Data And Safety Monitoring Board
The primary responsibilities of the DSMB will include periodical review and evaluation of the study data for participant safety, study conduct and progress and make recommendations to investigators and relevant other parties concerning the continuation, modification or termination of the trial. The DSMB will consider study-specific data as well as relevant background data about the differentiated thyroid CA, RAI treatment, use of prednisolone and patient population under study.
During the trial, the DSMB will review cumulative study data to evaluate safety of prednisolone, study conduct and scientific validity and integrity of the trial. DSMB members will look into the timeliness, completeness and accuracy of the data to ensure safety and welfare of study participants. The DSMB will also assess the performance of overall study operations and any other relevant issues, as necessary. Members of the DSMB will meet every 8weeks to review the study data and make recommendation to the research team on conduct of the study. The DSMB will include three independent experts in the field .
How Can I Prepare For Rai
One way to maximize the effects of RAI is by raising your TSH level. There are 2 ways to do this:
For either, it is also recommended that you go on a Low Iodine Diet.
Because you are receiving a radioactive substance, there are some precautions you should be aware of. The resources below can help you prepare:
- A list of RAI Isolation Room Essentials to bring if you are in a hospital isolation room, following your RAI treatment
- RAI precautions, by Ian Adam
What Is Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Radioactive iodine can be used for the treatment of overactive thyroid and certain types of thyroid cancer. The term radioactive may sound frightening, but it is a safe, generally well-tolerated, and reliable treatment that targets thyroid cells so there is little exposure to the rest of your bodys cells.
Read Also: How To Fix Hair Loss From Thyroid
Are There Long Term Risks Of I
In general, RAI is a safe and effective treatment for the thyroid disorders mentioned above. Hypothyroidism is a common side effect of RAI for hyperthyroidism and always seen after RAI for thyroid cancer. This is usually easily treated with thyroid hormone replacement . Some studies suggest a slight increase in thyroid cancers may be seen after RAI treatment for hyperthyroidism. Loss of taste and dry mouth due to salivary gland damage may be seen. The use of lemon drops, vitamin C or sour stimulation to potentially decrease the exposure of the salivary glands to RAI is controversial and should be discussed with your physician. Importantly, once you have been treated with RAI, regular medical follow-up is lifelong.
Preparation Of A Follicular Thyroid Cancer Patient For Radioactive Iodine Treatment

Follicular thyroid cancer patients must be taken off of levothyroxine thyroid hormone for a minimum of four weeks, taken off of liothyrionine thyroid hormone for a minimum of two weeks, or receive a medication which is TSH . Additionally, follicular thyroid cancer patients must be on a low iodine diet for a minimum of four weeks to starve their body of iodine. Those patients which have undergone CAT scans with intravenous contrast must wait until their blood iodine levels have been adequately decreased . Note, a desire to treat with radioactive iodine should never prevent the use of necessary CAT scans for the evaluation of a follicular thyroid cancer patient.
- Dry mouth and or eyes
- Narrowing of the drainage duct of the eye’s tears leading to excessive tearing down the cheek
- Swelling in your cheeks from inflammation or damage to the saliva producing glands
- Short term changes to taste and smell
- Lowered testosterone levels in males
- Change in periods in women
Recommended Reading: Most Common Form Of Thyroid Cancer
Radioactive Iodine Therapy For Thyroid Cancer
Your thyroid gland absorbs nearly all of the iodine in your body. Because of this, radioactive iodine can be used to treat thyroid cancer. The RAI collects mainly in thyroid cells, where the radiation can destroy the thyroid gland and any other thyroid cells that take up iodine, with little effect on the rest of your body. The radiation dose used here is much stronger than the one used in radioiodine scans, which are described in Tests for Thyroid Cancer.
This treatment can be used to ablate any thyroid tissue not removed by surgery or to treat some types of thyroid cancer that have spread to lymph nodes and other parts of the body.
