Thyroid Cancer Causes And Risk Factors
Its not clear exactly what causes thyroid cancer to develop. However, there are a number of known potential risk factors, some of which can be modified and others that cant. According to the National Cancer Institute, risk factors for developing thyroid cancer include:
Other research led by Dr. Harari is looking at whether certain environmental exposures, including to pesticides and flame retardants, have a link to thyroid cancer.
Will I Be Cared For Mainly By One Provider Or Will There Be Multiple Ones
Thyroid cancer care is a team sport. Dr. Lieb says you can expect to be cared for by many people during your cancer treatment, including your primary care physician, your endocrinologist, and your surgeon. There will also be pathologists and social workers. Depending on the type of thyroid cancer, you may also see a nuclear medicine team, vascular surgeon, voice specialist, and imaging professionals.
Standard Treatment Options For Papillary And Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Localized/regional papillary and follicular thyroid cancer
Surgery is the therapy of choice for all primary lesions. Surgical optionsinclude total thyroidectomy or lobectomy. The choice of procedure isinfluenced mainly by the age of the patient and the size of the nodule. Survival results with the two procedures are similar for early-stage disease, with differences in the ratesof surgical complications and local recurrences.
Standard treatment options for localized/regional papillary and follicular thyroid cancer
Standard treatment options for localized/regional papillary and follicular thyroid cancer include the following:
Surgery
The objective of surgery is to completely remove the primary tumor, while minimizing treatment-related morbidity, and to guide postoperative treatment with RAI. The goal of RAI is to ablate the remnant thyroid tissue to improve the specificity of thyroglobulin assays, which allows the detection of persistent disease by follow-up whole-body scanning. For patients undergoing RAI, removal of all normal thyroid tissue is an important surgical objective. Additionally, for accurate long-term surveillance, RAI whole-body scanning and measurement of serum thyroglobulin are affected by residual, normal thyroid tissue, and in these situations, near total or total thyroidectomy is required. This approach facilitates follow-up thyroid scanning.
Total thyroidectomy
Evidence :
Lobectomy
Radioactive iodine therapy
Evidence :
Also Check: Can Thyroid Disease Cause Hives
Data Sources And Definitions
Incidence
Cancer incidence data are from the November 2018 CCR tabulation file released January 29, 2019. The CCR is a person-oriented, population-based database comprised of cases diagnosed among Canadian residents since 1992.Note 17 Each provincial and territorial cancer registry provides demographic and cancer-specific information to Statistics Canada in a standard format. Annual submissions by jurisdiction include additions and revisions to data submitted in previous years.
Cancer cases were defined based on the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, Third Edition .Note 18 Cases were classified as TC if the topography code was C73.9, excluding histology types 9050 to 9055, 9140 and 9590 to 9992. Only malignant cases were considered. TC cases were divided into three main histologic types: papillary , non-papillary and unspecified . Non-papillary cases were further categorized into follicular , medullary , anaplastic and other specified subtypes.Note 19 The International Agency for Research on Cancer multiple primary coding rules were used for this study.Note 20
Mortality
Population
Population data were obtained from Canadaâs population estimates by age and sex released on January 25, 2019.Note 24
Survival
Thyroid Cancer Causes And Types

There are four major types of thyroid cancers, listed below in order of decreasing frequency:
Papillary
Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer and accounts for more than two-thirds of all thyroid cancers. There is a higher risk of developing this tumor in persons who have had previous head and neck radiation.
Most patients will not die from papillary thyroid cancer. They are considered low risk if:
- They are younger than 45 years of age.
- They have small tumors.
- There is no invasion of surrounding structures and no metastasis .
The spread of papillary thyroid cancer to lymph nodes may indicate recurrence, but it is not associated with a higher chance of death. If distant metastases occur, the pattern of spread includes the lung, bone, and other soft tissue – usually in older people.
Follicular variant papillary thyroid cancer is a type of papillary thyroid cancer that has a survival rate similar to that of papillary thyroid cancer. Overall, papillary thyroid cancer is associated with a high survival rate.
Follicular
Follicular thyroid cancer occurs more in older patients compared to papillary thyroid cancer. The diagnosis of “malignancy” depends on the spread to local tissue and blood vessels. Like papillary thyroid cancer, the patient’s age, the size of the tumor, and the extent that the tumor has spread can predict the severity of the disease.
