What Other Issues Might I Encounter During Treatment
Cancer can be expensive. Dr. Lieb says that young adults with thyroid cancer have one of the highest rates of healthcare-related bankruptcy. This is partly due to the cost of imaging studies. Another factor is that many people only have insurance through their workplace and cancer treatment can impact your ability to work. Be sure you have support to help you examine medical bills and proactively engage with your insurance provider.
How Do I Know If I Have Thyroid Cancer
Articles On Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid nodules, or lumps, are very common. Most arent cancer.
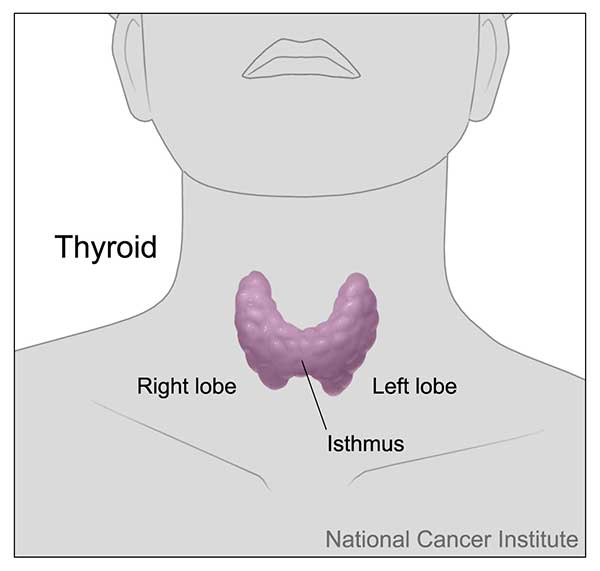
Your thyroid is the small, butterfly-shaped gland usually located at the bottom front of your neck. If you have a lump on it, chances are you found it yourself, though your doctor may have detected it during a physical exam. If you have discovered a lump on your own, you should get your doctor to check it.
Physical Exam
Your doctor will examine any lumps, or nodules, you have on your neck. They might ask you some questions to find out if youre at risk. The questions might be about whether youve been exposed to too much radiation, or if you have a family history of thyroid cancer or thyroid disease.
ishonestNo.181 – Post-Sun Exposure
There is no blood test that can detect thyroid cancer. Still, your doctor may want you to get one to help figure out whether your thyroid gland is working right.
Genetic Tests
Based on your family history, your doctor might order genetic testing to find out if you have any genes that make you more likely to get cancer. It can also show genetic changes that could be a sign of certain types of thyroid cancer.
Biopsy
If you have a thyroid lump, you may need to have it tested. A biopsy will tell if its cancer or not.
To do a biopsy, your doctor uses a small, thin needle to take a little sample from the lump, and maybe other places around it.
Youll probably get this fine-needle biopsy in your doctors office. You wont need any recovery time afterward.
Are Radioactive Iodine Thyroid Scans Used To Diagnose Thyroid Cancer
If the thyroid blood tests are normal, radioactive iodine scans are seldom used in the United States in the evaluation of thyroid nodules. Radioactive iodine scans of the neck will document the location and general size of the isotope-concentrating thyroid but not as precisely as will an ultrasound. The portion of the gland which does not concentrate the radioisotope will not be visualized. It does provide a measure of the glands ability to pick-up or concentrate the radioactive isotope, a gross measure of thyroid function.
Most thyroid tumors, benign and malignant, will not concentrate the isotope but, on the contrary, a small portion of tumors that do so may be malignant. Thus, the radioactive isotope scan provides little help in distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors.
Don’t Miss: Thyroid Eye Disease Double Vision Treatment
How Do I Choose A Thyroid Surgeon
A high-volume surgeon is best. Whether you opt for a general, endocrine, or head and neck surgeon, you want to choose a provider who does a lot of these surgeries every year, says Dr. Lieb. Dr. Chen says a good volume to shoot for is 100 per year or more.