Radioactive iodine therapy helps people live longer if they have papillary or follicular thyroid cancer that has spread to the neck or other body parts, and it is now standard practice in such cases. But the benefits of RAI therapy are less clear for people with small cancers of the thyroid gland that do not seem to have spread, which can often be removed completely with surgery. Discuss your risks and benefits of RAI therapy with your doctor. Radioactive iodine therapy cannot be used to treat anaplastic and medullary thyroid carcinomas because these types of cancer do not take up iodine.
Radioactive Iodine Refractory Disease
The ATA defines RAI-refractory DTC in patients with structural evident disease after appropriate iodine preparation and TSH stimulation in one of four ways: no uptake outside the thyroid bed at the first therapeutic RAI treatment, the tumor tissue loses the ability to concentrate RAI after previous evidence of RAI-avid disease, RAI is concentrated in some lesions, but not others, and metastatic disease progresses despite significant concentration of RAI . A joint statement between Endocrinology and Nuclear Medicine experts supports these basic definitions and applies this to common clinical scenarios . Others consider significant 18FDG uptake on PET/CT imaging as a criterion for RAI-refractory disease.
Don’t Miss: How To Regrow Hair Loss From Thyroid
Radioactive Iodine Treatment For Follicular Thyroid Cancer
The mechanism of how Radioactive Iodine Treatment works to treat thyroid cancer was not discovered until years following its use to treat follicular thyroid cancers. We now know today that follicular thyroid cancers can possess a type of key hole on the surface of their cell called a symporter that allows iodine to be taken into the cell. Under normal circumstances, iodine is taken up by normal thyroid cells in the process of producing the body’s thyroid hormone. Although follicular thyroid cancer rarely produces any significant amounts of thyroid hormone itself, it frequently maintains this iodine symporter and ability to take up iodine. In the treatment of follicular thyroid cancer, this can be taken advantage of by having the patient swallow an iodine pill that has been radioactively charged.
The follicular thyroid cancer patient swallows a radioactive iodine form of iodine called iodine 131 in a liquid or pill form. The RAI is absorbed through digestion and circulated throughout the body in bloodstream. Follicular thyroid cancer cells can pick up the radioactive iodine wherever they are located in the body. Once taken into the follicular thyroid cancer cells, the radioactive iodine delivers a local radiation treatment in the area where the iodine is concentrated.
Adverse Effects And Dose Of Rai
Short-term side effects in the weeks following RAI remnant ablation have been reported to be more frequent in patients treated with 3.7 GBq as compared to 1.1 GBq in recent multi-center randomized trials . As most of the short-term side effects are reversible and can be managed with the attention of physicians, the long-term irreversible adverse effects of RAI ablation including secondary primary malignancy, xerostomia, and infertility should be more carefully considered . Weighting risks versus benefits of low-dose and high-dose RAI ablation for individual patients is warranted for deciding on an optimal personalized RAI dose.
Xerostomia is a common side effect of RAI therapy, which hampers the quality of life of patients. The reported incidence of xerostomia is variable there were no significant differences in xerostomia symptoms between 1.1-GBq and 3.7-GBq RAI therapy in two prospective randomized clinical trials . However, the incidence and severity were increased in patients who underwent 5.5 GBq of RAI therapy compared with the patients who underwent 3.7-GBq RAI therapy . Therefore, in patients who need high-dose RAI therapy, an emphasis should be placed on appropriate protection of the salivary gland .
Don’t Miss: What Hormones Do The Thyroid Gland Produce
Dose Toxicity: Adverse Effects
The most reliable data concerning acute effects of RAI originate from the major, multi-institutional randomized trials , which systematically collected acute toxicity data as a secondary endpoint, employing an internationally accepted, standardized quality-of-life scale . Higher rates of nausea, neck pain, lacrimal gland dysfunction, salivary gland dysfunction, and altered taste were described for 100 mCi compared with 30 mCi . Further, patients treated with 100 mCi also had a longer average hospital stay than patients treated with 30 mCi, though variable institutional regulations regarding post-RAI discharge is a probable confounding variable.