Like papillary cancer, follicular cancer develops from the follicular cells and tends to grow slowly.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Thyroid Cancer Returning
Side Effects Of Thyroid Hormone Treatment
Thyroid hormone pills themselves do not usually cause side effects, but it can take some time to get the dosage right, and you may experience symptoms of either or while you and your doctor work to determine the correct dose.
Symptoms of too much thyroid hormone may include:
-
Increased heart rate
Symptoms of too little thyroid hormone may include:
-
dry skin and hair
Definitely check in with your doctor if you feel you are experiencing any of the above symptoms so that your dosage can be properly adjusted.
Multivariable Cox Proportional Hazards Model
Predictors of 5-year DSS included advanced disease and larger tumor size . There was no association between 5-year DSS and gender, number of co-morbidities, race, type of surgery performed, insurance coverage, or hospital volume. The administration of radioactive iodine was protective . The hazard ratio for death from PTC at 5 years was 38 times higher in patients 60 years, compared to patients < 45 years of age . Harrells c-statistic was 0.9452.
Table 2 Multivariable Cox-proportional hazards analysis of predictors of 5-year disease-specific survival
Predictors of 10-year DSS included advanced disease and larger tumor size . There was no association between 10-year DSS and hospital volume, race, co-morbidities, insurance, surgery performed, or gender. The administrative of RAI was protective, with hazard ratio of 0.60. The hazard ratio for death from PTC at 10 years after diagnosis was nearly 30 times higher in patients 60 years, compared to patients < 45 years of age . Harrells c-statistic was 0.9328.
Table 3 Multivariable Cox-proportional hazards analysis of predictors of 10- year disease-specific survivalTable 4 Multivariable Cox-proportional hazards analysis of predictors of 5- year disease-free survivalTable 5 Multivariable Cox-proportional hazards analysis of predictors of 10- year disease-free survival
Read Also: Np Thyroid Covered By Medicare
Cellular Classification Of Thyroid Cancer
In thyroid cancer, cell type is an important determinant of prognosis and treatment. The thyroid has two cell types: follicular cells and parafollicular C cells. The management of thyroid cancer depends on the cell of origin and how well the integrity of the cell type is maintained. The four main types of thyroid cancer are divided into the following two categories for clinical management:
Differentiated thyroid cancers.
Parafollicular C cell thyroid cancers.
Other types .
References
Whats The Thyroid Cancer Survival Rate
Eight out of 10 people who have thyroid cancer develop the papillary type. Papillary thyroid cancer has a five-year survival rate of almost 100% when the cancer is in their gland . Even when the cancer spreads , the survival rate is close to 80%. This rate means that, on average, youâre about 80% as likely to live for at least five years after diagnosis as someone who doesnât have metastatic papillary thyroid cancer.
Five-year survival rates for other thyroid cancer types include:
- Follicular: Close to 100% for localized around 63% for metastasized.
- Medullary: Close to 100% for localized around 40% for metastasized.
- Anaplastic: Close to 31% for localized 4% for metastasized.
Is thyroid cancer curable?
Yes, most thyroid cancers are curable with treatment, especially if the cancer cells havenât spread to distant parts of your body. If treatment doesnât fully cure thyroid cancer, your healthcare provider can design a treatment plan to destroy as much of the tumor as possible and prevent it from growing back or spreading.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Rid Of Thyroid Cancer
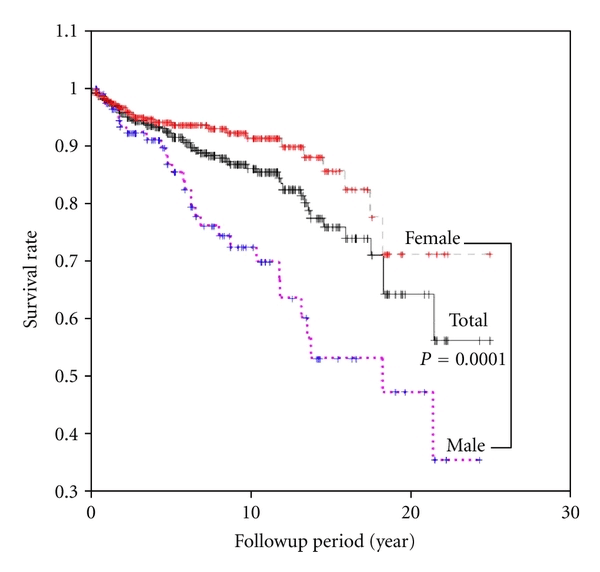
Overall Survival By Gender
Kaplan-Meier estimates of OS and DSS from diagnosis for PTC patients and OS for the age- and gender-matched U.S. population are illustrated in AC. In both genders, survival in PTC patients was worse than in the matched U.S. population . The DSS for PTC patients overlaps with the OS of the U.S. population for each gender . The gender difference in DSS seen in PTC patients mirrors the gender difference in OS for the U.S. population, with greater survival of females in both cases . DSS appears to plateau after 10 yr in both genders, although fewer patients contributed to the data as the duration of follow-up lengthened.
