Faq: Symptoms Of Thyroid Cancer In 2022
Q.1 What does thyroid cancer feel like in the beginning?
Answer The most common symptom is a lump in the neck, which can be felt by a doctor during a physical exam. Other symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, and goitre. Thyroid cancer is an uncommon type of cancer that affects the thyroid gland.
Q.2 What are the warning signs of thyroid cancer?
Answer Thyroid cancer is the most common type of endocrine cancer. It starts in cells that produce thyroid hormones, and it can grow in different areas of the gland. The symptoms of thyroid cancer vary depending on how large the tumour is, where its located, and if the tumour has spread to other parts of the body.
Q.3 Where does thyroid cancer usually start?
Answer Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the thyroid gland. We know that it can spread to other organs in the body, but often times it will remain in the thyroid.
Q4. How can you test for thyroid cancer at home?
Answer One simple way to do this is by simply feeling your neck for any lumps or bumps that might be present and check your neck for any changes in texture. A lump can also develop on the thyroid gland itself, causing a thyroid nodule. These are typically painless and may be discovered when you do a diagnostic neck X-ray or ultrasound scan.
Q.5 What does cancer feel like in your neck?
Read More
How Is Thyroid Cancer Diagnosed
Most thyroid nodules are benign, not cancerous. If a nodule is discovered in the thyroid by physical examination or imaging, it should be further described by the radiologist with attention given to certain details used to estimate the likelihood that a nodule is malignant. An important characteristic is the size of the nodule. Tiny thyroid cancers exist undetected in the glands of as many as one-third of all adults, and the vast majority of these are never detected or cause any clinical problems. For this reason, and because tiny nodules are difficult to biopsy accurately, any nodule of less than 1 centimeter in size may not need to be further evaluated. For nodules of more than 1 centimeter, a grading system is applied and biopsy recommended if the score indicates an appropriate level of concern. Nodules that are not judged to need biopsy may be monitored with repeat ultrasound examinations.
Signs And Symptoms Of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer
5 percent of thyroid cancer diagnoses. Detecting the cancer early can be difficult.
Medullary thyroid cancer commonly advances from the thyroid into the lymph nodes. Undiagnosed medullary thyroid cancer can spread into other neck tissues and eventually reach the liver, lungs, bone, and brain. Once it reaches distant parts of the body its unlikely to be cured.
Read Also: Home Thyroid Test Kit Walgreens
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of thyroid cancer. The symptoms may be caused by less serious conditions, such as an enlarged thyroid , so it’s important to get them checked.
A GP will examine your neck and can organise a blood test to check how well your thyroid is working.
If they think you could have cancer or they’re not sure what’s causing your symptoms, you’ll be referred to a hospital specialist for more tests.
Find out more about how thyroid cancer is diagnosed.
What About Other Treatments I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Thyroid Pills
Staging Of Thyroid Cancer
- Stages for papillary and follicular thyroid cancers are stages I IV, depending on extent of the disease and age of the patient at diagnosis.
- For medullary thyroid cancer, stages are from I-IV, depending on size of the tumor and spread.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer is all considered Stage IV because of its aggressiveness, and because it has usually spread when it is discovered.
The prognosis depends on the following:
- The size of the tumor
- Whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body and where it has spread
- The type of cancer
- Whether the cancer is primary or has recurred after treatment
Thyroid cancers are best controlled when they are small and can be removed by surgery. Clinical trials are a good option for getting the latest treatment. For thyroid cancers that have metastasized and no longer respond to radioactive iodine, the standard of care is clinical trials.
Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Sporadic medullary thyroid cancer comes from the C cells of your thyroid gland. These cells make a hormone that controls the amount of calcium in your blood.
Between of medullary thyroid cancers are sporadic, meaning they arent hereditary. Sporadic medullary thyroid cancer occurs mainly in older adults.
If diagnosed in stages I through III, MTC can have a good outlook.
Read Also: Thyroid Cancer Lymph Node Metastasis
How Do I Choose A Thyroid Surgeon
A high-volume surgeon is best. Whether you opt for a general, endocrine, or head and neck surgeon, you want to choose a provider who does a lot of these surgeries every year, says Dr. Lieb. Dr. Chen says a good volume to shoot for is 100 per year or more.