Table 3.
Radioiodine adverse effect comparison by dose level
RAI therapy also increases the risk of long-term sialoadenitis and nasolacrimal duct obstruction . This evidence is based upon the administration of high single or cumulative doses of RAI therapy in retrospective cohort studies, and high-quality evidence regarding this risk in the context of lower doses is lacking at this time.
When Do You Have Radioactive Iodine
You might have radioactive iodine treatment:
- after surgery, to kill any cancer cells that may have been left behind
- to treat thyroid cancer that has spread
- to treat thyroid cancer that has come back after it was first treated
You may only need to have this treatment once. But it can be repeated every 3 months if needed, until there is no sign of any thyroid cancer on your scans.
You May Like: Are Natural Thyroid Supplements Safe
Group A: Bir To Initial Treatment
Sixty-one patients were included in group A. Data on basal nonstimulated Tg levels both before and 1 to 2 years after the second RAI treatment were available for 51 patients data on stTg were available for 31 patients. There was a substantial decrease in mean stTg level at 1 to 2 years after the second RAI treatment .
Before receiving the second RAI treatment, all group A patients had a stimulated and/or suppressed Tg level compatible with the definition of BIR to total thyroidectomy and initial RAI treatment. At 1 to 2 years from the second RAI treatment, 44 of the 60 patients with complete data still had an elevated Tg level . Comparison with the level before the second RAI revealed a more than 20% increase in Tg in 10 patients, stable level in 18, and a more than 20% decrease in 16. Within 2 years after the second RAI dose, 9/58 patients with available data in group A had positive locoregional imaging findings .
What Does Rai Do
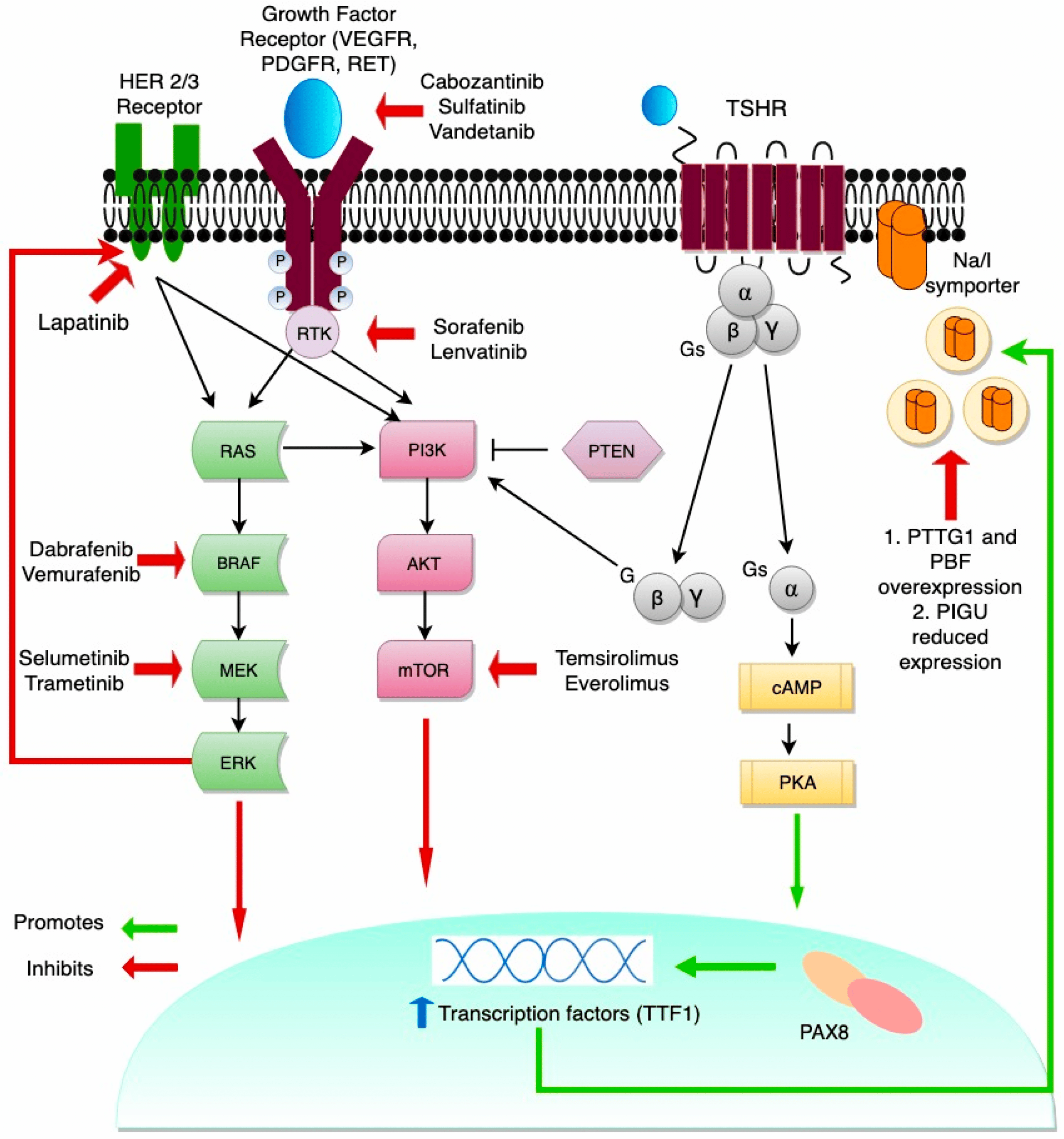
RAI treatment destroys any remaining thyroid cells after surgery, minimizing the risk of the cancer coming back. It is also called ablation therapy.
The initial RAI treatment may be given anytime, but usually 6 weeks to 6 months after surgery. The reason for a delay may be because your doctor wants to see how youre doing after surgery before deciding if RAI is necessary.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Take To Much Thyroid Medication
