Relative Incidences And Clinicoradiological Characteristics Of Pd And Rd
Table shows the incidence rates and clinicoradiological characteristics of patients with structural PD and RD. Of the 121 patients, PD was evident in 81.0% and RD in 19% . The mean time to reoperation was 25.5 months for PD patients and 54.1 months for RD patients . PD was found in the previously dissected neck in 32.7% of patients , and in the non-dissected neck in 67.3% of patients . RD was evident in the previously dissected neck in 56.5% of patients , and in the non-dissected neck in 43.5% of patients . Compared to RD, PD was more commonly detected in the non-dissected neck . In both groups, tumor multiplicity and the number of pathologically positive lymph nodes after reoperation were significantly greater in the non-dissected than dissected neck .
Table 2 Clinical and radiological characteristics of patients with persistent disease and recurrent disease.
Management Of Advanced Thyroid Cancer And Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
For advanced thyroid cancer that persists or recurs after surgery, radioactive iodine ablation, and thyroid hormone TSH suppression, additional therapies may be required. Furthermore, patients with poorly differentiated or anaplastic thyroid cancer often require systemic targeted therapy or immunotherapy given in collaboration with medical oncologists.
Improved understanding of the pathogenesis of these cancers is leading to the development of new agents aimed at specific oncogenic mechanisms, called targeted therapies. Targeted therapies approved for the treatment of advanced thyroid cancer include tyrosine kinase inhibitors , multi-kinase inhibitor vandetinib, and RET fusion inhibitor selpercatinib. Additionally, clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate BRAF inhibitors and immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced thyroid cancers.
Papillary Thyroid Cancer Recurrence Risk Factors
Hannah R Nieto, Caitlin E M Thornton, Katie Brookes, Albert Nobre de Menezes, Alice Fletcher, Mohammed Alshahrani, Merve Kocbiyik, Neil Sharma, Kristien Boelaert, Jean-Baptiste Cazier, Hisham Mehanna, Vicki E Smith, Martin L Read, Christopher J McCabeThe Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Volume 107, Issue 5, May 2022, Pages 13921406
You May Like: Can Taking Thyroid Medication Help You Lose Weight
Living As A Thyroid Cancer Survivor
For many people with thyroid cancer, treatment may remove or destroy the cancer. Completing treatment can be both stressful and exciting. You may be relieved to finish treatment, but find it hard not to worry about cancer growing or coming back. This is very common concern if you have had cancer.
For other people, thyroid cancer may never go away completely, or it might come back in another part of the body. These people may get regular treatments with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or other therapies to help keep the cancer under control for as long as possible. Learning to live with cancer that does not go away can be difficult and very stressful.
Thyroid Surgery Recovery Side Effects And Complications
If you are having thyroid surgery, known as a thyroidectomy, to remove all or part of your thyroid glanda butterfly shaped organ at the base of your neckit’s important to know what to expect as you recover.
Side effects, such as neck pain and stiffness or sore throat, are common after surgery. Complications are rare but can be serious and even potentially life-threatening if they do occur.
This article explores common side effects of thyroid surgery, what to expect during the recovery process, and warning signs of complications.
You May Like: Where Does Thyroid Cancer Usually Metastasize To
Genetic Testing For Men And Fmtc
Genetic testing is now the mainstay in the diagnosis of the FMTC syndromes. RET proto-oncogene mutations have been discovered in each of the MTC syndromes. The RET proto-oncogene is a receptor tyrosine kinase whose exact function and role in these syndromes has not been elucidated. Patients with MEN 2A have germline RET mutations resulting in substitutions of conserved cysteine residues in exons 10 and 11. All patients with MEN 2B have a germline mutation resulting in a threonine-for-methionine substitution in codon 918 of exon 16. Mutations are described in exons 13 and 14 in patients with FMTC.
Genetic screening with sensitive PCR assays for germline RET mutations is routinely performed in at-risk patients. Children of parents known to have MEN or FMTC are tested for RET mutations to guide therapy and future genetic counseling. In addition, patients presenting with sporadic MTC should undergo RET mutational analysis to rule out new spontaneous germline mutations, which should prompt the testing of offspring for similar mutations.
Patient Demographics And Characteristics After Initial Surgery
Table summarizes the baseline clinicopathological characteristics of the patients with structural PD and RD after the initial surgery. The mean age at diagnosis was 44.5 years and the mean initial tumor size was 1.7±1.3 cm . The mean follow-up duration after surgery was 76±38 months. Almost all of the patients underwent surgery to treat conventional papillary thyroid cancer . Compared to patients with PD, those with RD were more often likely to be male and to have unilateral disease . We found no significant difference in age, tumor size or histology, the extent of gross extrathyroidal extension or lymphovascular invasion, TNM stage, or the extent of initial surgery between patients with PD and RD.
Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of all patients.