You can find directories of qualified surgeons at the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons or the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
Genetic Testing For Men And Fmtc
Genetic testing is now the mainstay in the diagnosis of the FMTC syndromes. RET proto-oncogene mutations have been discovered in each of the MTC syndromes. The RET proto-oncogene is a receptor tyrosine kinase whose exact function and role in these syndromes has not been elucidated. Patients with MEN 2A have germline RET mutations resulting in substitutions of conserved cysteine residues in exons 10 and 11. All patients with MEN 2B have a germline mutation resulting in a threonine-for-methionine substitution in codon 918 of exon 16. Mutations are described in exons 13 and 14 in patients with FMTC.
Genetic screening with sensitive PCR assays for germline RET mutations is routinely performed in at-risk patients. Children of parents known to have MEN or FMTC are tested for RET mutations to guide therapy and future genetic counseling. In addition, patients presenting with sporadic MTC should undergo RET mutational analysis to rule out new spontaneous germline mutations, which should prompt the testing of offspring for similar mutations.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Take To Much Thyroid Medication
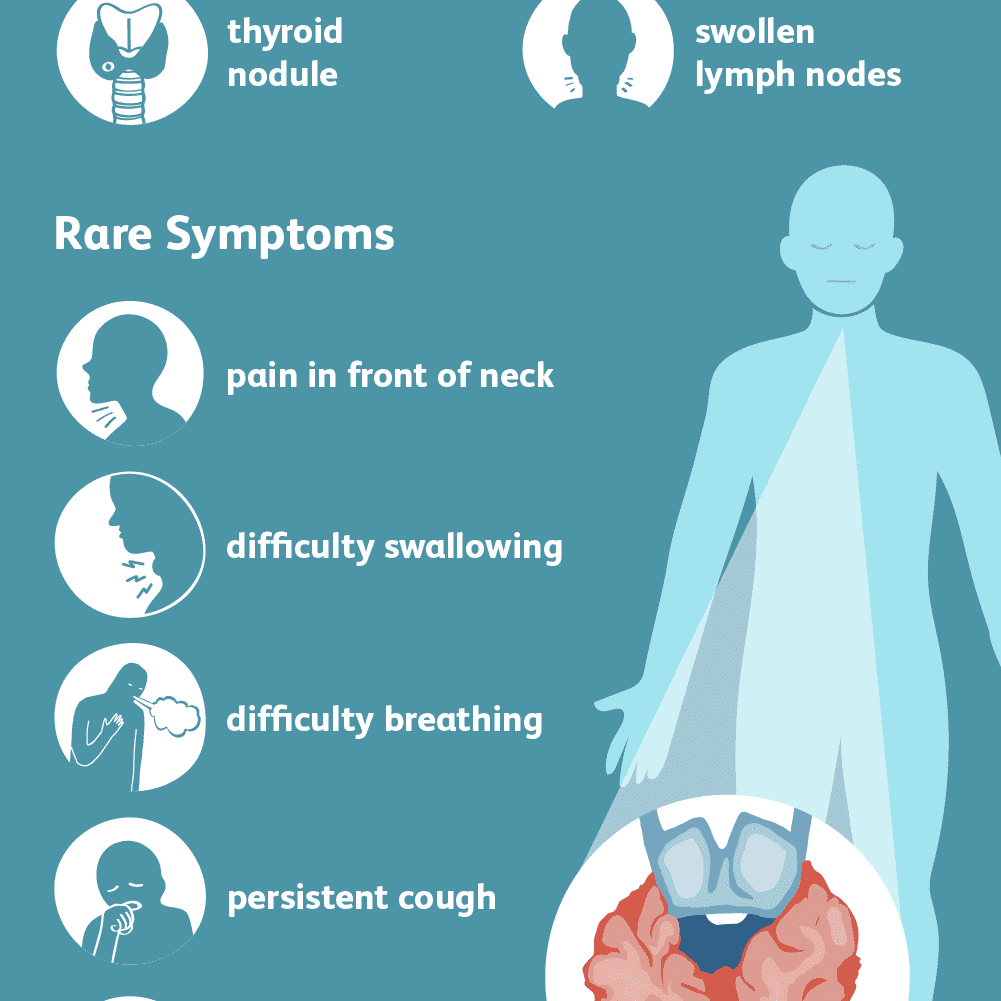
What Are The Warning Signs Of Thyroid Cancer
You or your healthcare provider might feel a lump or growth in your neck called a thyroid nodule. Donât panic if you have a thyroid nodule. Most nodules are benign . Only about 3 out of 20 thyroid nodules turn out to be cancerous .
