidism can cause depression and hyperthyroidism can cause anxiety.
- Your digestive system: Your thyroid is involved with how food moves through your digestive system .
- Your reproductive system: If your thyroid isnt working properly, it can cause irregular menstrual periods and issues with fertility.
Recommended Reading: Stop The Thyroid Madness Com
Other Thyroid Gland Disorders
Other disorders of the thyroid gland include:
- Nodules – lumps in the thyroid. Some are groups of uncontrollably overactive thyroid cells. These are called hot nodules and cause hyperthyroidism. Other nodules are cold. These are generally harmless, but about 20 per cent will be cancerous.
- Cancer – thyroid cancer is uncommon and is readily treatable, especially if detected early.
Actions Of Thyroid Hormone
The substances produced in increased quantities in response to triiodothyronine secretion include many enzymes, cell constituents, and hormones. Key among them are proteins that regulate the utilization of nutrients and the consumption of oxygen by the mitochondria of cells. Mitochondria are the sites at which energy is produced in the form of adenosine triphosphate or is dissipated in the form of heat. Triiodothyronine activates substances that increase the proportion of energy that is dissipated as heat. It also stimulates carbohydrate utilization, lipid production and metabolism , and central and autonomic nervous system activation, resulting in increased contraction of cardiac muscle and increased heart rate. During fetal life and in infancy this stimulatory activity of triiodothyronine is critically important for normal neural and skeletal growth and development in both the unborn and the newborn, thyroid deficiency is associated with dwarfism and intellectual disability.
Also Check: Doctors Who Specialize In Thyroid
What Are The Risk Factors For Developing A Thyroid Condition
Thyroid conditions are common and can affect anyone at any age. However, some factors put you at a higher risk of developing a thyroid condition, including:
- Having a family history of thyroid disease.
- Having an autoimmune condition, such as Type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
- Taking a medication thats high in iodine.
Being older than 60, especially if youre a woman or a person who was assigned female at birth .
When To Contact A Doctor
If an individual has a family history of thyroid disease, they should have regular blood work to monitor their thyroid hormone levels and ensure they remain within an acceptable range.
Anyone experiencing symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism should visit a doctor to review their hormone levels. People should also contact their doctor if they can feel a new lump in their neck or experience any symptoms affecting their throats, such as difficulty eating or breathing.
Doctors can diagnose thyroid diseases through:
- physical examination
- thyroid tests
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Thyroid Booster
How The Body Adjusts Thyroid Hormones
The body has a complex mechanism for adjusting the level of thyroid hormones. First, the hypothalamus, located just above the pituitary gland in the brain, secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone, which causes the pituitary gland to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone . Just as the name suggests, TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. The pituitary gland slows or speeds the release of TSH, depending on whether the levels of thyroid hormones circulating in the blood are getting too high or too low.
Superior Thyroid Artery And Superior Laryngeal Nerve
The superior thyroid artery is the first anterior branch of the external carotid artery. In rare cases, it may arise from the common carotid artery just before its bifurcation. The superior thyroid artery descends laterally to the larynx under the cover of the omohyoid and sternohyoid muscles. The artery runs superficially on the anterior border of the lateral lobe, sending a branch deep into the gland before curving toward the isthmus, where it anastomoses with the contralateral artery.
Cephalad to the superior pole, the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve runs with the superior thyroid artery before turning medially to supply the cricothyroid muscle. High ligation of the superior thyroid artery during thyroidectomy places this nerve at risk of inadvertent injury, which would produce dysphonia by altering pitch regulation. The cricothyroid artery, a potentially bothersome branch of the superior thyroid artery, runs cephalad to the upper pole and runs toward the midline on the cricothyroid ligament. This vessel can be lacerated during emergent cricothyroidotomy.
You May Like: If Thyroid Levels Are High
Can I Check My Thyroid At Home
You can do a quick and easy self-exam of your thyroid at home. The only tools you need to do this self-exam are a mirror and a glass of water.
To do the thyroid self-exam, follow these steps:
- Start by identifying where your thyroid is located. Generally, youll find the thyroid on the front of your neck, between your collar bone and Adams apple. In men, the Adams apple is much easier to see. For women, its usually easiest to look from the collar bone up.
- Tip your head back while looking in a mirror. Look at your neck and try to hone in on the space you will be looking once you start the exam.
- Once youre ready, take a drink of water while your head is tilted back. Watch your thyroid as you swallow. During this test, youre looking for lumps or bumps. You may be able to see them when you swallow the water.
Repeat this test a few times to get a good look at your thyroid. If you see any lumps or bumps, reach out to your healthcare provider.
