How Is Thyroid Cancer Diagnosed
Most thyroid nodules are benign, not cancerous. If a nodule is discovered in the thyroid by physical examination or imaging, it should be further described by the radiologist with attention given to certain details used to estimate the likelihood that a nodule is malignant. An important characteristic is the size of the nodule. Tiny thyroid cancers exist undetected in the glands of as many as one-third of all adults, and the vast majority of these are never detected or cause any clinical problems. For this reason, and because tiny nodules are difficult to biopsy accurately, any nodule of less than 1 centimeter in size may not need to be further evaluated. For nodules of more than 1 centimeter, a grading system is applied and biopsy recommended if the score indicates an appropriate level of concern. Nodules that are not judged to need biopsy may be monitored with repeat ultrasound examinations.
What About Other Treatments I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
How Is Papillary Thyroid Cancer Diagnosed
Papillary thyroid cancer usually presents as a lump or nodule on your thyroid gland. You may notice it, or your healthcare provider may discover it during a routine neck examination. Sometimes, the nodule is discovered incidentally by imaging tests you get for other medical reasons.
Your healthcare provider will likely order the following tests to help diagnose PTC:
- Imaging tests: Your provider may order imaging tests to identify the nodule on your thyroid. These tests might include thyroid ultrasound, CT scan and/or magnetic resonance imaging .
- Fine needle aspiration : Your provider will likely want to take a small tissue sample, called a biopsy, from the nodule on your thyroid using a very thin needle. A pathologist will look at the tissue under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells and, if so, what type of thyroid cancer it is.
Your healthcare provider may also recommend genetic counseling to see if you have a genetic condition that may have caused PTC and may cause other types of tumors.
Read Also: T Balance Plus Thyroid Supplement
How Is Parathyroid Cancer Diagnosed
Parathyroid cancer can be challenging to diagnose. One reason for this is that the cells of a benign parathyroid adenoma and the cells of parathyroid cancer look similar.
A diagnosis of parathyroid cancer is most often made after your abnormal, overactive parathyroid gland has been surgically removed and further testing is done with the tissue. Sometimes, the surgeon is able to tell during the surgery that its parathyroid cancer.
What Are The Symptoms Of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
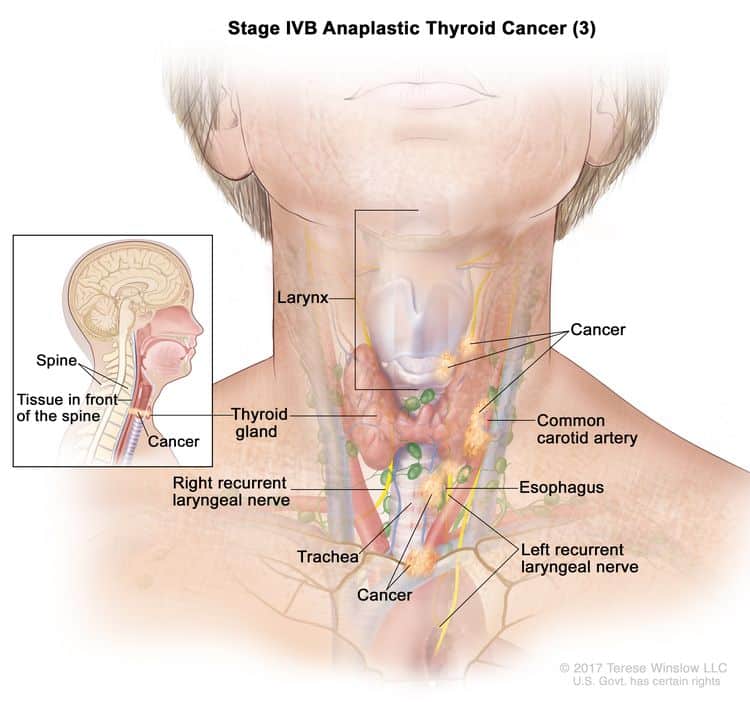
The main sign of papillary thyroid cancer is a painless lump or nodule on your thyroid gland. PTC usually doesnt cause any other symptoms.
