What Are The Causes Of Papillary Carcinoma Of The Thyroid
The exact cause of papillary carcinoma of the thyroid is unknown. There may be a genetic mutation involved but more research is need to confirm this hypothesis.
One risk factor for the disease is exposure of the head, neck, or chest to radiation. This happened more often before the 1960s when radiation was a common treatment for conditions like acne and inflamed tonsils. Radiation is still sometimes used to treat certain cancers.
People exposed to nuclear disasters or have lived within 200 miles of a nuclear disaster are at high risk. They may need to take potassium iodide to reduce their risk of developing cancer.
What Are Some Other Papillary Thyroid Cancer Treatments
The other surgical option for patients with papillary thyroid cancer is a total thyroidectomy . An expert pre-operative evaluation of the papillary thyroid cancer patient is required to determine whether there is any involvement of the lymph nodes in the neck. In most circumstances, the involvement of neck lymph nodes can be determined prior to the thyroid surgery procedure. When there is evidence that the papillary thyroid cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the neck, surgical approaches to the central and lateral neck lymph nodes should be performed.
When neck lymph nodes are involved with papillary thyroid cancer, either during the evaluation of the papillary thyroid cancer or during surgery for the papillary thyroid cancer, the recommended operation is a total thyroidectomy.
Often, other characteristics of the tumor that can be seen under the microscope which may have an influence on whether the surgeon should remove the entire thyroid .
The surgical options are covered in greater detail in our article on for thyroid cancer. A more detailed discussion of thyroid surgery for the thyroid gland and lymph nodes of the neck can be found here.
How Is Papillary Thyroid Cancer Treated
Treatments for papillary thyroid cancer depend on the tumor size and whether the cancer has spread .
Surgery is the most common treatment for PTC. Depending on the tumors size and location, your surgeon may remove part of your thyroid gland or all of your gland . If you have cancer present in the lymph nodes of your neck, your surgeon may remove the affected lymph nodes at the time of the initial thyroid surgery or as a second procedure.
If you have a total thyroidectomy, youll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication for the rest of your life.
Additional treatments for PTC include:
- Radioiodine therapy: Thyroid cells and papillary thyroid cancer cells absorb iodine, a mineral found in some food. Because of this, healthcare providers sometimes use a radioactive form of iodine to destroy all remaining normal thyroid tissue and potentially destroy residual cancerous thyroid tissue after a thyroidectomy.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation kills cancer cells and stops them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver strong beams of energy directly to the tumor site. Internal radiation therapy involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Intravenous or oral chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stop cancer growth. Very few people diagnosed with thyroid cancer will ever need chemotherapy.
You May Like: Blood Test For Thyroid Levels
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if thyroid cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually thyroid cancer cells. The disease is metastatic thyroid cancer, not lung cancer.
Age Gender And Being Exposed To Radiation Can Affect The Risk Of Thyroid Cancer
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for thyroid cancer include the following:
- Being between 25 and 65 years old.
- Being exposed to radiation to the head and neck as an infant or child or being exposed to radioactive fallout. The cancer may occur as soon as 5 years after exposure.
- Having a history of goiter .
- Having a family history of thyroid disease or thyroid cancer.
- Having certain geneticconditions such as familial medullary thyroid cancer , multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A syndrome , or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B syndrome .
Also Check: Np Thyroid Over The Counter
Papillary Thyroid Cancer Market Is Anticipated To Surpass A Valuation Of Us$ 439 Billion By 2032
During the forecast period, The Papillary Thyroid Cancer Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.80% on average. The market is currently valued at US$ 2.75 billion in 2022. The market for papillary thyroid cancer is expected to exceed $4.39 billion by 2032. Future Market Insights analysis revealed a historical market valuation of US$ 2.62 Billion.
With the latest insights and statistics from the biggest pharmaceutical and healthcare device manufacturers across the globe, FMI presents an extensive analysis on Papillary Thyroid Cancer market.
FMI offers insights into the market data on over 5000+ drugs for more than 100 countries, which further aids the research on current and upcoming market scenario for the Papillary Thyroid Cancer market. Our expert researchers and analysts for healthcare tracks the data of established players as well as new entrants in medical industry to provide an unbiased analysis for a sound and financial decision.