Other thyroid cancer symptoms include:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck.
What are the signs that thyroid cancer has spread?
If you have thyroid cancer that has spread to other areas of your body, you may experience symptoms such as:
- Exposure to radioactive fallout from nuclear weapons or a power plant accident.
Side Effects Of Thyroid Hormone Treatment
Thyroid hormone pills themselves do not usually cause side effects, but it can take some time to get the dosage right, and you may experience symptoms of either or while you and your doctor work to determine the correct dose.
Symptoms of too much thyroid hormone may include:
-
Increased heart rate
Symptoms of too little thyroid hormone may include:
-
dry skin and hair
Definitely check in with your doctor if you feel you are experiencing any of the above symptoms so that your dosage can be properly adjusted.
Also Check: Different Types Of Thyroid Cancer
How Is Thyroid Cancer Managed Or Treated
Treatments for thyroid cancer depend on the tumor size and whether the cancer has spread. Treatments include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer. Depending on the tumorâs size and location, a surgeon may remove part of your thyroid gland or all of the gland . The surgeon also removes any nearby lymph nodes where cancer cells have spread.
- Radioiodine therapy: With radioiodine therapy, you swallow a pill or liquid containing a higher dose of radioactive iodine than whatâs used in a diagnostic radioiodine scan. The radioiodine shrinks and destroys the diseased thyroid gland along with cancer cells. This treatment is very safe. Your thyroid gland absorbs almost all of the radioiodine and the rest of your body has minimal radiation exposure.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation kills cancer cells and stops them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver strong beams of energy directly to the tumor site. Internal radiation therapy involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Intravenous or oral chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stops cancer growth. Very few people diagnosed with thyroid cancer will ever need chemotherapy.
- Hormone therapy: This treatment blocks the release of hormones that can cause cancer to spread or come back.
What are the complications of thyroid cancer?
How does thyroid cancer affect pregnancy?
Risk Factors For Thyroid Cancer

There are some things that can make it more likely to develop thyroid cancer. These are called risk factors and they include:
- Exposure to radiation a small number of thyroid cancers are due to having radiation therapy to the head and neck area as a child or living in an area with high levels of radiation.
- Family history only around 5% of thyroid cancer runs in families. Some inherited genetic conditions, such as familial adenomatous polyposis or Cowden syndrome, or inheriting the RET gene may also increase your risk.
- Other factors people who are overweight or obese possibly have a higher risk of developing thyroid cancer. Other thyroid conditions only slightly increase the chance of developing thyroid cancer.
Having these risk factors doesnt mean you will develop thyroid cancer. Often there is no clear reason for getting thyroid cancer. If you are worried about your risk factors, ask your doctor for advice.
Don’t Miss: Thyroid Diet Plan For Weight Loss
What Are The Types Of Thyroid Cancer
PAPILLARY THYROID CANCER. Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type, making up about 70% to 80% of all thyroid cancers. Papillary thyroid cancer can occur at any age. It tends to grow slowly and often spreads to lymph nodes in the neck. Papillary cancer has a generally excellent outlook, even if there is spread to the lymph nodes.
FOLLICULAR THYROID CANCER. Follicular thyroid cancer makes up about 10% to 15% of all thyroid cancers in the United States. Follicular cancer can spread through the blood to distant organs, particularly the lungs and bones.
Papillary and follicular thyroid cancers are also known as wellDifferentiated Thyroid Cancers . The information in this brochure refers to these differentiated thyroid cancers. The other types of thyroid cancer listed below will be covered in other brochures.
MEDULLARY THYROID CANCER. Medullary thyroid cancer , accounts for approximately 2% of all thyroid cancers. Approximately 25% of all MTC runs in families and is associated with other endocrine tumors . In family members of an affected person, a test for a genetic mutation in the RET proto-oncogene can lead to an early diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer and, as a result, to curative surgery. 75% of patients with Medullary thyroid cancer do not have a hereditary form.