You can find directories of qualified surgeons at the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons or the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have thyroid cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get thyroid cancer?
- What type of thyroid cancer do I have?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the thyroid gland?
- What is the best treatment for this type of thyroid cancer?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Will I need thyroid replacement hormone therapy?
- Is my family at risk for developing this type of thyroid cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Can I get thyroid cancer again?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Receiving a cancer diagnosis is unsettling, regardless of the type. Fortunately, most thyroid cancers respond extremely well to treatment. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for the type of thyroid cancer you have. After treatment, you may need to take synthetic thyroid hormones for life. These hormones support vital body functions. They usually dont cause any significant side effects, but youll have regular checkups to monitor your health.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/13/2020.
References
You May Like: Ringing In Ears Thyroid Cancer
How To Check Your Thyroid
This article was medically reviewed by Ricardo Correa, MD. Dr. Correa is a board certified Endocrinologist. Dr. Correa is the Program Director of the Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Fellowship at the University of Arizona College of Medicine and was a previous Assistant Professor of Medicine at Brown University. He completed his MD at the University of Panama and completed an internal medicine residency at the Jackson Memorial Hospital – University of Miami. He has been voted one of the 40 Under 40 Leaders in Health by the National Minority Quality Forum in 2019.There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 59,126 times.
The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. It is a very important gland that produces a hormone that helps regulate your entire bodys metabolism, temperature, heart rate, growth, and development. The thyroid gland can be functionally underactive or overactive. The thyroid can be enlarged, have benign nodules and, more rarely, malignant nodules.
Trends In Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis By Sex And Cancer Type
As seen in previous studies, the researchers found that diagnoses of thyroid cancer increased sharply beginning in the 1990s. At the peak of this trend, in 2013, about 22 cases of thyroid cancer were diagnosed per 100,000 women, compared with only about 8 per 100,000 men. Papillary thyroid cancer accounted for around 75%80% of cases diagnosed between 1975 and 1989. This increased to 90% between 2010 and 2017.
Correspondingly, between 1983 and 2017, women were more than four times as likely as men to receive a diagnosis of a small, localized papillary thyroid tumor. When larger and more advanced papillary thyroid cancers were included, women were only about 2.5 times as likely as men to receive such a diagnosis.
For more deadly types of thyroid cancer, such as medullary thyroid cancer and anaplastic thyroid cancer, the gap between sexes nearly disappeared, with diagnoses being about equally likely for men and women. And from 1992 to 2017, the overall annual death rate from any thyroid cancer diagnosed during life was approximately the same for women and men.
The researchers also identified eight studiesincluding more than 23,000 people in totalthat reported the prevalence of undiagnosed thyroid cancer on autopsy. Unlike diagnoses made in the living, the prevalence of undiagnosed small papillary thyroid cancer did not differ substantially between women and men.
Recommended Reading: Braf Mutation Papillary Thyroid Cancer
What Is A Thyroid Nodule
A thyroid nodule is a collection of cells within the thyroid that grow and produce a lump. Sometimes these lumps can be felt by physical examination of the thyroid gland, but oftentimes they are detected as an incidental finding on radiology studies done for an unrelated reason. Fortunately, about 90-95% of thyroid nodules are benign .
How Is Thyroid Cancer Managed Or Treated
Treatments for thyroid cancer depend on the tumor size and whether the cancer has spread. Treatments include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer. Depending on the tumors size and location, your surgeon may remove part of the thyroid gland or all of the gland . Your surgeon also removes any nearby lymph nodes where cancer cells have spread.
- Radioiodine therapy: With radioiodine therapy, you swallow a pill or liquid containing a higher dose of radioactive iodine than whats used in a diagnostic radioiodine scan. The radioiodine shrinks and destroys the diseased thyroid gland along with cancer cells. Dont be alarmed this treatment is very safe. Your thyroid gland absorbs almost all of the radioiodine. The rest of your body has minimal radiation exposure.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation kills cancer cells and stops them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver strong beams of energy directly to the tumor site. Internal radiation therapy involves placing radioactive seeds in or around the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Intravenous or oral chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells and stops cancer growth. Very few patients diagnosed with thyroid cancer will ever need chemotherapy.