Can A Person Live Without A Thyroid
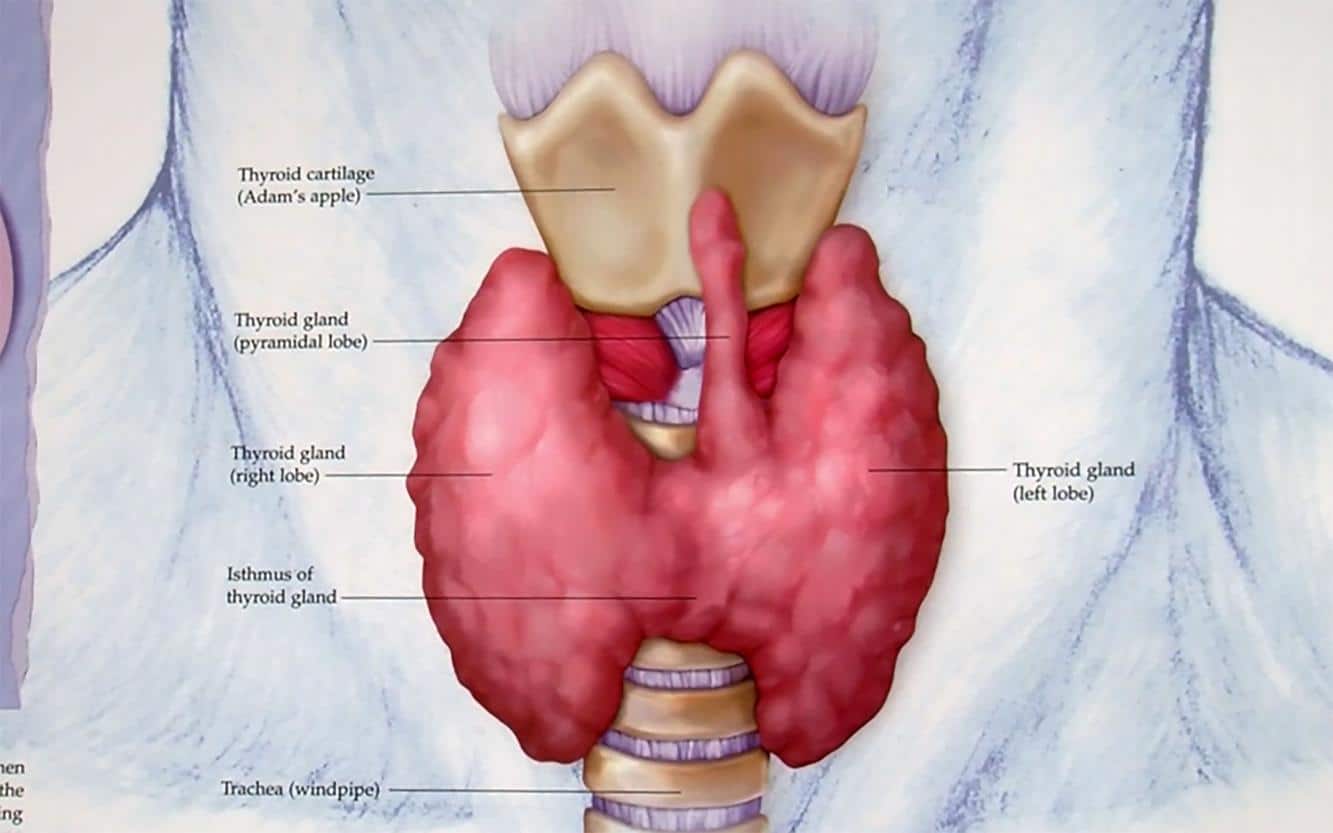
Yes, you can live without your thyroid. However, youll need to take hormone replacement medication for the rest of your life in order to stay healthy and prevent certain side effects and symptoms. Thyroid removal surgery, known as a thyroidectomy, is a common surgery that can treat certain thyroid conditions.
Read Also: When Should I Have My Thyroid Checked
What Are Thyroid Nodules
A thyroid nodule is a lump in or on the thyroid gland 7). Thyroid nodules are common, but are usually not diagnosed. They are detected in about six percent of women and one to two percent of men. They are 10 times as common in older individuals than in younger ones. Sometimes several nodules will develop in the same person. Any time a lump is discovered in thyroid tissue, the possibility of malignancy must be considered. Fortunately, the vast majority of thyroid nodules are benign 8).
What causes a thyroid nodule ?
Nodules can be caused by a simple overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue, fluid-filled cysts, inflammation , or a tumor .
What are the signs and symptoms of a thyroid nodule ?
Most patients with thyroid nodules have no symptoms whatsoever. Many are found by chance to have a lump in the thyroid gland on a routine physical exam or an imaging study of the neck done for unrelated reasons . In addition, a substantial number of nodules are first noticed by patients or those they know who see a lump in the front portion of the neck, which may or may not cause symptoms, such as a vague pressure sensation or discomfort when swallowing.
Obviously, finding a lump in the neck should be brought to the attention of your physician, even in the absence of symptoms.
How is a thyroid nodule diagnosed ?
How is a thyroid nodule treated ?
