What Is A Normal Thyroid Level
Tests often used to assess thyroid hormone status include TSH and FT4 tests. The normal value for a laboratory test is determined by measuring the hormone in a large population of healthy individuals and finding the normal reference range. Normal ranges for thyroid tests may vary slightly among different laboratories, and typical ranges for common tests are given below.
TSH normal values are 0.5 to 5.0 mIU/L. Pregnancy, a history of thyroid cancer, history of pituitary gland disease, and older age are some situations when TSH is optimally maintained in different range as guided by an endocrinologist.
FT4 normal values are 0.7 to 1.9ng/dL. Individuals taking medications that modify thyroid hormone metabolism and those with a history of thyroid cancer or pituitary disease may be optimally managed with a different normal FT4 range.
Total T4 and Total T3 levels measure bound and free thyroid hormone in the blood. These levels are influenced by many factors that affect protein levels in the body, including medications, sex hormones, and liver disease. A normal Total T4 level in adults ranges from 5.0 to 12.0g/dL. A normal Total T3 level in adults ranges from 80-220 ng/dL.
Free T3 assays are often unreliable and not routinely used to assess thyroid function.
Who Should Get Testing
Thyroid function testing is often ordered when patients have symptoms of a thyroid disorder. Testing can assist with diagnosing or ruling out thyroid problems as a cause of your symptoms.
Many of the symptoms of common thyroid problems are nonspecific there is a wide range of diseases and disorders which may cause them. Thyroid function testing, which may be referred to as a full thyroid panel, complete thyroid panel, extended thyroid panel or other thyroid lab tests, may be included with other tests to evaluate if you are having trouble with a non-specific symptom like fatigue, depression, or difficulty becoming or staying pregnant.
In addition to being used for diagnosis, thyroid function tests may be performed to screen for thyroid disease in patients who have no symptoms. Newborn infants are routinely screened for hypothyroidism shortly after birth.
Screening for thyroid disease in adults is controversial. Some experts recommend screening certain groups who are at higher risk of having an underactive thyroid. These risk factors may include:
- Family history of thyroid disease
- Personal history of type I diabetes
- Personal history of autoimmune disease
- Personal history of radiation to the head and neck
Thyroid function tests are also used for treatment monitoring. Patients with known thyroid disorders will have periodic thyroid function testing to ensure their treatment is effective.
Drawing Blood For Thyroid Function Tests
Before you get a blood draw to check your thyroid levels, talk with your doctor about any medications youre taking. Also let them know if youre pregnant. Certain medications and being pregnant may influence your test results.
A blood draw, also known as venipuncture, is a procedure performed at a lab or a doctors office. When you arrive for the test, youll be asked to sit in a comfortable chair or lie down on a cot or gurney. If youre wearing long sleeves, youll be asked to roll up one sleeve or to remove your arm from the sleeve.
A healthcare professional, like a technician or nurse, will tie a band of rubber tightly around your upper arm to make the veins swell with blood. Once the healthcare professional has found an appropriate vein, theyll insert a needle under the skin and into the vein.
You may feel a sharp prick when the needle punctures your skin. The healthcare professional will collect your blood in test tubes and send it to a laboratory for analysis.
When the healthcare professional has gathered the amount of blood needed for the tests, theyll withdraw the needle and place pressure on the puncture wound until the bleeding stops. They will then place a small bandage over the wound.
You should be able to return to your typical daily activities immediately.
Recommended Reading: How To Get My Thyroid Levels Up
What Blood Tests Do Doctors Use To Check Thyroid Function
Doctors may order one or more blood tests to check your thyroid function. Tests may include thyroid stimulating hormone , T4, T3, and thyroid antibody tests.
For these tests, a health care professional will draw blood from your arm and send it to a lab for testing. Your doctor will talk to you about your test results.
