Thyroid Cancer Causes And Risk Factors
Its not clear exactly what causes thyroid cancer to develop. However, there are a number of known potential risk factors, some of which can be modified and others that cant. According to the National Cancer Institute, risk factors for developing thyroid cancer include:
Other research led by Dr. Harari is looking at whether certain environmental exposures, including to pesticides and flame retardants, have a link to thyroid cancer.
New Uchicago Medicine Research Sheds Light On Outcomes As Cases Increase Dramatically
Thyroid cancer survivors report poor quality of life after diagnosis and treatment compared with other patients who are diagnosed with more lethal cancers, according to new research from the University of Chicago Medicine.
The findings, published Dec. 11 in the journal Thyroid, shed light on a rarely studied outcome for a growing group of patients who are expected to soon account for 10 percent of all of American cancer survivors.
Thyroid cancer patients have a nearly 98 percent five-year survival rate, according to the National Cancer Institute. More than 95 percent survive a decade, leading some to call it a “good cancer.” But those successful outcomes mean few thyroid cancer survivorship studies have been conducted.
UChicago Medicine researchers Briseis Aschebrook-Kilfoy, PhD, assistant research professor in epidemiology, and Raymon Grogan, MD, assistant professor of surgery, are trying to address that data gap. Together, they lead the North American Thyroid Cancer Survivorship Study .
For their most recent research, Aschebrook-Kilfoy and Grogan recruited 1,174 thyroid cancer survivors 89.9 percent female with an average age of 48 from across the U.S. and Canada. Participants were recruited through the thyroid cancer clinics at UChicago Chicago Medicine, the clinics of six other universities, as well as through thyroid cancer survivor support groups and social media.
The researchers will continue to track participants to further understand this data.
How Do I Choose A Thyroid Surgeon
A high-volume surgeon is best. Whether you opt for a general, endocrine, or head and neck surgeon, you want to choose a provider who does a lot of these surgeries every year, says Dr. Lieb. Dr. Chen says a good volume to shoot for is 100 per year or more.
You can find directories of qualified surgeons at the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons or the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
Read Also: Armor Thyroid And Weight Loss
Nomogram Predicts Overall Survival In Patients With Stage Iv Thyroid Cancer : A Population
- Department of Pediatrics, Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
Background: Stage IV Thyroid cancer has a relatively poor prognosis and lacks a precise and efficient instrument to forecast prognosis. Our study aimed to construct a nomogram for predicting the prognosis of patients with stage IV TC based on data from the SEER programme.
Methods: We enrolled patients diagnosed with TC from 2004 to 2015 in the study. Furthermore, the median survival time for the patients equalled 25 months. The patients were split into two groups: the training group and validation group. We used descriptive statistics to calculate demographic and clinical variables, Students t test was used to describe continuous variables, and the chi-square test was used to describe classified variables. We used the concordance index to evaluate discrimination ability and calibration plots to evaluate calibration ability. The improvement of the nomogram compared with the AJCC TNM system was evaluated by the net weight classification index , comprehensive discriminant rate improvement and decision curve analysis .
Our nomogram can be used to forecast the survival of patients with stage IV TC.
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of thyroid cancer. The symptoms may be caused by less serious conditions, such as an enlarged thyroid , so its important to get them checked.
A GP will examine your neck and can organise a blood test to check how well your thyroid is working.
If they think you could have cancer or theyre not sure whats causing your symptoms, youll be referred to a hospital specialist for more tests.
Read Also: When Should I Have My Thyroid Checked
Don’t Miss: What Percentage Of Thyroid Biopsies Are Cancerous
How Is Thyroid Cancer Managed Or Treated
Treatments for thyroid cancer depend on the tumor size and whether the cancer has spread. Treatments include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer. Depending on the tumors size and location, your surgeon may remove part of the thyroid gland or all of the gland . Your surgeon also removes any nearby lymph nodes where cancer cells have spread.
- Radioiodine therapy: With radioiodine therapy, you swallow a pill or liquid containing a higher dose of radioactive iodine than whats used in a diagnostic radioiodine scan. The radioiodine shrinks and destroys the diseased thyroid gland along with cancer cells. Dont be alarmed this treatment is very safe. Your thyroid gland absorbs almost all of the radioiodine. The rest of your body has minimal radiation exposure.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation kills cancer cells and stops them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver strong beams of energy directly to the tumor site. Internal radiation therapy involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Intravenous or oral chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stops cancer growth. Very few patients diagnosed with thyroid cancer will ever need chemotherapy.
- Hormone therapy: This treatment blocks the release of hormones that can cause cancer to spread or come back.
What Are The Types Of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is classified based on the type of cells from which the cancer grows. Thyroid cancer types include:
- Papillary: Up to 80% of all thyroid cancers are papillary. This cancer type grows slowly. Although papillary thyroid cancer often spreads to lymph nodes in the neck, the disease responds very well to treatment. Papillary thyroid cancer is highly curable and rarely fatal.
- Follicular: Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for up to 15% of thyroid cancer diagnoses. This cancer is more likely to spread to bones and organs, like the lungs. Metastatic cancer can be more challenging to treat.