Clearing The Radioactive Iodine From Your Body
Some of the radioactive iodine will be taken up by your thyroid cells, but there will be some left over. Most of the extra radioactive iodine will leave your body through your urine , and smaller amounts will leave your body in your saliva , sweat, and bowel movements .
Follow these guidelines to help the radioactive iodine leave your body quickly.
- Drink lots of liquids. Starting right after your treatment, try to drink at least 1 cup of low-iodine liquid every hour while youre awake. Keep doing this for 2 to 3 days after your treatment. You dont have to wake up at night to drink liquids.
- Your urine will be radioactive so urinate as much as you can to empty your bladder. Try not to get urine outside of the toilet. If you do get urine outside of the toilet, wear gloves and clean up it up with an all-purpose cleaning disinfectant. If you normally stand while urinating, sit for 2 days after your treatment unless your healthcare provider gives you other instructions. This is so you can avoid getting urine anywhere but the toilet. Try to urinate every time you feel the urge instead of holding it in your bladder.
- Your bowel movements will also be radioactive. Go to the bathroom as much as you can so your bowel movements dont stay in your colon.
- If youre often constipated , ask your doctor about taking laxatives before your treatment. If you dont have a bowel movement within 24 hours after your treatment, call your doctor.
Discuss Your Treatment Plan
Your doctor will discuss your treatment plan with you.
Your treatment plan will follow these steps that will take place over a few days:
1. On the first day, youll have blood tests. After those tests, youll see your doctor and get a thyrotropin alfa injection to help you get ready for your treatment. This injection will help any leftover thyroid tissue absorb the radioactive iodine.
2. On the second day, youll get another thyrotropin alfa injection. Then youll get a small diagnostic dose of radioactive iodine in a pill. You wont have to follow any precautions after getting this small diagnostic dose of radioactive iodine. After you take this pill, youll have a whole-body scan. This scan will show your doctor how the radioactive iodine is being taken up in your body.