Fit And Healthy Mother Who Fought Thyroid Cancer At 27 Shares 4 Symptoms She Ignored
A mother who battled thyroid cancer aged 27 has revealed the symptoms she ignored weeks before her diagnosis, from dry skin to brittle hair.
Christina McKnight, now 35, thought little of the signs for weeks and was only diagnosed after her husband, Matthew Mcknight, 36, forced her to see a doctor.
She was diagnosed with thyroid cancer in the autumn of 2014, despite having no family history and being young, fit and healthy.
Christina – who now has a five-year-old son – thought her symptoms were caused by stress after she landed a promotion at her job at a commercial bank.
However, her fatigue, brain fog, dry skin and brittle hair were all signs of something far more sinister.
Christina, a content creator, from Oklahoma City, US, said: It was one of those things that I never thought would happen to me.
I was young, fit and healthy. Id just run a half marathon, did CrossFit for three years and had no known hereditary thyroid disease in the family at all.
I just started to feel very tired and had loads of brain fog, but I thought it was just because of my promotion.
Then my husband noticed how tired I was and my lack of interest in things like the gym, which I usually love.
I couldnt get stuff done like I used to. I would have to go to work on a Sunday to catch up because my brain was so foggy.
Christina said she started to notice her hair become weirdly brittle, while her skin grew drier.
I kept brushing it all off, she said.
Don’t Miss: Doctors Who Specialize In Thyroid
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will this treatment affect my ability to have children? Do I need to avoid pregnancy for a while?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too? Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Management Of Thyroid Cancer
Malignant diagnoses require surgical intervention. Papillary thyroid carcinoma and medullary thyroid carcinoma are often positively identified on the basis of FNAB results alone. Cervical metastases discovered preoperatively or intraoperatively should be removed by means of en bloc lymphatic dissection of the respective cervical compartment while sparing the nonlymphatic structures.
Well-differentiated neoplasms
Patients with follicular neoplasm, as determined with FNAB results, should undergo surgery for thyroid lobectomy for tissue diagnosis. The extent of surgical therapy for well-differentiated neoplasms is controversial. Primary treatment for papillary and follicular carcinoma is surgical excision whenever possible. Total thyroidectomy has been the mainstay for treating well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Modifications to total thyroidectomy include subtotal thyroidectomy to reduce the risk of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury and hypoparathyroidism.
A 2015 consensus statement from the American Thyroid Association on the management of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer who have recurrent/persistent nodal disease stated the following :
Hürthle cell carcinomas
Medullary thyroid carcinomas and familialmedullary thyroid carcinomas
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, primary thyroid lymphoma, thyroid sarcoma
The treatment for thyroid sarcomas is total thyroidectomy. Radiation therapy may be used in an adjunctive setting.
Postsurgical management
Read Also: How Does Thyroid Cancer Affect The Body
Thyroid Cancer Survivor Lists 5 Initial Signs That Shouldnt Be Ignored
Pintrest
Bonus Thyroid Cancer Symptom #: Uncomfortable Pressure Sensation In The Neck
Even though the thyroid cancer may not be very large, it may still produce symptoms of pressure or sometimes even a tight or strangling sensation in the neck. This thyroid cancer symptom of pressure may seem disproportional to the size of the thyroid cancer itself. The explanation of this pressure or strangling sensation, is, once again, the special nerve endings which sense pressure.
Read Also: Can T Lose Weight Thyroid
Can I Prevent Thyroid Cancer
Many people develop thyroid cancer for no known reason, so prevention isnât really possible. But if you know youâre at risk for thyroid cancer, you may be able to take these steps:
- Preventive surgery: Genetic tests can determine if you carry an altered gene that increases your risk for medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia. If you have the faulty gene, you may opt to have preventive surgery to remove your thyroid gland before cancer develops.
- Potassium iodide: If youâve had radiation exposure during a nuclear disaster, such as the 2011 incident at Fukushima, Japan, taking potassium iodide within 24 hours of exposure can lower your risk of eventually getting thyroid cancer. Potassium iodide blocks your thyroid gland from absorbing too much radioiodine. As a result, your gland stays healthy.