A, Overall survival of United States population compared with overall survival of thyroid cancer registry patients, with survival displayed separately for males and females . B, Overall survival of United States population compared with disease-specific survival of thyroid cancer registry patients, with survival displayed separately for males and females . C, Disease-specific survival of thyroid cancer registry patients by gender and overall survival of United States population by gender .
Age As A Prognostic Variable
Table 2 shows the impact that age had on outcome as a binary variable. All cutoff ages from 30 to 70 years showed that the older cohort had poorer DSS . Multivariable analysis for age at different cutoffs, adjusting for the other predictor variables using Cox proportional hazards regression, also showed that age was significant at all cutoff values from 30 to 70 years. The HRs for adjusted age cutoffs were ranging from 7.09 to 19.03.
Ten year disease-specific survival at different age cutoffs from age 30 to age 70 years.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Thyroid Medicine Without Insurance
How Is Thyroid Cancer Diagnosed
If you have an enlarged thyroid nodule or other signs of thyroid cancer, your healthcare provider may order one or more of these tests:
- Blood tests: A thyroid blood test checks hormone levels and gauges whether your thyroid is functioning properly.
- Biopsy: During a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, your healthcare provider removes cells from your thyroid to test for cancer cells. A sentinel node biopsy can determine if cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes. Your provider may use ultrasound technology to guide these biopsy procedures.
- Radioiodine scan: This test can detect thyroid cancer and determine if cancer has spread. You swallow a pill containing a safe amount of radioactive iodine . Over a few hours, your thyroid gland absorbs the iodine. Your healthcare provider uses a special device to measure the amount of radiation in the gland. Areas with less radioactivity need more testing to confirm the presence of cancer.
- Imaging scans:Radioactive iodine scan, computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans can detect thyroid cancer and cancer spread.
Clinical Features And Prognosis
The clinical features and prognosis of well-differentiated thyroid tumors vary by stage.
Most papillary cancers have some follicular elements. These follicular elements may outnumber the papillary formations, but they do notchange the prognosis.
Follicular adenomas, which are characterized by their lack of invasion throughthe capsule into the surrounding thyroid tissue, must be distinguished from follicular thyroid carcinoma. While follicular cancer has a good prognosis, itis less favorable than that of papillary carcinoma. The 10-year survival is better forpatients with follicular carcinoma without vascular invasion than it is forpatients with vascular invasion.
Papillary carcinomas metastasize more frequently to regional lymph nodes thanto distant sites. Follicular carcinomas more commonly invade blood vessels and metastasize hematogenously to the lungs and to the bone rather than through thelymphatic system. When metastases occur, treatment with radioiodine is initially effective, but prognosis worsens as resistance to radioiodine ensues.
Staging and prognosis of papillary and follicular thyroid cancer are determined by the age and site of the disease. The clinical features and prognoses for papillary thyroid cancer include the following:
Hürthle cell carcinoma is a variant of follicular carcinoma with a similar prognosis and is treated in the same way as equivalent stage non-Hürthle cell follicular carcinoma.