Also Check: Treatment Of Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Where Does Thyroid Cancer Usually Recur
Treatment for thyroid cancer varies widely and may include surgery, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. The type of treatment used depends on the type of cancer, the location of the tumor, and your overall health. Although most people with thyroid cancer survive their initial treatment, you are still at risk of recurrence after several years or even decades.
Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer. Although it can occur at any age, it usually affects people in their thirties and forties. Most papillary thyroid cancers are small and respond well to treatment, but a small percentage of these cancers can be aggressive and spread to other parts of the body.
Thyroid cancer usually recurs in lymph nodes located in the neck and paratracheal region. Patients with thyroid cancer of any size are more likely to develop a recurrence if the tumor has spread to lymph nodes. However, the location of the recurrence is not always clear.
What Are The Signs Of Thyroid Cancer Returning
If youve been diagnosed with thyroid cancer, its important to have it checked regularly. A physical exam will involve palpating your neck and lymph nodes, gathering your medical history, and asking about any symptoms or risk factors that may be contributing to your cancer. If your doctor suspects that your cancer is returning, a magnetic resonance imaging scan can help you find out where the cancer has spread.
One of the most common symptoms of thyroid cancer is a lump in the neck. This lump may be painless, or it may be hard to detect. It can also change your voice. You may have trouble swallowing, or you may feel as if you are breathing through a straw.
You should also talk to your doctor about the risk of relapse. The risk of relapse varies depending on the type of cancer and the stage. You may have symptoms for years after your diagnosis, but its important to make sure your doctor is aware of any symptoms you may notice.
Read Also: Does Selenium Help Thyroid Eye Disease
Key Components Of Differentiated* Thyroid Cancer Management
- Radioactive iodine ablation
- Dynamic Risk Stratification informed by ongoing surveillance with tumor markers and imaging
* Differentiated thyroid cancer includes Papillary, Follicular, and Hurthle cell thyroid cancer. Treatment for poorly differentiated, anaplastic, and medullary thyroid cancers are distinct and discussed separately.
Patients And Study Design
We conducted a retrospective analysis of data collected prospectively in 8 hospital-based referral centers for thyroid disease in Italy. Since 1990, all 8 centers have been using a common postoperative follow-up protocol for PTC patients, which is described in detail below. The cohort examined in this study consisted of individuals consecutively diagnosed with PTC since January 1, 1990. The only inclusion criteria applied were negative thyroglobulin antibody levels at the time of diagnosis and 3 or more years of follow-up before study data lock .
Also Check: For Thyroid Test Is Fasting Needed
Hoarseness And Voice Problems
After surgery, your voice may be hoarse or whispery, and it may feel tiring to talk. This is very common and expected during the first week or two after surgery. While around 1% of people may have damage to the nerves supplying the vocal cords, around 5% to 10% of people will have temporary symptoms due to irritation of the nerves during surgery or inflammation around the nerves afterward.
Symptoms usually improve in the first few weeks but may persist up to six months after surgery. While there is no specific treatment for this hoarseness, it’s helpful for your loved ones to be aware of the problem so that you don’t feel the need to talk loudly or more often than is comfortable. If the nerve was injured, more severe symptoms may be noted after surgery.
What Can You Do
After completing treatment for thyroid cancer, you should see your doctor regularly. You may also have tests to look for signs that the cancer has come back or spread. Experts do not recommend any additional testing to look for second cancers in patients without symptoms. Let your doctor know about any new symptoms or problems, because they could be caused by the thyroid cancer coming back or by a new disease or second cancer.
Patients who have completed treatment should keep up with early detection tests for other types of cancer.
All patients should be encouraged to avoid tobacco smoke, as smoking increases the risk of many cancers.
To help maintain good health, survivors should also:
- Get to and stay at a healthy weight
- Keep physically active and limit the time you spend sitting or lying down
- Follow a healthy eating pattern that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limits or avoids red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and highly processed foods
- Not drink alcohol. If you do drink, have no more than 1 drink per day for women or 2 per day for men
These steps may also lower the risk of some other health problems.
See Second Cancers in Adults for more information about causes of second cancers.
You May Like: What Are Some Thyroid Medications
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Thyroid cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Learn more about the importance of tracking side effects in another part of this guide. Learn more about palliative care in a separate section of this website.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if thyroid cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually thyroid cancer cells. The disease is metastatic thyroid cancer, not lung cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Stage 4 Thyroid Cancer
What Is Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Papillary thyroid cancer begins in the follicular cells in your thyroid that produce thyroglobulin . Its the most common type of thyroid cancer.
Your thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of your neck under your skin. Its a part of your endocrine system and controls many of your bodys important functions by producing and releasing certain hormones.
PTC tends to grow very slowly and usually develops in only one lobe of your thyroid gland.