- Hormone therapy: This treatment blocks the release of hormones that can cause cancer to spread or come back.
You May Like: Thyroid Dry Mouth And Eyes
What Is The Role Of Molecular Testing In The Evaluation Of Thyroid Nodules
The last 10 years has seen an explosion in our understanding of the molecular basis of thyroid cancer. This improved understanding has led to the development of several molecular tests that can provide clinically useful information with regard to whether a thyroid nodule is likely to be benign or cancerous. These tests are always used within the context of an understanding of the risk that a nodule is likely to be cancer based on ultrasonographic findings, clinical findings, and the results of the fine needle aspiration biopsy.
When the FNA classifies a nodules as benign, malignant or suspicious for malignancy, the molecular testing probably plays very little role. However, when the FNA biopsy is read as inconclusive , molecular testing has been shown to be of help in determining if that nodule is more likely to be benign or malignant.
Why Have Thyroid Cancer Diagnoses Spiked For Us Women
Since the 1990s, a boom in the use of thyroid ultrasound has led to thyroid cancer diagnoses more than tripling.
Thyroid cancer is diagnosed more often in women than men. And over the past few decades, this sex-based gap has grownsubstantially.
A new study, however, indicates that this disparity isnt what it seems on the surface. A large contributor appears to be that women are more likely to be diagnosed with small thyroid cancers that would have been unlikely to cause problems during their lifetime, researchers reported August 30 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Women were more than four times as likely as men to be diagnosed with a small papillary thyroid cancer during their lives, the study found. Such cancers are rarely fatal. In contrast, diagnoses of aggressive and often deadly types of thyroid cancer were nearly equal in men and women. There was also no real difference between sexes in small papillary thyroid cancers found on autopsy, which werent detected during life.
The study wasnt designed to pinpoint the cause of this imbalance. But women are more likely than men to undergo tests for other medical reasons that can detect these small cancers that otherwise would have probably not been found. And as clinicians, were primed to think about thyroid problems more often in women, said Louise Davies, M.D., M.S., of the Department of Veterans Affairs, who led the new research.
Also Check: Prescription Thyroid Food For Cats
But What If Its Thyroid Cancer
A cancer diagnosis is always worrisome, but even if a nodule turns out to be thyroid cancer, you still have plenty of reasons to be hopeful.
Thyroid cancer is one of the most treatable kinds of cancer. Surgery to remove the gland typically addresses the problem, and recurrences or spread of the cancer cells are both uncommon. People who undergo thyroid gland surgery may need to take thyroid hormone afterward to keep their body chemistry in balance.
Whether its benign or not, a bothersome thyroid nodule can often be successfully managed. Choosing an experienced specialist can mean more options to help personalize your treatment and achieve better results.
Do All Thyroid Nodules Require Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
No. As a general rule, thyroid nodules less than 1 cm can be followed with observation without the need for fine needle aspiration. These small nodules are often found incidentally on CT, MRI or neck ultrasound done for some other reason. They are very common and are rarely thyroid cancer. Therefore, in the absence of other high risk features, these small nodules are usually observed with a repeat thyroid ultrasound in 6-12 months reserving biopsy for those few nodules that increase in size over time
The 2016 ATA guidelines also note that a biopsy may not be required for nodules as large as 2 cm if the ultrasonographic features suggest that the nodule is not likely to be thyroid cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Thyroid Cancer Returning
Thyroid Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide And The Top 6 Ways To Prevent It
Breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer we know so much about these cancers, and we know how serious they are to our health. But do you know that the fastest increase in cancer, among both men and woman, is thyroid cancer?
In the last several years, rates of thyroid cancer have gone up four-fold! Please check out this article, and share it with your loved ones, so that everyone can learn more about thyroid cancer prevention today.