What Is It Used For
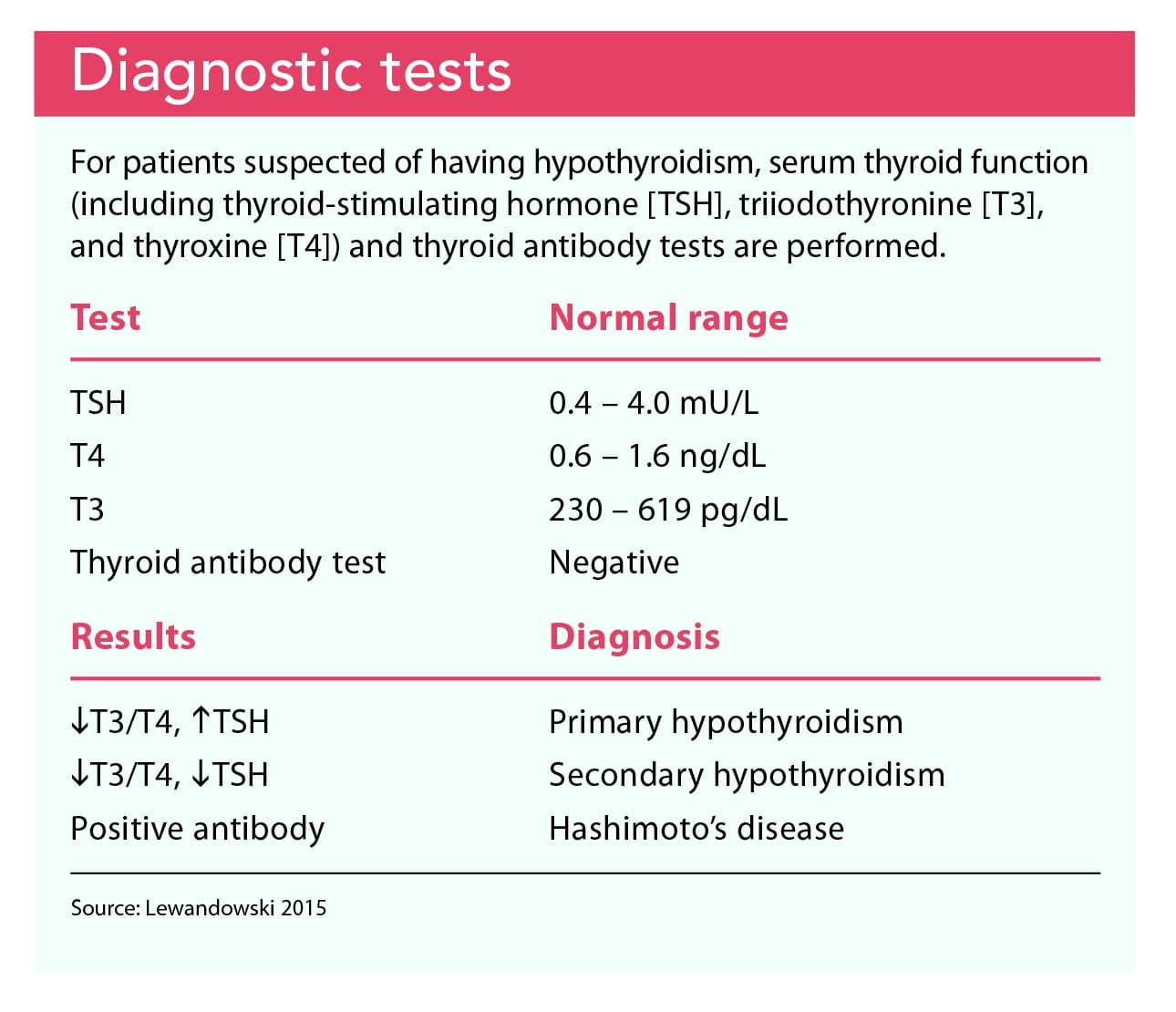
A TSH test is used to find out how well your thyroid is working. It can tell if you have hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism in your blood. But a TSH test can’t show what is causing a thyroid problem.
If you take prescription thyroid hormone medicine because of hypothyroidism or because you had your thyroid removed, you’ll have regular TSH tests to check your thyroid hormone levels. TSH tests are also used to monitor your thyroid hormone levels after treatment for hyperthyroidism.