Sample of Research Report:
Over the past decade, healthcare sector has been expanding remarkably, following the advent of artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things integrated medical devices. Advancement in technology has created impressive scope within the medical sector for diagnostics and therapeutics.
Papillary Thyroid Cancer Market has been classified on the basis of treatment and end user.
Papillary Thyroid Cancer by Treatment:
What Is The Treatment For Thyroid Cancer
Radioactive iodine therapy . Thyroid cells and most differentiated thyroid cancers absorb iodine so radioactive iodine can be used to eliminate all remaining normal thyroid tissue and potentially destroy residual cancerous thyroid tissue after thyroidectomy . The procedure to eliminate residual thyroid tissue is called radioactive iodine ablation. Since most other tissues in the body do not efficiently absorb or concentrate iodine, radioactive iodine used during the ablation procedure usually has little or no effect on tissues outside of the thyroid. However, in some patients who receive larger doses of radioactive iodine for treatment of thyroid cancer metastases, radioactive iodine can affect the glands that produce saliva and result in a dry mouth. If higher doses of radioactive iodine are necessary, there may also be a small risk of developing other cancers later in life. This risk is very small, and increases as the dose of radioactive iodine increases. The potential risks of treatment can be minimized by using the smallest dose possible. Balancing potential risks against the benefits of radioactive iodine therapy is an important discussion that you should have with your doctor if radioactive iodine therapy is recommended.
If your doctor recommends radioactive iodine therapy, your TSH level will need to be elevated prior to the treatment. This can be done in one of two ways.
Read Also: What’s The Best Thyroid Medication
Different Kinds Of Thyroid Cancer
There are 4 main types of thyroid cancer. They are listed below. Your doctor can tell you more about the kind you have.
- Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common kind of thyroid cancer. It may also be called differentiated thyroid cancer. This kind tends to grow very slowly and is most often in only one lobe of the thyroid gland. Even though they grow slowly, papillary cancers often spread to the lymph nodes in the neck.
- Follicular cancer is the next most common type. Its more common in countries where people dont get enough iodine in their diet. These cancers do not tend to spread to lymph nodes, but they can spread to other parts of the body, like the lungs or bones.
- Medullary cancer is a rare type of thyroid cancer. It starts in a group of thyroid cells called C-cells. C-cells make calcitonin, a hormone that helps control the amount of calcium in the blood.
- Anaplastic cancer is a rare type of thyroid cancer. It often spreads quickly into the neck and to other parts of the body, and is very hard to treat.
Other Reasons That Might Necessitate An Ultrasound
Expert ultrasound may also help confirm a diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer which has spread to the lymph nodes of the neck. The ultrasonographer will look for multiple changes. Although unskilled observers might believe that size is a major issue, in fact, it is not. High-resolution ultrasound is able to detect a diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer in the lymph nodes as small as 1-2 mm .
When looking at the lymph nodes in the neck with ultrasound, the following criteria are important considerations in confirming the presence of thyroid cancer:
-
enlarged or cystic lymph nodes
-
changes in the normal architecture of a lymph nodes
-
small calcifications within lymph nodes
-
disorganized or irregular blood flow to the lymph node
-
asymmetric lymph nodes when comparing one side of the neck to the other
In the end, the most important factor will be location, location, location. A diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer that has spread to neck lymph nodes is quite predictable.
There is one important weakness in relying on ultrasound findingsit cannot distinguish cancerous from inflammatory lymph nodes. Both conditionsenlarged and inflammatory lymph nodesmay appear very similar on ultrasound. Therefore, ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy would be a necessary next step to confirm or rule out a diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer.
The quality of the ultrasound will depend upon four critical and equally important factors. The best quality will be determined by:
Also Check: How To Fix Hair Loss From Thyroid
Where Thyroid Cancer Starts
The thyroid gland is in the front part of the neck, below the thyroid cartilage . In most people, the thyroid cannot be seen or felt. It is shaped like a butterfly, with 2 lobes the right lobe and the left lobe joined by a narrow piece of gland called the isthmus.