Causes Of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer happens when there’s a change to the DNA inside thyroid cells which causes them to grow uncontrollably and produce a lump.
It’s not usually clear what causes this change, but there are a number of things that can increase your risk.
These include:
- other thyroid conditions, such as an inflamed thyroid or goitre but not an overactive thyroid or underactive thyroid
- a family history of thyroid cancer your risk is higher if a close relative has had thyroid cancer
- radiation exposure in childhood such as radiotherapy
- a bowel condition called familial adenomatous polyposis
- acromegaly a rare condition where the body produces too much growth hormone
You May Like: Does Victoza Cause Thyroid Cancer
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Thyroid Cancer
Most thyroid cancers are found when patients see a doctor because of new neck lumps . Sometimes doctors find neck lumps during a physical exam. Yet other times thyroid cancer may be found during an ultrasound test for other health problems.
If signs are pointing to thyroid cancer, more tests will be done.
How Common Is Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is a rare form of cancer, accounting for less than 1% of all cancer cases in the UK.
It’s most common in people aged 35 to 39 years and in those aged 70 years or over.
Women are 2 to 3 times more likely to develop thyroid cancer than men. It’s unclear why this is, but it may be a result of the hormonal changes associated with the female reproductive system.
Recommended Reading: Radiofrequency Ablation Thyroid Nodule Cost
How Does Thyroid Cancer Occur
We will start by thinking more about the nature of your thyroid. It is pretty safe to say that your thyroid is a bit of a hoarder, in that the thyroid gland has the capacity to concentrate iodine. This is unique because it is a relationship that we do not really see anywhere else in our body.
Key Insight: Our thyroid gland concentrates iodine, because the amount that it needs is far greater than the amount of iodine it might be able to find in our bloodstream. You will have between 50 100 times more iodine in your thyroid, than you would in your blood, at any given time.
The drawback of this is that the pump in your thyroid which concentrates iodine is also hoarding things which may not be good for you. So, you get foreign things into this important gland. That definitely does not sound good and its not. This is the first step in the process.
The next problem can be found in your genes. Your genes might be programmed to either make this hoarding problem worse, by attacking your thyroid gland and causing inflammation.
The third step is the high level of engagement of your immune system. When something weird gets stuck in your thyroid, and your genetics are not able to process it, your immune system essentially goes haywire. This leads to an inflamed gland, which affects cell division. This is basically what causes thyroid cancer, right then and there.
What Will Happen After Treatment
Most people do very well after treatment, but you may need follow-up care for the rest of your life. This is because most thyroid cancers grow slowly and can come back even 10 to 20 years after treatment. Your cancer care team will tell you what tests you need and how often they should be done.
Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests to see if the cancer has come back. At first, your visits may be every 3 to 6 months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed.
Sometimes treatments may not cure your cancer. You many need to keep getting treatment and care. From time to time tests will be done to see how your treatment is working.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life.
You May Like: What Hormones Do The Thyroid Gland Produce
Different Kinds Of Thyroid Cancer
There are 4 main types of thyroid cancer. They are listed below. Your doctor can tell you more about the kind you have.
- Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common kind of thyroid cancer. It may also be called differentiated thyroid cancer. This kind tends to grow very slowly and is most often in only one lobe of the thyroid gland. Even though they grow slowly, papillary cancers often spread to the lymph nodes in the neck.
- Follicular cancer is the next most common type. Its more common in countries where people dont get enough iodine in their diet. These cancers do not tend to spread to lymph nodes, but they can spread to other parts of the body, like the lungs or bones.
- Medullary cancer is a rare type of thyroid cancer. It starts in a group of thyroid cells called C-cells. C-cells make calcitonin, a hormone that helps control the amount of calcium in the blood.
- Anaplastic cancer is a rare type of thyroid cancer. It often spreads quickly into the neck and to other parts of the body, and is very hard to treat.