Also Check: Thyroid Healing By Anthony William
Comparing High/low Tsh And T3/t4 Levels
- Normal TSH + normal T4 = normal thyroid function
- High TSH + normal T4 = you may have a higher risk of developing an underactive thyroid
- Low TSH + high T4 = overactive thyroid
- High TSH + low T4 = underactive thyroid
- Low TSH + low T4 = low thyroid function due to another problem, such as pituitary gland dysfunction
Looking at TSH alongside T3 test results can also help with diagnosis:
- Low T3 + high TSH = low thyroid function
- High T3 + low TSH = overactive thyroid
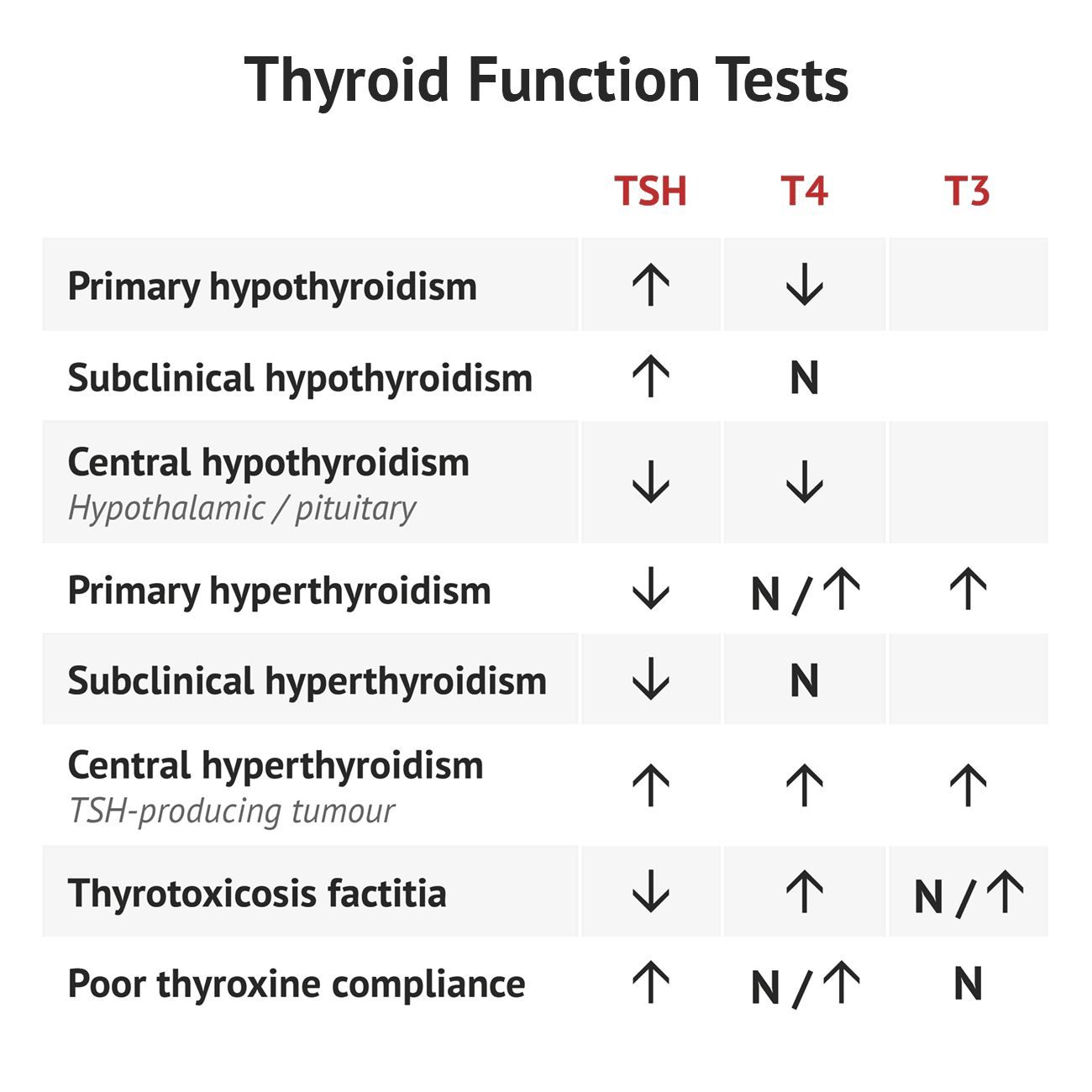
Normal And Abnormal Tsh Ranges
-
0.4 mU/L to 4.0 mU/L is considered the , and people who have a normally functioning thyroid gland usually fall within this range.
-
If TSH measures more than 4.0 mU/L, a second test is performed to verify the results. TSH of more than 4.0/mU/L with a low T4 level indicates hypothyroidism.
-
If your TSH is more than 4.0 mU/L and your T4 level is normal, this may prompt your physician to test your serum anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies. When these antibodies are present, it may indicate an autoimmune thyroid disorder, which is a risk factor for developing hypothyroidism. If you have these antibodies, your doctor will most likely perform a TSH test at least once per year.
An easy way to remember how the thyroid worksthink about supply and demand. As the T4 level falls, the TSH rises. As the T4 level rises, the TSH falls. However, not everyone with hypothyroidism has elevated levels of TSH.
If your pituitary gland is not working properly, it may not send out normal TSH amountsand if this is the casethe thyroid may be healthy. However, if the amount of TSH is off, the thyroid wont make the right amount of T4. This is rare and is known as secondary or central hypothyroidism.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Take To Much Thyroid Medication
What Are Thyroid Function Tests Used For
Thyroid function tests are usually done to find out whether the thyroid gland is working properly. This is mainly to diagnose an underactive thyroid gland and an overactive thyroid gland .