In rare cases, you may experience pain in your neck, jaw or ear from PTC. If the nodule is large enough to compress your windpipe or esophagus, it may cause difficulty with breathing or swallowing.
Also Check: How Do You Develop Thyroid Cancer
Risk Factors For Thyroid Cancer
There are some things that can make it more likely to develop thyroid cancer. These are called risk factors and they include:
- Exposure to radiation a small number of thyroid cancers are due to having radiation therapy to the head and neck area as a child or living in an area with high levels of radiation.
- Family history only around 5% of thyroid cancer runs in families. Some inherited genetic conditions, such as familial adenomatous polyposis or Cowden syndrome, or inheriting the RET gene may also increase your risk.
- Other factors people who are overweight or obese possibly have a higher risk of developing thyroid cancer. Other thyroid conditions only slightly increase the chance of developing thyroid cancer.
Having these risk factors doesnt mean you will develop thyroid cancer. Often there is no clear reason for getting thyroid cancer. If you are worried about your risk factors, ask your doctor for advice.
Risks Of Thyroid Surgery
The two most common risks of thyroid surgery include damage to the parathyroid glands or the recurrent laryngeal nerves, structures that are directly attached to the thyroid gland.
- Parathyroid glands: There are four parathyroid glands, two attached to the back of each thyroid lobe. They are about the size of a pencil eraser or pea. The parathyroid glands control the level of calcium in the body. Damage to the parathyroid glands can affect calcium levels and cause significant health risks if left untreated.
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve : The RLN is very thin, about the diameter of a piece of angel hair pasta. The RLN controls the vocal cords and helps protect the airway so food, liquid or other items do not enter the lungs.
The risks of thyroid surgery can be decreased by having the operation performed by an experienced surgical team that completed at least 30 thyroid surgeries per year. The surgeons at the Pediatric Thyroid Center at CHOP perform more than 75 thyroid surgeries a year. The permanent complication rate for thyroid surgery patients at CHOP is less than 2 percent significantly lower than the national average.
Also Check: Weight Loss After Thyroid Surgery
Use Of Radioactive Iodine And Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cells are unique in that they have the cellular mechanism to absorb iodine. The iodine is used by thyroid cells to make thyroid hormone. No other cell in the body can absorb or concentrate iodine in a similar fashion than does the thyroid. Physicians can take advantage of this fact and give radioactive iodine to patients as a treatment option for papillary thyroid cancer. The use of iodine as a cancer therapy was the first targeted therapy ever developed for any type of human cancer.
There are several types of radioactive iodine, with one type being highly toxic to cells. Papillary thyroid cancer cells absorb iodine therefore, they can be destroyed by giving the toxic isotope . Again, not everyone with papillary thyroid cancer needs this treatment, but those with larger tumors, tumors that have spread to lymph nodes or other areas including distant sites, tumors that are aggressive microscopically may benefit from this treatment.
Radioactive iodine therapy is particularly effective in children with thyroid cancer which has spread extensively to lymph nodes and even to distant sites in the body such as the lungs. Although in theory, radioactive iodine is a very attractive treatment approach for papillary thyroid cancer, its use has decreased over the years except for the specific indications as described above.
Thyroid Cancer In Patients Younger Than 45
The prognosis of a patient under the age of 45 with a differentiated thyroid cancer is good. The thyroid cancer staging system takes this information into account, and classifies these cancers simply into two groups based on whether they have spread to distant organs:
Stage 1: The primary tumor can be any size and the cancer may or may not have spread to lymph nodes. Distant sites in the body are not affected.
Stage 2: The primary tumor can be any size and the cancer may or may not have spread to lymph nodes, but cancer cells have spread to distant areas of the body.
You May Like: What Supplements To Take For Low Thyroid
Stages For Thyroid Cancer
The thyroid cancer staging classification system is very similar for older patients with differentiated tumors and for those with medullary thyroid cancer. Age is not a consideration when classifying medullary cancers.