You May Like: Foods For Healthy Thyroid Support
Survival For All Types And Stages Of Thyroid Cancer
There are no UK-wide statistics available for thyroid cancer survival by stage. Survival statistics are available for each stage of thyroid cancer in England. These statistics are for people diagnosed between 2013 and 2017. There are some differences between men and women:
1 year survival
- 90 out of every 100 men survive thyroid cancer for at least 1 year after diagnosis
- More than 90 out of every 100 women survive thyroid cancer for at least 1 year after diagnosis
5 year survival
- Almost 85 out of every 100 men survive thyroid cancer for at least 5 years
- 90 out of every 100 women survive thyroid cancer for at least 5 years after diagnosis
10 year survival
- Around 85 out of every 100 people survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These figures are for net survival of people diagnosed between 2013 and 2017.
Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
Linear Logistic Regression Analysis For The Risk Of Clinicopathological Factors Between Tcvptc And Classic Ptc With Tcf
Table 4 shows the results of linear logistic regression analysis to identify independent risk factors associated with TCVPTC. Tumor size > 2 cm , bilaterality , and lateral LN metastasis were significantly associated with TCVPTC. Moreover, ETE showed a significant association with TCVPTC compared with classic PTC with TCF .
Dont Miss: Are Home Thyroid Tests Accurate
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Overactive Thyroid Gland
Spectrum Of Risk Exists For Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .Allen S. Ho
Aggressive papillary thyroid carcinoma variants appeared associated with a wide range of survival outcomes, suggesting greater emphasis should be placed on tailored treatment approaches for patients with histologically and prognostically distinct subtypes, according to study results published in JAMA Oncology.
We have empirically noted an increase in incidence of more exotic papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes over time however, the literature on these rare variants is not as robust as we would like,Allen S. Ho, MD, director of the head and neck cancer program at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, told Healio. For instance, some papers find diffuse sclerosing variant to be aggressive, others find it to be indolent. We furthermore saw that modern guidelines consolidate all papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes as intermediate risk, when we were clearly seeing that they have different phenotypes. A spectrum of risk exists for thyroid cancers.
Investigators examined incidence, clinicopathologic characteristics and outcomes of 5,447 aggressive variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma identified from hospital-based and population-based U.S. cancer registries. These included 415 diffuse sclerosing variant, 3,339 tall cell variant, 362 insular variant and 1,331 poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma cases.
Median follow-up was 51.2 months .
Thyroid Cancer: Survival Rates And Prognosis
After a thyroid cancer diagnosis, theres a lot of information to process. The cancers stage is an important piece of your diagnosis. Staging helps guide thyroid cancer treatment. The cancers stage is also one of factors doctors use to help you understand your thyroid cancer prognosis. In general, thyroid cancer has a better outlook compared to other types of cancers. Heres a look at the survival rates for the different types and stages of thyroid cancer.
You May Like: Thyroid Medication Made From Pigs
Stage Information For Papillary And Follicular Thyroid Cancer
| Stage | Illustration | |
|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor N = regional lymph node M = distant metastasis. | ||
| aReprinted with permission from AJCC: Thyroid–Differentiated and Anaplastic Carcinoma. In: Amin, MB, Edge Sb, Greene FL et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp 87390. | ||
| bAll categories may be subdivided: solitary tumor and multifocal tumor . | ||
| Age at diagnosis is 55 years: | ||
| III | T4a, Any N, M0 | T4a = Gross extrathyroidal extension invading subcutaneous soft tissues, larynx, trachea, esophagus, or recurrent laryngeal nerve from a tumor of any size. |
| Any N = See descriptions in Table 2. | ||
| M0 = No distant metastasis. |
Living With Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer usually means cancer that is unlikely to be cured. During this time palliative care services can help. Most people with thyroid cancer respond well to treatment and do not need to access palliative care services. However, people at any stage of advanced thyroid cancer may benefit from palliative treatment.
Most people continue to have treatment for advanced cancer as part of palliative care, as it helps manage the cancer and improve their day-to-day lives. Many people think that palliative care is for people who are dying but palliative care is for any stage of advanced cancer. There are doctors, nurses and other people who specialise in palliative care.
Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy or another type of treatment. It can help in these ways:
- Slow down how fast the cancer is growing.
- Shrink the cancer.
- Help you to live more comfortably by managing symptoms, like pain.
Treatment depends on:
- how far it has spread
- your general health
Read Also: Eyelid Retraction Surgery Thyroid Eye Disease