People with some conditions have an increased risk of thyroid problems and so are often advised to have thyroid function tests undertaken each year. This conditions include:
Certain medicines can also affect the function of your thyroid – for example, amiodarone and lithium.
Thyroid function tests can also be done to:
- Monitor treatment with thyroid replacement medicine for people who have hypothyroidism.
- Check thyroid gland function in people who are being treated for hyperthyroidism.
- Screen newborn babies for inherited problems with the thyroid gland.
What Do The Results From My Thyroid Function Test Mean
If a result in your thyroid function blood test is outside the normal range it can be flagged as high or low . Interpretation of the many variations in test results is complex and an abnormal result may not mean that anything is wrong. Other health conditions, extreme stress and pregnancy affect the levels of thyroid hormones, as well as medicines. Talking with your doctor about what your results mean for you is important.An abnormal TSH usually indicates a deficiency or an excess of thyroid hormones available to your body, but it does not indicate why this is happening. An abnormal TSH result is usually followed by additional testing of FT3 and/or FT4 to investigate the cause.A high TSH result:
- often means an underactive thyroid gland
- can also occur if you have an underactive thyroid gland and are receiving too little thyroid hormone medication
- can, in rare cases, indicate that you have a problem with your pituitary gland, eg, a tumour.
A low TSH result:
- can indicate an overactive thyroid gland or damage to your pituitary gland that is preventing it from producing TSH
- can also occur if you have an underactive thyroid gland and are receiving too much thyroid hormone medication.
Don’t Miss: What Can Help An Underactive Thyroid
Where Is Colloid Found In The Body
Colloids are found in the body in many places, including the mouth, eyes, and intestines. They play an important role in the bodyâs ability to absorb nutrients and create waste products.
Colloids are found in the body in many places, including the mouth, eyes, and intestines. They play an important role in the bodyâs ability to absorb nutrients and create waste products.
Where Is The Thyroid Located
Your thyroid gland is located in the front of your neck, straddling your windpipe . Its shaped like a butterfly smaller in the middle with two wide wings that extend around the side of your throat. A healthy thyroid gland is not usually visible from the outside , and you cant feel it when you press your finger to the front of your neck.
Read Also: Stop The Thyroid Madness Com
What Should I Do To Prepare For A Thyroid Function Test
Thyroid function tests usually require very little preparation.
You don’t need to fast before the blood test. And it doesn’t matter if you have taken your thyroid medicine just before the blood test.
Tell your doctor if you are taking any medication, as some medicines can alter the test results and how they are interpreted.
It is also important to mention if you have had any X-ray tests that have used a special contrast dye, as this may contain iodine which can affect the results. Levels of thyroid chemicals also change in pregnancy, so tell your doctor if you are pregnant when the test is taken.
Note: all newborn children have their thyroid function tested as part of the heel prick test which is offered to all babies and undertaken when they are 5 days old. See the separate leaflet called Newborn Baby Screening Tests for more information.
How Do I Know If My Thyroid Dose Is Correct
Monitoring thyroid levels on medication Correct dosing of thyroid hormone is usually assessed using the same tests for diagnosis of thyroid disease, including TSH and FT4. Thyroid tests are typically checked every 4-6 weeks initially and then every 6 to 12 months once stable. In special circumstances, such as pregnancy, a history of thyroid cancer, central hypothyroidism, amiodarone therapy, or use of combination T4 and T3 thyroid hormone replacement, your endocrinologist may check different thyroid tests. Additionally, your endocrinologist will evaluate for symptoms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism and peform a physicial exam.
Women who are pregnant and women who may become pregnant should only be treated with levothyroxine . Only T4 efficiently crosses the placenta to provide thyroid hormone to the developing fetus. Thyroid hormone is critical in early pregnancy for brain development. Normal ranges for thyroid tests in pregnancy are different and change by trimester. Women with thyroid disease in pregnancy or who are considering pregnancy should be under the care of an endocrinologist to guide therapy.
Got Questions About Normal Thyroid Hormone Levels?
Also Check: Thyroid Diet Plan For Weight Loss
Side Effects Of Thyroid Blood Tests And Care
Thyroid blood tests are performed using a routine blood draw. That’s when blood is drawn from you with a syringe and sent to a lab. This is a safe procedure with few potential side effects.
It’s rare, but some people get nauseous or feel faint when they have blood drawn. Let the medical personnel know immediately if you experience these side effects.
Later, you may notice a small bruise or have some tenderness at the needle insertion site. An over-the-counter pain reliever or an ice pack can help with this.
You should get medical attention if the insertion site is:
These are signs of an infection, which needs to be treated with antibiotics.