Stage 1 thyroid cancer: The tumor is 2 cm or smaller , and has not grown outside the thyroid. It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant sites.
Stage 2 thyroid cancer: The cancer meets one of the following criteria:
- The diameter of the primary tumor ranges from 2 to 4 cm. There are no cancer cells in regional lymph nodes or distant sites in the body.
- The primary tumor is larger than four cm in diameter or has started to grow outside of the thyroid gland. No cancer was found in the lymph nodes or other parts of the body .
Stage 3 thyroid cancer: The cancer meets one of the following criteria:
- The primary tumor is larger than 4 cm, or has grown outside the thyroid, but has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or beyond .
- The tumor can be any size or be growing outside the thyroid, and has spread to lymph nodes in the neck but no farther.
Thyroid cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Your multidisciplinary team will work with you to develop a personalized plan to treat your thyroid cancer in a way that fits your individual needs and goals.
Stage 4 thyroid cancer: This is the most advanced stage of thyroid cancer, is further subdivided depending on where the cancer has spread:
What Is Hypercalcemia And How Is It Related To Parathyroid Cancer
Hypercalcemia means that there are higher than normal levels of calcium in your blood. People with parathyroid cancer often have hypercalcemia because the cancer causes your parathyroid gland to become overactive and release large amounts of parathyroid hormone . Parathyroid hormone regulates the amount of calcium in your blood, so too much parathyroid hormone means youll have too much calcium in your blood.
Hypercalcemia can be harmful to your health and body. Because of that, its just as important to treat hypercalcemia caused by parathyroid cancer as it is to treat the cancer itself.
Recommended Reading: I 131 For Thyroid Cancer Treatment
What Tests Will I Have To Diagnose Parathyroid Cancer
Parathyroid cancer is most often diagnosed after your abnormal, overactive parathyroid gland has been surgically removed because you were diagnosed with primary hyperparathyroidism. Sometimes, the surgeon is able to diagnose parathyroid cancer during the surgery.
Prior to the surgery to remove your overactive parathyroid gland, you may undergo the following tests and procedures:
- Blood calcium test.
- Blood PTH test.
- Parathyroid scan .
If youve been diagnosed with parathyroid cancer, you may undergo the following imaging tests so your healthcare provider can determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body:
- CT scan: A CT scan uses X-rays and a computer to produce many 3D images of your body.
- MRI : MRI uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed images of your body. It doesnt use X-rays .
Treating Prostate Cancer That Doesnt Go Away Or Comes Back After Treatment
If your prostate-specific antigen blood level shows that your prostate cancer has not been cured or has come back after the initial treatment, further treatment can often still be helpful. Follow-up treatment will depend on where the cancer is thought to be and what treatment youve already had. Imaging tests such as CT, MRI, or bone scans may be done to get a better idea about where the cancer is.
Recommended Reading: Doctors That Treat Thyroid Problems
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The age of the patient at the time of diagnosis.
- The type of thyroid cancer.
- The stage of the cancer.
- Whether the cancer was completely removed by surgery.
- Whether the patient has multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B .
- The patients general health.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Read Also: Are Home Thyroid Tests Accurate
What Are Symptoms Of Thyroid Cancer
Most thyroid cancers are asymptomatic. Some can cause symptoms such as pain, difficulty swallowing, enlarged lymph nodes and voice changes. Thyroid cancer is typically diagnosed by discovery of a lump or nodule that is either felt or seen incidentally on ultrasound or another imaging study. A biopsy must be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Doctor Treats Thyroid Conditions
Pattern Of Nodal Spread
Like other primary malignancies of the head and neck, thyroid cancer follows a consistent pattern of spread in the cervical LNs. The central compartment, level 6 and 7, is the first echelon of involvement followed by spread to the lateral compartments levels 25, followed by the contralateral side . Involvement of LNs in the submental or submandibular region is rare. Skip metastases to the lateral LNs in the absence of central compartment disease has between reported in up to 20% of cases .