3. On the third day, youll have your full dose of radioactive iodine treatment. This is an outpatient procedure, so you wont be admitted to the hospital.
4. Youll have another whole-body scan several days after your treatment. This helps your doctor see where the dose of radioactive iodine was taken up in your body.
Recommended Reading: Natural Ways To Help Thyroid
Pathologic Factors For Dose Determination
In daily practice, dosimetric methods are reserved for complex clinical situations, such as in children, elderly patients, and patients with renal insufficiency and diffuse pulmonary metastases . Doses of RAI are generally empirically determined, based on characteristics of patient and cancer status. Risk stratification system is widely used for guide the dose determination of RAI therapy.
The 2015 ATA guidelines adapt a three-tiered risk stratification system , and European Consensus Conference also suggests similar classification system . Many factors are associated for classification :2): tumors confined to thyroid gland , microscopic extrathyroidal extension, macroscopic invasion into perithyroidal structures, status of lymph node metastasis, number and size of metastatic lymph nodes, aggressive histology , vascular invasion, and genetic mutations .
What Is Radioactive Iodine
Iodine, in the form of iodide, is made into two radioactive forms of iodine that are commonly used in patients with thyroid diseases: I-123 and I-131 . The radiation emitted by each of these forms of iodine can be detected from outside the patient to gain information about thyroid function and take pictures of the size and location of thyroid tissues. RAI is safe to use in individuals who have had allergic reactions to seafood or X-ray contrast agents, since the reaction is to the compound containing iodine, not the iodine itself. RAI is given by mouth in pill or liquid form.
Don’t Miss: Thyroid And Menopause Weight Gain
Having Your Radioactive Iodine Treatment
You are usually admitted to the ward on the day of your RAI treatment. You usually have radioactive iodine as a capsule. Before and after the treatment, you can eat normally. Your nurse will encourage you to drink plenty of fluids.
Because the iodine is radioactive, you will be radioactive for a while after the treatment. The radioactivity will slowly leave your body in your:
Dose Efficacy: Cancer Control
While the 2 recent large randomized trials have thus far reported only rates of remnant ablation , preliminary findings from the ESTIMABL-1 trial update suggest low rates of recurrence and no cancer-specific mortality at 5 years, independent of RAI dose . Further, several smaller trials also have sufficient follow-up to report cancer control outcomes. The Finnish trial reported by Maenpaa et al. did not demonstrate a difference in cancer recurrence at a median follow-up of 51 months . Similarly, the Polish randomized trial reported by Kukulska et al. did not identify differences in local recurrence at a median follow-up of 10 years . The observational series, while suffering from the aforementioned treatment group imbalances, do provide the opportunity for long-term outcome reporting however, no differences in outcome have been recognized , excepting 1 study demonstrating superior cancer control for the low-dose group .
Recommended Reading: How To Fix Thyroid Problems Naturally
Radioactive Iodine Therapy For Hyperthyroidism
Radioiodine therapy is a nuclear medicine treatment. Doctors use it to treat an overactive thyroid, a condition called hyperthyroidism. They also may use it to treat thyroid cancer. When a small dose of radioactive iodine I-131 is swallowed, it is absorbed into the bloodstream. The isotope is concentrated by the thyroid gland, where it begins destroying the gland’s cells.
Your doctor will instruct you on how to prepare, how to take any necessary radiation safety precautions, and when to stop taking anti-thyroid medications. Tell your doctor if there’s a possibility you are pregnant or if you are breastfeeding. Discuss any recent illnesses, medical conditions, allergies, and medications you’re taking. This procedure requires little to no special preparation. However, you should not eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of treatment.
Pregnancy And Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Dont get pregnant or get your partner pregnant for at least 6 months after getting radioactive iodine therapy, or as long as your doctor tells you to. Use birth control after treatment for at least 6 months after getting this treatment. If youre planning to have a child, talk with your doctor about your plans before your treatment.
Recommended Reading: Normal Range For Thyroid Antibodies