The thyroid gland has 2 main types of cells:
- Follicular cells use iodine from the blood to make thyroid hormones, which help regulate a persons metabolism. Having too much thyroid hormone can cause a fast or irregular heartbeat, trouble sleeping, nervousness, hunger, weight loss, and a feeling of being too warm. Having too little hormone causes a person to slow down, feel tired, and gain weight. The amount of thyroid hormone released by the thyroid is regulated by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain, which makes a substance called thyroid-stimulating hormone .
- C cells make calcitonin, a hormone that helps control how the body uses calcium.
Other, less common cells in the thyroid gland include immune system cells and supportive cells.
Different cancers develop from each kind of cell. The differences are important because they affect how serious the cancer is and what type of treatment is needed.
Many types of growths and tumors can develop in the thyroid gland. Most of these are benign but others are malignant , which means they can spread into nearby tissues and to other parts of the body.
What Are The Warning Signs Of Thyroid Cancer
You or your healthcare provider might feel a lump or growth in your neck called a thyroid nodule. Donât panic if you have a thyroid nodule. Most nodules are benign . Only about 3 out of 20 thyroid nodules turn out to be cancerous .
Other thyroid cancer symptoms include:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck.
What are the signs that thyroid cancer has spread?
If you have thyroid cancer that has spread to other areas of your body, you may experience symptoms such as:
- Exposure to radioactive fallout from nuclear weapons or a power plant accident.
Also Check: What Is Thyroid Peroxidase Ab
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have thyroid cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. You may have heard other people say that their cancer was stage 1 or stage 2. Your doctor will want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the spread of the cancer through the thyroid gland. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other organs of your body that are close by or far away.
Your cancer can be stage 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread outside of the thyroid gland. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
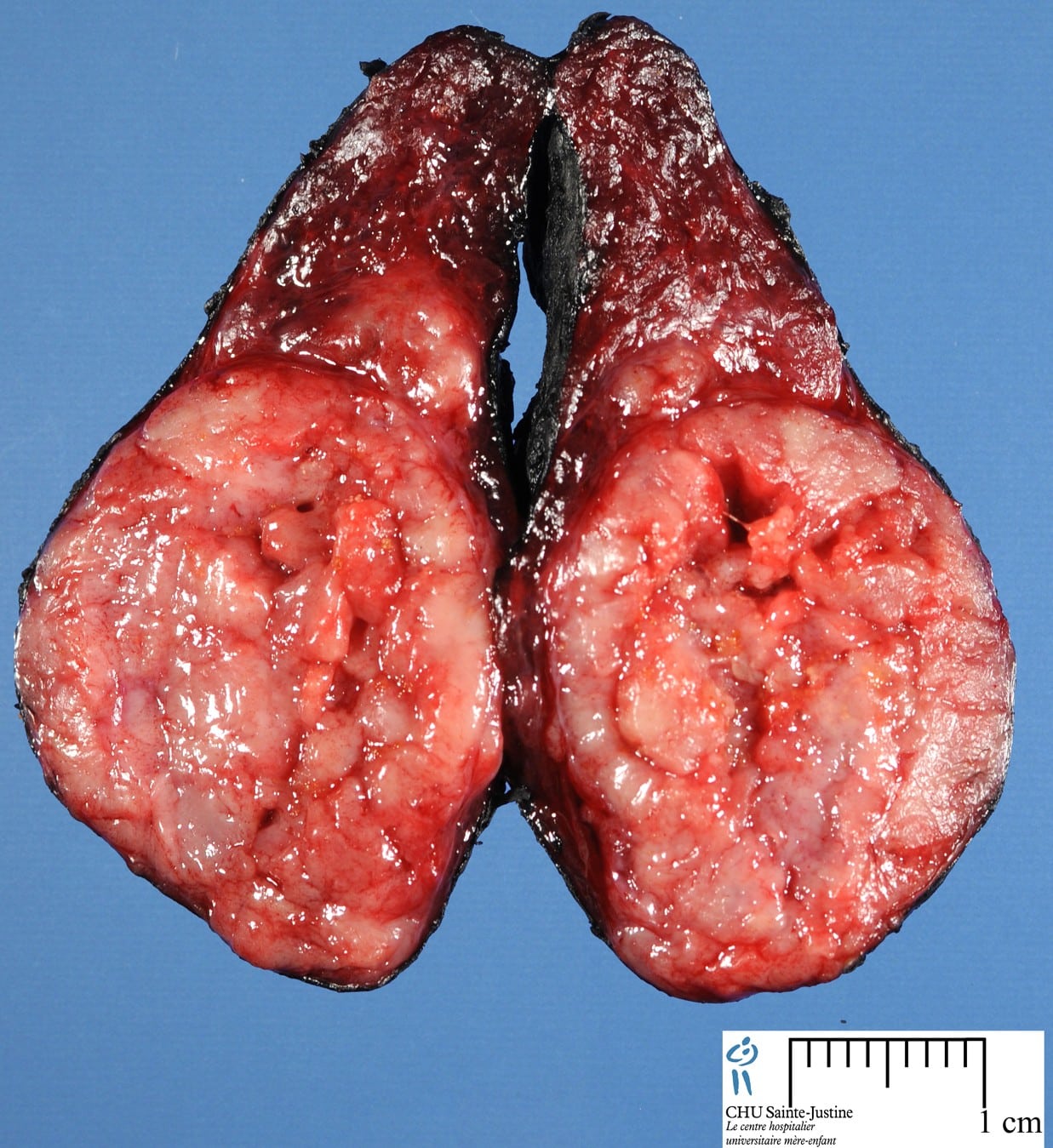
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Overview

Editorial Board Member: Editor-in-Chief: Last author update:Last staff update:Copyright: Page views in 2021:Page views in 2022 to date:Cite this page:
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma is the most common type of thyroid carcinoma, defined by a set of distinctive nuclear features, including:
- Change of nuclear size and shape: nuclear enlargement, elongation and overlapping
- Chromatin characteristics: chromatin clearing, margination and glassy nuclei
- Nuclear membrane irregularity: irregular nuclear contour, nuclear groove and nuclear pseudoinclusion