There are several subtypes of papillary thyroid cancers. Of these, the follicular subtype is the most common. Other subtypes of papillary cancer arent as common and tend to grow and spread more quickly. They include:
Papillary thyroid cancer is also called papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Age Gender And Being Exposed To Radiation Can Affect The Risk Of Thyroid Cancer
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for thyroid cancer include the following:
- Being between 25 and 65 years old.
- Being exposed to radiation to the head and neck as an infant or child or being exposed to radioactive fallout. The cancer may occur as soon as 5 years after exposure.
- Having a history of goiter .
- Having a family history of thyroid disease or thyroid cancer.
- Having certain geneticconditions such as familial medullary thyroid cancer , multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A syndrome , or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B syndrome .
Recommended Reading: Can Thyroid Issues Cause Erectile Dysfunction
What To Do If You Notice Signs Of Thyroid Cancer
If you experience signs of thyroid cancer, its important to consult with your doctor to get an accurate diagnosis.
First, your doctor may conduct a physical examination, manually palpating your neck and throat to check for abnormal growths or areas of swelling, including the thyroid and lymph nodes. Your doctor may also gather your personal and family medical history, ask about your symptoms and risk factors, including any inherited genetic mutations.
A blood test called a tumor marker test may be recommended to check for high levels of certain hormones, such as:
- Triiodothyronine
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone
If cancer is suspected, one or more of the following diagnostic tests may be ordered:
Ultrasound. An ultrasound over the neck region may be done to locate any nodules that are present on your thyroid and determine whether theyre made up of solid or liquid material.
Chest X-ray: This basic imaging test may be done if your doctor suspects the cancer has metastasized to your lungs.
Magnetic resonance imaging scan: Using magnets, an MRI scan creates highly detailed images of the thyroid and surrounding areas.
Computed tomography scan or positron emission tomography scan: A CT scan uses contrast dye that helps your doctor pinpoint the size and location of your cancer, and whether it has metastasized to surrounding tissues. A PET scan is similar but uses an injection of radioactive sugar instead of contrast dye .
Expert cancer care
Early Rai Related Symptoms
The first survey was answered at a median of 2.5 months after initial treatment. The following RAI related symptoms were more frequent among patients who received RAI: periorbital edema , excessive tearing , salivary gland swelling , salivary gland pain , dry mouth , taste disorders , smell impairment , and nausea . Intensity of symptoms was also significantly higher in patients receiving RAI treatment compared with those who did not .
You May Like: Can You Die Of Thyroid Cancer
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
Often the treatment plan will include the treatments described above, such as surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, targeted therapy, external-beam radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy. However, they may be used in a different combination or given at a different pace. Your doctor may suggest clinical trials that are studying new ways to treat this type of recurrent cancer. Whichever treatment plan you choose, palliative care will be important for relieving symptoms and side effects.
How Is Papillary Thyroid Cancer Treated
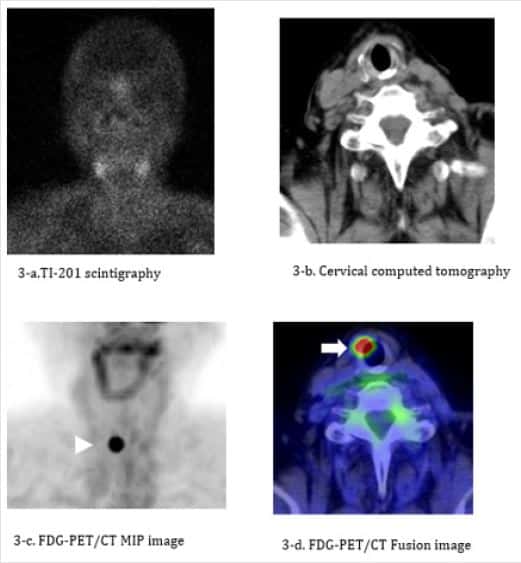
Treatments for papillary thyroid cancer depend on the tumor size and whether the cancer has spread .
Surgery is the most common treatment for PTC. Depending on the tumors size and location, your surgeon may remove part of your thyroid gland or all of your gland . If you have cancer present in the lymph nodes of your neck, your surgeon may remove the affected lymph nodes at the time of the initial thyroid surgery or as a second procedure.
If you have a total thyroidectomy, youll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication for the rest of your life.
Additional treatments for PTC include:
- Radioiodine therapy: Thyroid cells and papillary thyroid cancer cells absorb iodine, a mineral found in some food. Because of this, healthcare providers sometimes use a radioactive form of iodine to destroy all remaining normal thyroid tissue and potentially destroy residual cancerous thyroid tissue after a thyroidectomy.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation kills cancer cells and stops them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver strong beams of energy directly to the tumor site. Internal radiation therapy involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Intravenous or oral chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stop cancer growth. Very few people diagnosed with thyroid cancer will ever need chemotherapy.
Recommended Reading: Best Thyroid Medication Weight Loss