- Medullary: About 2% of thyroid cancers are medullary. A quarter of people with medullary thyroid cancer have a family history of the disease. A faulty gene may be to blame.
- Anaplastic: This aggressive thyroid cancer is the hardest type to treat. It can grow quickly and often spreads into surrounding tissue and other parts of the body. This rare cancer type accounts for about 2% of thyroid cancer diagnoses.
Read Also: How To Check The Thyroid
What Can I Expect If I Have Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
Just as each person is unique, each case of anaplastic thyroid cancer presents differently and responds to treatment differently. ATC is characteristically difficult to predict.
Scientists are making advancements every day in the treatment of advanced thyroid cancers, including ATC. The treatment is challenging, but its important to not give up hope when youre first diagnosed.
Its important to work with a team of healthcare providers who have experience with anaplastic thyroid cancer. If youre unable to travel to a major medical facility that has experience with ATC, dont be afraid to ask your local providers to collaborate with experts at more experienced centers on your treatment plan.
Understanding the risks and benefits involved with various treatment options is essential. You must advocate for yourself and lean on family and friends for support.
Also Check: Alpha Lipoic Acid Side Effects Thyroid
How Age Affects The Risk Of Thyroid Cancer Recurrence
Several factors determine if your thyroid cancer may return or relapse after treatment, with age being an independent risk factor. Typically, the older population is at a greater risk of experiencing a reoccurrence of thyroid cancer after an initial diagnosis. However, it is not a must that thyroid cancer will return. Other factors that increase the chances of thyroid cancer reoccurrence after diagnosis and treatment include stage, obesity, and genetics.
You May Like: Lose Weight On Thyroid Medication
Clinical And Pathological Characteristics
The demographic data of the 23 included patients are presented in Tables 1,2. Among the 23 patients, 11 were men and 12 were women, with a median age of 58.3 years . A total of 19 patients had symptoms. Thirteen patients had a palpable mass, 4 had localised pain, and 2 had dyspnoea. Overall, 9 patients had distant metastasis .
What Is The Thyroid Gland
Your thyroid gland is one of many glands that make up your endocrine system. Endocrine glands release hormones that control different bodily functions.
The pituitary gland in your brain controls your thyroid gland and other endocrine glands. It releases thyroid-stimulating hormone . As the name suggests, TSH stimulates your thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone.
Your thyroid needs iodine, a mineral, to make these hormones. Iodine-rich foods include cod, tuna, dairy products, whole-grain bread and iodized salt.
You May Like: How To Get My Thyroid Checked
Side Effects Of Thyroid Surgery
The risks of thyroid surgery include:
-
Damage to the laryngeal nerve. It can be stunned, or one vocal cord wont move the same way as the other, Dr. Harari explains. About 5% of people temporarily experience this complication, and 1% have permanent damage. There are procedures to regain vocal strength, and an ENT specialist can assist the patient in these efforts.
-
Hypoparathyroidism, or, as sometimes surgeons decide to remove one or more of the parathyroid glands four tiny glands that regulate the bodys calcium levels and are located near the back of the thyroid. People whose thyroid surgery involves a central neck incision have a 10% risk of parathyroid complications.
-
Vagus nerve issues. Lateral neck incisions can risk impacting the vagus nerve, Dr. Harari says. This can have effects on the voice as well as the shoulder or tongue.
-
Loss of thyroid function. After surgery, you will probably need to take pills for the rest of your life to replace lost thyroid hormones. If your parathyroid glands are also removed, you may also need to take calcium and vitamin D.
Deaths Related To Differentiated Thyroid Cancer

Of the 23 deaths observed, 91.3% were aged 45 years or 87.0% were aged 55 years and 56.5% had distant metastasis . All patients with FTC who died had distant metastasis. Among PTC deaths, the proportion of patients with distant metastasis was 47.4%. Compared with PTC, FTC deaths had smaller tumors and higher mean age at diagnosis , with no significant difference. In both histological types, 50% of the deaths had regional lymph node metastasis.
Table 2
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Thyroid Medication
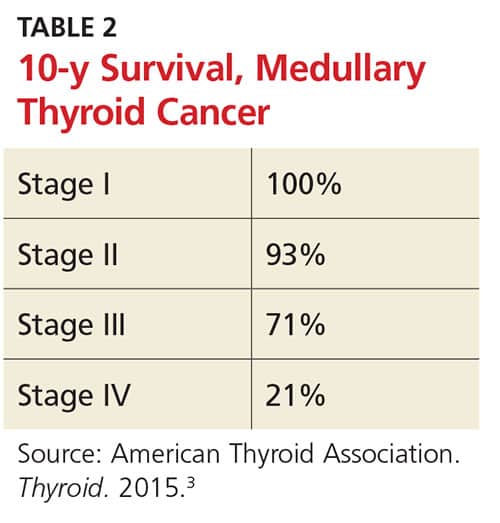
Thyroid Cancer Survival Rates By Type And Stage
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They can’t tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Your doctor is familiar with yoursituation ask how these numbers may apply to you.