- Diagnosis is based on nuclear features
- Subtyping is based on a combination of architecture / pattern, cytologic features, size and encapsulation
- BRAFV600E is the most frequent mutation, particularly in tall cell and classic variants
- Predominant form of thyroid carcinoma, accounting for 80 – 93% in contemporary series
- There is a growing number of papillary thyroid carcinoma in the last 15 – 20 years due to increasing recognition of thyroid nodules on imaging , sometimes referred as thyroid cancer epidemics most of these tumors are of low risk
Images hosted on other servers:
TCGA
You May Like: Treatment Of Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Testing For And Diagnosing Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Your doctor can diagnose papillary carcinoma of the thyroid using a variety of tests. A clinical exam will uncover any swelling of the thyroid gland and nearby tissues. Your doctor may then order a fine needle aspiration of the thyroid. This is a biopsy in which your doctor collects tissue from the lump on your thyroid. This tissue is then examined under a microscope for cancer cells.
What Are The Symptoms
Often, you won’t have any. You might only find out about it because of an imaging test for another problem. Or, during a routine physical exam, your doctor might just happen to feel a lump, called a nodule, on your thyroid.
Nodules are growths that may be solid or filled with fluid. They’re very common and often don’t cause any trouble. But about 1 in 20 are cancer.
As a nodule gets bigger, you may start to have symptoms like:
- Lump in your neck that you can see or feel
- Hard time swallowing
- Sore throat or hoarseness that doesn’t go away
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck
- Trouble breathing, especially when you lie down
Doctors aren’t sure. It’s most common in women under age 40.
You may have a higher chance of getting papillary thyroid carcinoma because of things like:
Certain genetic conditions. Diseases like familial adenomatous polyposis , Gardner syndrome, and Cowden disease can raise your odds.
Family history. In a small number of cases, papillary thyroid carcinoma runs in the family.
Radiation therapy. If you had radiation to treat cancer for another condition when you were a child, it can raise your chances.
Gender. It’s much more common in women than men, but doctors aren’t sure why.
You May Like: Who Tests For Thyroid Problems
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The age of the patient at the time of diagnosis.
- The type of thyroid cancer.
- The stage of the cancer.
- Whether the cancer was completely removed by surgery.
- Whether the patient has multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B .
- The patient’s general health.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will this treatment affect my ability to have children? Do I need to avoid pregnancy for a while?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too? Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Read Also: How Do You Check Your Thyroid Function