What Is The Best Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Depending on each case, treatment options for men with prostate cancer might include:
- Observation or Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer.
- Surgery for Prostate Cancer.
- Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer.
- Cryotherapy for Prostate Cancer.
- Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer.
- Chemotherapy for Prostate Cancer.
Don’t Miss: Treatment Of Medullary Thyroid Cancer
What Causes Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Scientists still dont know the exact cause of papillary thyroid cancer, but they have identified risk factors that increase your risk of developing PTC, including radiation exposure and certain genetic conditions.
Radiation exposure and papillary thyroid cancer
The rates of papillary thyroid cancer are higher in people who have a history of exposure to significant ionizing radiation. This exposure could be due to:
- High-dose external radiation treatments to your neck, especially during childhood, used to treat cancer or some noncancerous conditions.
- Radiation exposure from nuclear plant disasters. The Chernobyl nuclear accident in 1986 led to a 3- to 75-fold increase in PTC cases in fallout regions.
Genetics and papillary thyroid cancer
A few genetic conditions are associated with PTC, including:
Only 5% of all papillary thyroid cases are associated with these genetic conditions.
Signs And Symptoms Of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer
5 percent of thyroid cancer diagnoses. Detecting the cancer early can be difficult.
Medullary thyroid cancer commonly advances from the thyroid into the lymph nodes. Undiagnosed medullary thyroid cancer can spread into other neck tissues and eventually reach the liver, lungs, bone, and brain. Once it reaches distant parts of the body its unlikely to be cured.
Also Check: Papillary Thyroid Cancer Recurrence In Lymph Nodes
Stages Of Thyroid Cancer
When your doctor diagnoses you with thyroid cancer, they will use several key factors to determine the stage of the disease. Thyroid cancer staging can be complex and differs based on your cancer type, so it’s important to discuss this topic with your doctor thoroughly. There are three significant questions doctors will consider when determining the stagecollectively referred to as the “TNM” system:
- T: How big is the tumor? Has it grown out of the thyroid and into nearby organs or structures?
- N: Has the cancer spread to the lymph nodes?
- M: Has the cancer metastasized, or spread to distant organs?
Depending on how advanced each aspect of the TNM system is, your doctor will assign a number to each letter of the system. For example, a small tumor that has not grown outside the thyroid will be categorized as T1. A tumor that has grown outside the thyroid and into the blood vessels of the surrounding area would be categorized as T4.
With the help of the TNM system, your physician will determine your cancer’s stage. For people aged 55 and younger, doctors only utilize stages I and II to account for this population. For those over age 55, doctors use stages I through IV.
All anaplastic cancers are considered stage IV due to their poor prognosis, but there are substages within this depending on the size and spread of the tumor. Age is not a factor in the staging of medullary cancer, and follows a I through IV staging system with subdivisions within that.
How Is Stage 4 Thyroid Cancer Treated

Im about to sound like a broken record, but this again depends on the type of cancer. For almost all types the first step in treatment is a total thyroidectomy. For patients diagnosed at earlier stages, whose disease has progressed, any remaining thyroid tissue and involved lymph nodes will likely be removed. This is known as a radical neck dissection. Further treatment for papillary and follicular carcinomas involves radioactive iodine treatment. Sadly, these two types of thyroid cancer can become resistant to radioactive iodine, and thus may require radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Medullary and ananplastic diseases, however, are not sensitive to radioactive iodine at all, and must begin with surgery, followed by radiation/chemotherapy. Further targeted treatments are possible utilizing biomarkers and genetic traits of the tumor.
Surgical removal of metastases has been utilized in some patients, but it should be understood that the primary outcome with these surgeries is to improve quality of life.
Don’t Miss: Location Of The Thyroid Gland
Symptoms Of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer does not always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, what they are like and how often you have them will depend on the size and location of the metastatic tumors. Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:
- pain and fractures, when cancer has spread to the bone
- headache, seizures, or dizziness, when cancer has spread to the brain
- shortness of breath, when cancer has spread to the lung
- jaundice or swelling in the belly, when cancer has spread to the liver