References
Innervation Of Thyroid Gland
The autonomic nervous system provides innervation to the thyroid gland. Through cervical sympathetic ganglia and parasympathetic fibers of the vagus nerve, it contributes to the nerve network of the thyroid.
The cervical sympathetic ganglia contain three subdivisions – superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia – directly providing innervation from the sympathetic trunk. The fibers of the inferior ganglion create a plexus around the inferior thyroid artery. This plexus also communicates with the recurrent laryngeal nerve, external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve, superior cardiac nerve fibers, and the fibers of the common carotid artery plexus.
The parasympathetic nerve fibers that innervate the thyroid mainly arise from the superior laryngeal nerve and the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Both mentioned nerves are branches of the tenth cranial nerve – the vagus nerve .
Read Also: How To Stop Thyroid Medication
If Part Of My Thyroid Is Surgically Removed Will The Other Part Be Able To Make Enough Thyroid Hormones To Keep Me Off Of Medication
Sometimes, your surgeon may be able to remove part of your thyroid and leave the other part so that it can continue to create and release thyroid hormones. This is most likely in situations where you have a nodule thats causing your thyroid problem. About 75% of people who have only one side of the thyroid removed are able to make enough thyroid hormone after surgery without hormone replacement therapy.
Functions Of Thyroid Hormones
The thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, are often referred to as metabolic hormones because their levels influence the bodys basal metabolic rate, the amount of energy used by the body at rest. When T3 and T4 bind to intracellular receptors located on the mitochondria, they cause an increase in nutrient breakdown and the use of oxygen to produce ATP. In addition, T3 and T4 initiate the transcription of genes involved in glucose oxidation. These mechanisms prompt cells to produce more ATP which causes an increase in heat production. This so-called calorigenic effect raises body temperature.
Disorders of theEndocrine System: Iodine Deficiency, Hypothyroidism, and Hyperthyroidism
Dietary iodine deficiency can result in the impaired ability to synthesize T3 and T4, leading to a variety of severe disorders. When T3 and T4 cannot be produced, TSH is secreted in increasing amounts. As a result of this hyperstimulation, thyroglobulin accumulates in the thyroid gland follicles, increasing their deposits of colloid. The accumulation of colloid increases the overall size of the thyroid gland, a condition called a goiter . A goiter is only a visible indication of the deficiency. Other symptoms include impaired growth and development, decreased fertility, and prenatal and infant death. Neonatal hypothyroidism is characterized by severe cognitive deficits, short stature, and sometimes deafness and muteness in children and adults born to mothers who were iodine-deficient during pregnancy.
Can I Live A Normal Life With A Thyroid Disease
A thyroid disease is often a life-long medical condition that you will need to manage constantly. This often involves a daily medication. Your healthcare provider will monitor your treatments and make adjustments over time. However, you can usually live a normal life with a thyroid disease. It may take some time to find the right treatment option for you and control your hormone levels, but then people with these types of conditions can usually live life without many restrictions.
What Is Hashimotos Thyroiditis
Hashimotos thyroiditis is the most common thyroid disease in the United States 2). It is an inherited condition that affects over 10 million Americans and is about seven times more common in women than in men.
Hashimotos thyroiditis is characterized by the production of immune cells and autoantibodies by the bodys immune system that can damage thyroid cells and compromise their ability to make thyroid hormone. Hypothyroidism occurs if the amount of thyroid hormone which can be produced is not enough for the bodys needs. The thyroid gland may also enlarge, forming a goiter.
Causes of Hashimotos thyroiditis
Hashimotos thyroiditis results from a malfunction in the immune system. When working properly, the immune system is designed to protect the body against invaders such as bacteria, viruses and other foreign substances. The immune system of someone with Hashimotos thyroiditis mistakenly recognizes normal thyroid cells as foreign tissue, and it produces antibodies that may destroy these cells. Although various environmental factors have been studied, none have been positively proven to be the cause of Hashimotos thyroiditis.
Signs & Symptoms of Hashimotos thyroiditis
Although many of the symptoms associated with thyroid hormone deficiency occur commonly in patients without thyroid disease, patients with Hashimotos thyroiditis who develop hypothyroidism are more likely to experience the following:
- Heavy menstrual flow
- Increased sensitivity to many medications
Tests
What Is Thyroid Disease
Thyroid disease is a general term for a medical condition that keeps your thyroid from making the right amount of hormones. Your thyroid typically makes hormones that keep your body functioning normally. When the thyroid makes too much thyroid hormone, your body uses energy too quickly. This is called hyperthyroidism. Using energy too quickly will do more than make you tired it can make your heart beat faster, cause you to lose weight without trying and even make you feel nervous. On the flip-side of this, your thyroid can make too little thyroid hormone. This is called hypothyroidism. When you have too little thyroid hormone in your body, it can make you feel tired, you might gain weight and you may even be unable to tolerate cold temperatures.
These two main disorders can be caused by a variety of conditions. They can also be passed down through families .