What Affects Your Prognosis
Stage IV thyroid cancer is cancer that has spread from your thyroid gland to other parts of your neck, lymph nodes, or distant areas of your body like your lungs or bones. Several things have an impact on your prognosis, including:
Your type of thyroid cancer. There are four main kinds:
Each type acts differently. Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common kind. It has the best outlook because it grows slowly. Even when this cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, it responds well to treatment.
Follicular and medullary thyroid cancers are less common than papillary cancer, but their prognosis is good overall. Anaplastic is the fastest-growing type of thyroid cancer, and it doesn’t respond well to treatment.
Your age. People with papillary or follicular cancers who are younger than 40 may have a better outlook than those who are older.
Your health. When you start out in good health, you usually can handle treatment and its side effects better.
How far the cancer has spread. Cancers that have spread just outside the thyroid gland have a better prognosis than those that have spread to distant parts of the body.
Whether you have multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B . People who have this inherited disease have greater odds of getting medullary thyroid cancer. They are also often diagnosed at a late stage, when the cancer is harder to treat.
Also Check: Thyroid Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Differentiated Thyroid Cancer In Patients Younger Than 55
Younger people have a low likelihood of dying from differentiated thyroid cancer. The TNM stage groupings for these cancers take this fact into account. So, all people younger than 55 years with these cancers are stage I if they have no distant spread and stage II if they have distant spread. This table includes patients 55 or older as well as younger than 55.
|
AJCC Stage |
|
|
Any N |
The cancer is any size and might or might not have spread to nearby lymph nodes . It has spread to other parts of the body, such as distant lymph nodes, internal organs, bones, etc. . |
* The following additional categories are not listed on the table above:
- TX: Main tumor cannot be assessed due to lack of information.
- T0: No evidence of a primary tumor. The N categories are described in the table above, except for:
- NX: Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed due to lack of information.
Thyroid Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea . It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin piece of tissue, connects the two lobes. A healthy thyroid is a little larger than a quarter. It usually cannot be felt through the skin.
The thyroid uses iodine, a mineral found in some foods and in iodized salt, to help make several hormones. Thyroid hormones do the following:
- Control heart rate, body temperature, and how quickly food is changed into energy .
- Control the amount of calcium in the blood.
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Nomogram Model And Survival Prognostication Tool
A 2020 study used data from 1,237 patients with MTC having undergone total thyroidectomy and neck lymph nodes dissection who enrolled in the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database to construct a survival prognostication tool for 3- and 5-year overall survival, and cancer-specific survival.9
Tumor size, age, metastasis status, and lymph node ratio were identified as independent predictors of overall survival and cancer-specific survival.9
Whats The Prognosis For Stage Iv Thyroid Cancer
If you have stage IV thyroid cancer, you may want to know about your prognosis an estimate of how serious the disease is and how it will affect you in the future. Your outlook depends on a lot of things, including the type of thyroid cancer you have, your age, and your overall health.
Some people prefer not to learn their prognosis, and thats OK. But if you do want the information, the best person to ask is your doctor. They know best about your specific health situation and can answer any questions you have.
Also Check: Thyroid And Swollen Lymph Nodes
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Stage 4 Thyroid Cancer
The Effect Of Age And The High Point
According to Table 2, after adjusting for the variables described above, the hazard ratio for prognosis and overall age at diagnosis was 1.022 , P < 0.001.
Table 2 Adjusted Cox proportional hazards analyses of cancer-specific mortality for patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer.
The cut-off year for the age at diagnosis was determined to be 70 years old, using both the Youdens index and X-tile plots with data on cancer-specific and overall mortality. Results of sensitivity and 1-specificity are shown in Supplement Table 1 the maximum value was 0.075, corresponding to 70 years. The results of X-tile plots are shown for cancer-specific mortality and overall mortality for patients under and over 70 years of age. The survival curves indicated that patients under 70 years of age had less cancer-specific and overall mortality than patients over 70 years, with Kaplan-Meier curves showing greater cancer-specific and overall mortality for patients > 70 years than for those 70 years of age .
How Is Thyroid Cancer Diagnosed
If you have an enlarged thyroid nodule or other signs of thyroid cancer, your healthcare provider may order one or more of these tests:
- Blood tests: A thyroid blood test checks hormone levels and gauges whether your thyroid is functioning properly.
- Biopsy: During a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, your healthcare provider removes cells from your thyroid to test for cancer cells. A sentinel node biopsy can determine if cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes. Your provider may use ultrasound technology to guide these biopsy procedures.
- Radioiodine scan: This test can detect thyroid cancer and determine if cancer has spread. You swallow a pill containing a safe amount of radioactive iodine . Over a few hours, the thyroid gland absorbs the iodine. Your healthcare provider uses a special device to measure the amount of radiation in the gland. Areas with less radioactivity need more testing to confirm the presence of cancer.
- Imaging scans:Magnetic resonance imaging , computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans can detect thyroid cancer and cancer spread.
Recommended Reading: What Is Thyroid Peroxidase Ab