Thyroid Function Test Results Explained
The thyroid usually changes slowly. It hardly ever quickly changes to being overactive or underactive: it usually takes a few weeks at least, or even a few months. If you have a thyroid function test that shows something is wrong, it’s usually worth repeating it in 3-6 weeks. That is because there’s always the chance that your thyroid gland could have gone back to normal by itself.
The second thing to bear in mind about thyroid function tests is that medications, and even herbal remedies or vitamin supplements, can affect the accuracy of thyroid results.
For these two reasons it’s always recommended to have a thyroid function test if it is recommended to you by a doctor, rather than having it done privately or without a doctor suggesting it.
Recommended Reading: How To Make Your Thyroid Active
Taking A Thyroid Test
The thyroid panel test is performed on a blood sample. If a doctor performs the test, the blood sample comes from drawing blood from a vein with a needle. And if the test is being performed at home, the kit typically contains a lancet, which pricks the finger to draw blood that you place on a card to send back to the lab.
What Happens When T4 Levels Are Too High
If you have higher-than-normal T4 or free T4 levels, it could indicate thyrotoxicosis. This can result from several situations and conditions, including hyperthyroidism , thyroid inflammation and taking excessive amounts of thyroid medication.
Thyrotoxicosis speeds up your metabolism, which can be dangerous to your health. Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis include:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat .
If youre experiencing symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, its important to contact your healthcare provider.
Other conditions that could cause elevated total T4 levels with normal free T4 levels include pregnancy and estrogen-containing birth control pills. This is because estrogen levels are high in those two scenarios. Estrogen increases the proteins bound to T4 and causes the total T4 to be high.
Recommended Reading: Normal Range For Thyroid Antibodies
Why Hypothyroidism Is Not Diagnosed On Symptoms Alone
Many of the symptoms of hypothyroidism are fairly common complaints found in people with a normally functioning thyroid gland, so it can be hard to decipher if the symptoms are related to the thyroid. One of the best ways to figure out if your symptoms could be related to a thyroid condition is to consider how long you have been experiencing them.
For example, have you always felt cold when others were warm? Did you just start to notice decreased energy? If you are starting to notice new signs and symptoms, it could be related to a thyroid issue. However, only a physician can diagnose a thyroid problem.
What Conditions And Disorders Affect The Thyroid
There are several different types of thyroid disease. Thyroid disease is very common, with an estimated 20 million people in the United States having some type of thyroid disorder. Women and people assigned female at birth are about five to eight times more likely to be diagnosed with a thyroid condition than men and people assigned male at birth .
Thyroid diseases are split into two types: primary and secondary.
In primary thyroid disease, the disease originates in your thyroid gland. In secondary thyroid disease, the disease originates in your pituitary gland. As an example, if you have a nodule on your thyroid thats releasing excess amounts of thyroid hormones, it would be called primary hyperthyroidism. If a tumor in your pituitary gland is releasing excess amounts of thyroid-stimulating hormone , which then stimulates your thyroid to produce excess thyroid hormones, it would be called secondary hyperthyroidism.
The four main conditions that affect your thyroid include:
- Postpartum thyroiditis .
- Excess iodine in your blood from diet and/or medication.
- Over-treatment of hypothyroidism through medication.
- A benign tumor in your pituitary gland.
Goiter
Goiter is an enlargement of your thyroid gland. Goiters are relatively common they affect approximately 5% of people in the United States
Goiters have different causes, depending on their type.
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is classified based on the type of cells from which cancer grows. Thyroid cancer types include:
Also Check: Thyroid Cancer 20 Year Survival Rate
Which Are Examples Of Colloids
The following are examples of colloids: water droplets, flourpaste, blood plasma.Colloids are suspensions of particles that have a partially insoluble or soluble texture.
They are used to make up a variety of substances, from paint to vaccine. In physics, colloids are the result of two materials sitting in contact with each other.
What Blood Tests Are Done To Test The Thyroid
Thyroid blood tests include:
These tests alone arent meant to diagnose any illness but may prompt your healthcare provider to do additional testing to evaluate for a possible thyroid disorder.
Additional blood tests might include:
- Thyroid antibodies: These tests help identify different types of autoimmune thyroid conditions. Common thyroid antibody tests include microsomal antibodies , thyroglobulin antibodies , and thyroid receptor antibodies .
- Calcitonin: This test is used to diagnose C-cell hyperplasia and medullary thyroid cancer, both of which are rare thyroid disorders.
- Thyroglobulin: This test is used to diagnose thyroiditis and to monitor treatment of thyroid cancer.
Don’t Miss: Iodine Treatment For Thyroid Cancer